Unit test with ABAP Unit
Unit Testing
Unit testing is a process in which a developer ensures that the smallest testable units of their code - such as methods - are verifiable. This makes it easier to ensure quality, to refactor code, to perform regression testing, and to implement according to the test-driven development model. Unit testing is an integral part of the development phase.
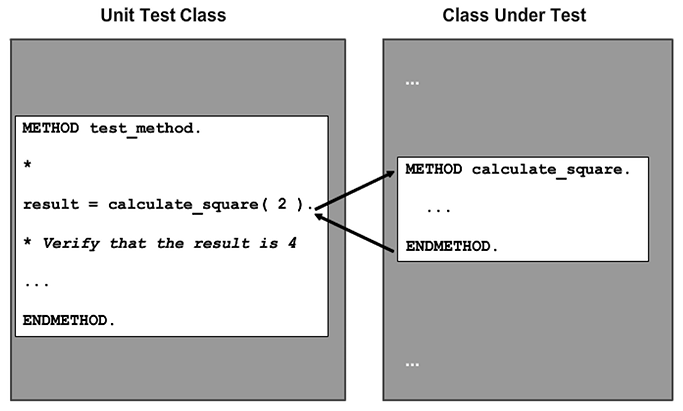
Unit tests are written as local classes within the main program of a global class (class pool). They act as users of the class, and as such, they may only access its public components. Each test is implemented as a method of the class, the aim being to perform remove operations on the class under test that lead to a particular verifiable state of the class. Each test method is executed independently.
Generation of Test Code
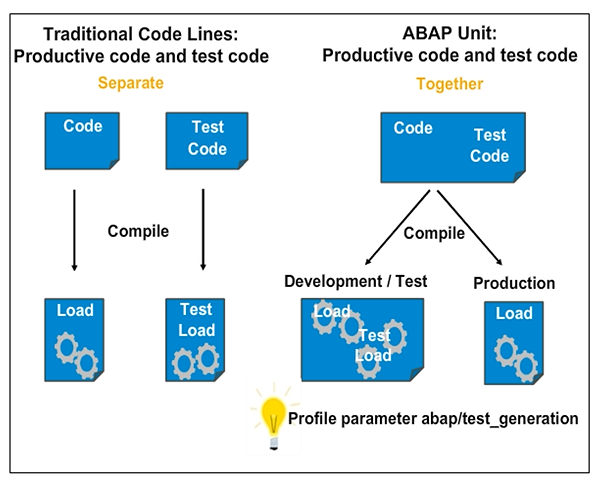
ABAP Unit is a unit-testing framework that is integrated into the ABAP language. ABAP Unit tests are transported with the ABAP repository objects that they test, therefore, the source code is available in all development, testing, and production systems.
However, this does not necessarily mean that ABAP Unit tests can be executed in every system. Profile parameter abap/test_generation specifies to which systems the load of the tests are generated. Typically, test coding is generated only in development and test systems. In production systems, test classes are excluded from the load versions to minimize the size of the loads. This prevents the test coding from having any impact on the function and performance in the production system.
Advantages of Unit Testing
- Define your tests in ABAP
- No need to learn a test script language
- Easy testing while you develop
- Test tool integrated in ABAP Workbench and ABAP Development Tools (ADT)
- Mass Testing
- Unit test integrated in Code Inspector and ABAP Test Cockpit
- Easy execution and evaluation
- Anybody can run a test without ABAP knowledge
- Integrated Test Coverage
- Evaluate which percentage of your code is covered by your tests
- No resource consumption in productive systems
- Decide in which systems test coding is generated and loaded
- Test classification with regard for time consumption and potential damage
- Identify time consuming or critical tests (e.g. tests updating persistent data)
Definition of a Unit Test Class
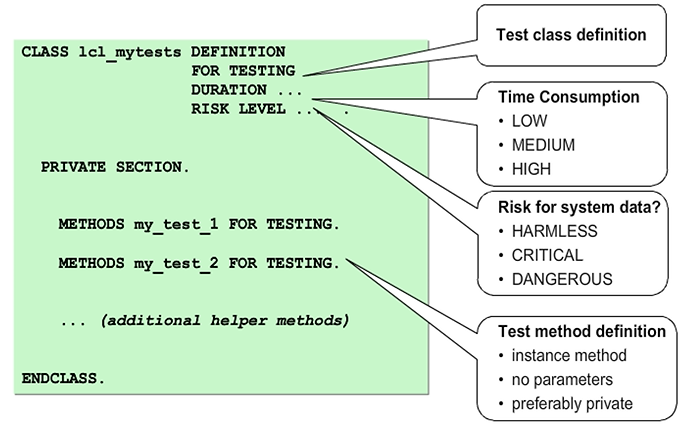
ABAP Unit tests are realized as local test classes with the required test methods in your application programs. You define local test classes by adding the FOR TESTING addition in the class definition. Further additions are used to classify the tests according to their time consumption and the impact on the data integrity. When you test your program using ABAP Unit, an instance is generated automatically for each test class, and the corresponding test methods are executed.
The definition of test classes provides a clear boundary between productive coding and test coding. You can call productive coding from within the test classes. But the compiler will not allow you to access a test class from an ordinary application class.
Test Methods
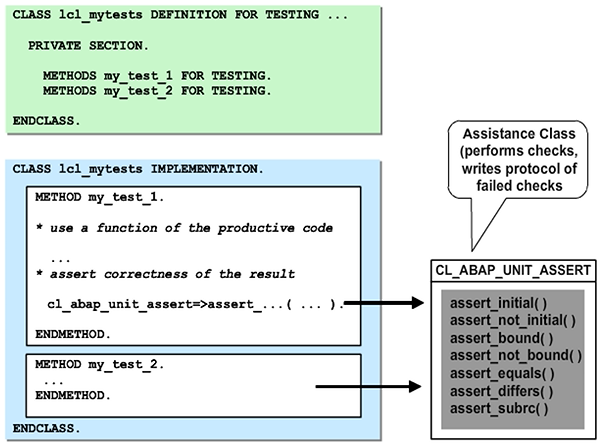
Test methods are defined as instance methods without parameters (preferably private) in your local test classes. Like a test class, their definition also requires the FOR TESTING addition.
The Service Class CL_ABAP_UNIT_ASSERT
A test method contains program code to be executed for testing, followed by a check of the results derived from the test code. The content of the variables to be tested is compared against expected values by calling standard check methods of service class CL_ABAP_UNIT_ASSERT (static methods ASSERT_...). If the respective values do not correspond to the expectation, the check method can enter a note, a warning, or even an error in the test log.
Method Import Parameters