Understanding CDS Table Functions
Basic Features of AMDP
As of the release of 7.40 SP05, ABAP supports database procedures that are stored in ABAP repository and transported with standard ABAP transport requests. This technique is known as ABAP-Managed Database Procedures (AMDP).
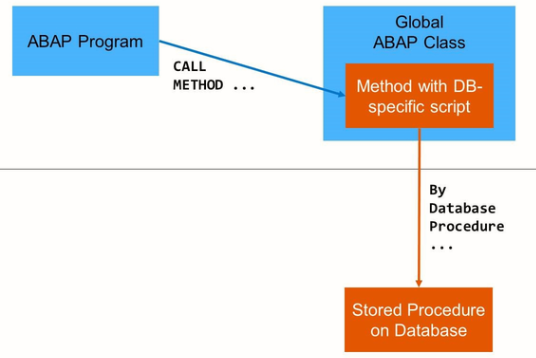
The basic idea of AMDP is the following:
The database procedure is defined and implemented as a method of a global class. The implementation of such a method consists of a database-specific script that can only be executed on the database but not on the ABAP stack.
The AMDP framework creates a stored procedure on the database and redirects any call of the AMDP method to this stored procedure.
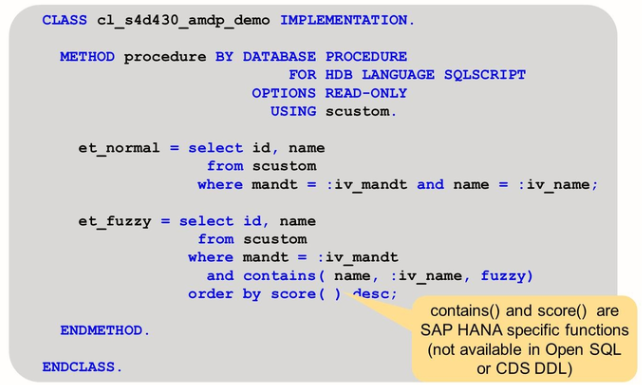
Although the class is an ABAP repository object, the source code between METHOD and ENDMETHOD is not ABAP.
The two statements are written in SQL scripts as it is understood by the SAP HANA database.
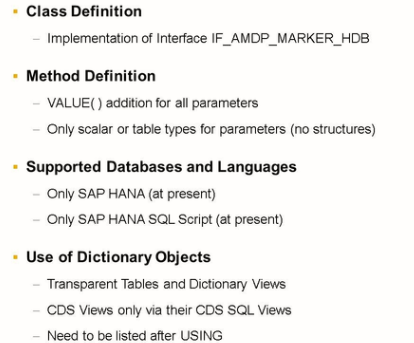
The following additions are needed in the ABAP statement METHOD:
FOR
Specifies the database on which the AMDP can run. In the example, HDB stands for the SAP HANA database. This is currently the only supported value.
LANGUAGE
Specifies the language of the implementation. In the example, it is a SQL script. This is currently the only value available to customers.
USING
Is required if the method implementation uses objects from the ABAP Dictionary. Transparent tables and Dictionary views are supported. CDS view names are not supported here. If you want to use a CDS view in an AMDP, you must access the corresponding CDS SQL view.
OPTIONS
It is intended for additional settings. Currently, READ-ONLY is the only supported opinion.
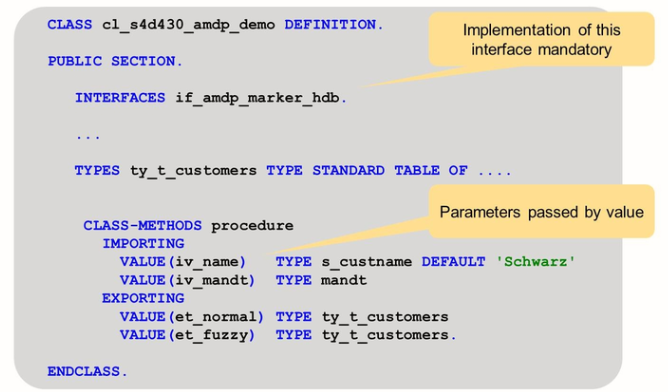
This slide shows the definition of an AMDP class. Implementation of interface IF_AMDP_MARKER_HDB is mandatory.
