Basic Interface Development
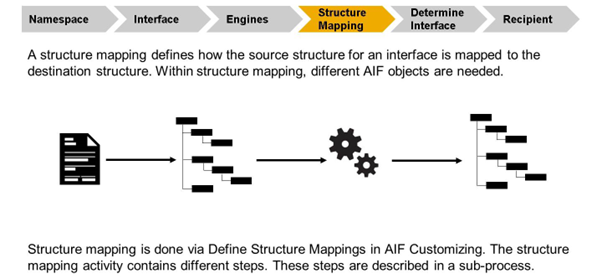
The source and destination structure of an interface usually differ. Therefore, structure mapping is needed. The structure mapping defines how the data from the source structure should be passed to the destination structure. To achieve this, some other AIF objects (for example, checks, value mappings, or fix values) are needed for structure mapping.
Mapping is one of the central parts of AIF. It happens quite seldom that a partner can deliver data in the way the SAP system needs, or SAP can deliver it in a way the partner needs it. So we will have very often mappings.
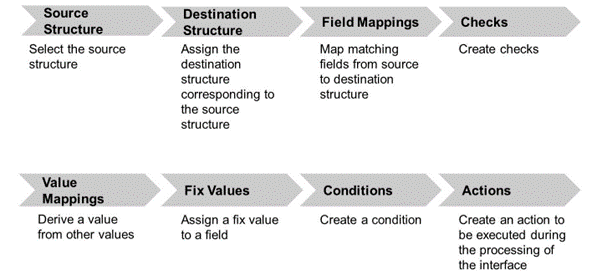
The first step always is to tell which field in the source structure shall be used for which target field. This is called the structure mapping.
If the relevant field is found it might be usable directly. But it is also possible that we have to convert it for example $ to USD or 10.05.2019 to 20191005. This conversion is called value mapping. If a source structure can not provide a field at all we might have to set fixed values.
Additionally, AIF gives us the possibility to use conditions and have different mappings depending on those conditions. This makes it possible to use a special field if a fit exists, and use a more global field if not.
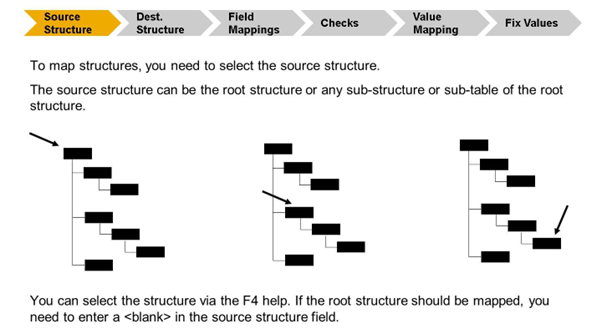
Depending on whether the processed interface is inbound or outbound, the source structure is:
- The raw data structure or a sub-structure/-table of it if the interface is an inbound interface
- The SAP data structure or a sub-structure/-table of it if the interface is an outbound interface
If the root structure should be selected, instead of entering the name of the root structure in the Source Structure field, you need to insert a space character (the field stays empty besides the ).
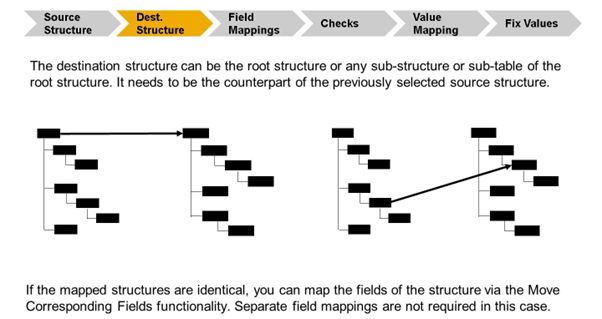
The destination structure is the counterpart to the selected source structure.
If you select the root structure as source structure, the destination structure can be left empty.
If the source and destination structure are identical, you can map the fields of the structures via the Move Corresponding Fields functionality. The Move Corresponding Fields functionality maps the entries from a source field to its counterpart in the destination structure. In this case, you do not need additional field mappings.
If you select the Move Corresponding Fields checkbox, the complete structure including the sub-structure and sub-tables are mapped.
If you select the Copy Fields only checkbox, in addition to the Move Corresponding Fields checkbox, only the fields are mapped.
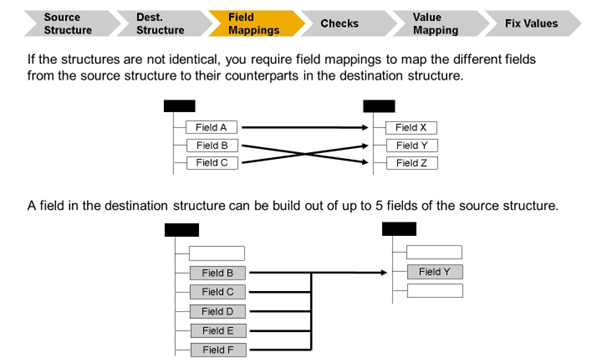
You have to map the fields of the source structure to the fields of the destination structure. You do this via field mappings.
To create a field mapping, at least the field in the destination structure and the field name of the source field is required. All other options are not mandatory.
In a field mapping, you can maintain the following information:
Field in Destination Structure
Defines a field in the destination structure to where the data is mapped.
Source Fields
You can insert up to five fields as source fields in the Field Name 1 to 5 fields. The fields contain the name of a field in the source structure. These field can also contain the field names of a destination structure field. In case a destination structure field was selected, an '@' sign must prepend the field name. The defined fields are available as parameters and can be used in value mappings or checks. An offset and a length can be defined, as well as a separator string. The contents of the Field Name fields are split by this character or symbol in the destination structure. If multiple field names are maintained and no further settings are made, the values of the fields are concatenated into the destination field.
Offset and Field Length