The parameters of the AMDP method must be passed by value, and the parameter types need to be elementary types or table types. Structure types are not allowed.
AMDP Functions
As of release 7.50, the AMDP framework supports AMDP functions alongside the existing AMDP procedures.
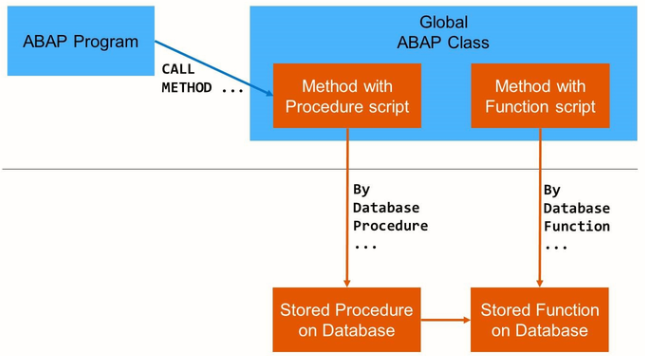
AMDP functions use the new addition BY DATABASE FUNCTION of the METHOD statement in AMDP classes.
Unlike AMDP procedure implementations, AMDP function implementations have no expert or changing parameters. They have exactly one tabular return value.
AMDP function implementations cannot be called by an AMDP program directly. But they can be called from other AMDP functions or procedures.
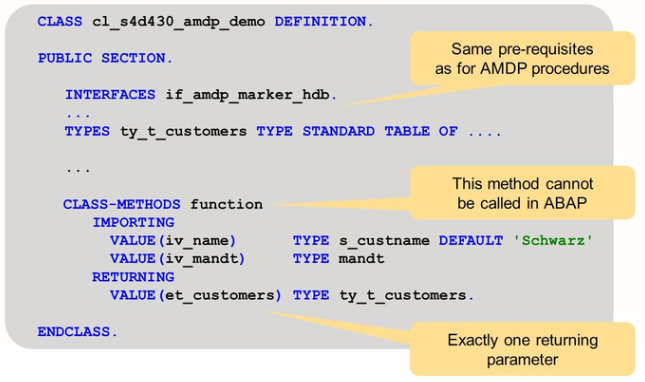
This slide shows the definition of an AMDP class. AMDP method FUNCTION is intended to be implemented by a database function. It is defined as a functional method, i.e., it has exactly one tabular returning parameter and besides that only import parameter.

This example shows the implementation of an AMDP function.
Addition BY DATABASE FUNCTION is used instead of BY DATABASE PROCEDURE. The remaining additions have the same meaning and values for database procedures.
In the script for a database function, the statement RETURN is mandatory. The RETURN statement defines the values for the return parameter.
AMDP Functions for CDS Table Functions
AMDP functions are functional methods of global classes that define functions stored and executed on the database. It is not allowed to call functional methods that define AMDP functions directly in ABAP.
ABAP CDS introduced CDS table functions to make AMDP functions available as data sources of SELECT statements.
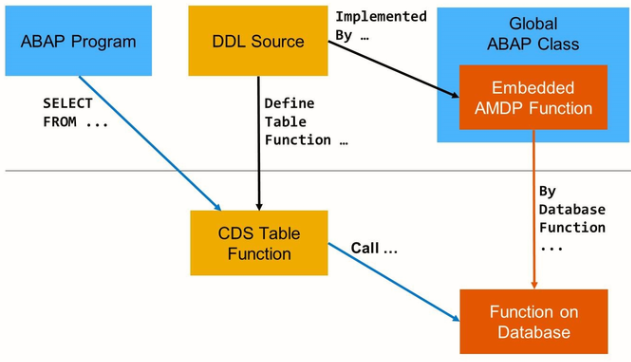
The basic idea of CDS table functions is illustrated in the figure above:
A CDS table function is defined in a DDL source via keyword DEFINE TABLE FUNCTION. The definition of the CDS table function refers to an existing AMDP function via addition IMPLEMENTED BY.