Implementing a Gateway Service
Building the OData Model
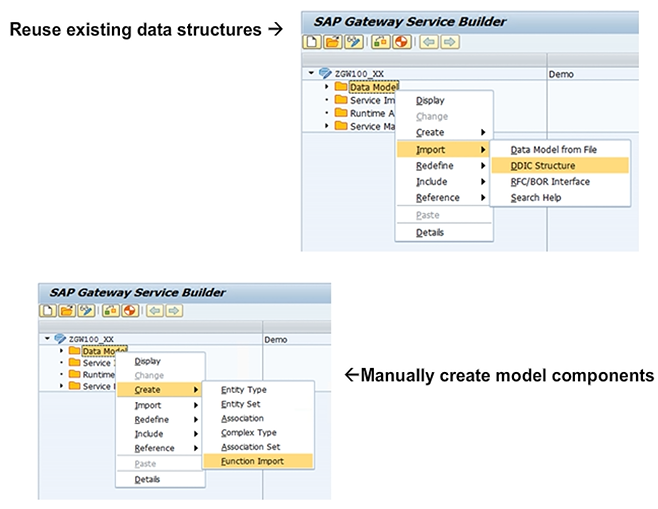
When building the OData model in the Service Builder, you can reuse existing data structures, or manually create model components.
Gateway Service Implementation
An OData service is based on two regular ABAP classes:
- A Model Provider Class (MPC)
- A Data Provider Class (DPC)
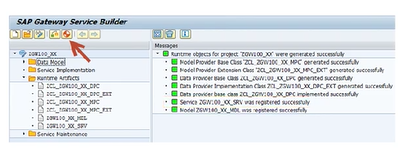
The MPC defines the model and metadata of the service. The DPC provides the functionality of the Gateway Service. Both the MPC and the DPC are registered as a service by the Service Builder when the project is generated.
To create the ABAP classes and register the service, choose the Generate Runtime Objects icon. In the dialog box that appears, the Service Builder suggests names for the runtime artifacts to be created. The suggested values can be modified.
Runtime Artifacts of an OData Service
The two base classes contain logic, which is generated by the Service Builder. The logic in the base classes is overwritten every time the project is regenerated. For this reason, you should not modify the code in these classes, as the Service Builder overwrites their contents.
The extension class names have the suffix EXT. An extension class is a subclass of the base class that is created once, only when the project is generated for the first time. An extension class initially contains no logic. The Service Builder provides the extension class for you to write your own code. Regenerating the project does not overwrite your code in the extension classes, therefore the service implementation takes place in the data provider extension class.
Usually, there is no need to maintain the MPC_EXT also.
HTTP Requests —> OData Operations —> ABAP Methods
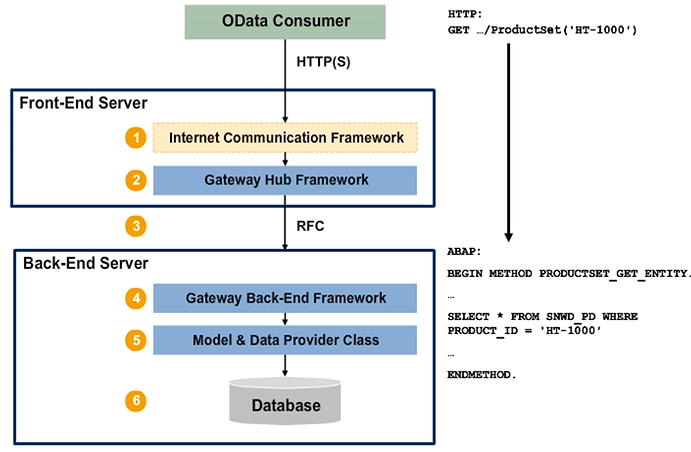
Any OData consumer from the outside world can connect to an SAP Gateway using either HTTP or HTTPS. When this happens, the following actions take place:
- The HTTP request enters the Internet Communication Framework (ICF) on the hub.
- The ICF performs authentication and basic checks such as same origin policy or Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) tokens.
- The ICF forwards the request to the Gateway Hub Framework. The Hub Framework components belong to the namespaces /IWFND/ and /GWCORE/ and are contained in the add-ons IW_FND and GW_CORE or, as of 7.40, in the software component, SAP_GWFND.
- The Gateway framework analyzes the incoming request and performs a transformation of the OData request into the SAP internal representation.
- From the Gateway framework on the hub, a Remote Function Call (RFC) takes place to the Gateway framework in the Business Suite backend. These backend framework components belong to the namespace /IWBEP/ and are contained in the add-on IW_BEP or, as of 7.40, in the software component, SAP_GWFND.
- The Gateway framework on the backend ensures that the appropriate method in the Data Provider Extension class is called. In this case, the method PRODUCTSET_GET_ENTITY is called and the value of the key that has been used by the OData client can be retrieved in the ABAP code used for the service implementation in the backend.
- The service implementation then gathers the requested data and sends it back via the different frameworks as an HTTP response.
Code Base Implementation
The Service Builder allows you to easily navigate to the ABAP methods that need to be implemented to support the different OData operations of an entity set. For each entity set in the data model, the Service Builder generates specific methods in the base class to reflect the CRUD and query operations of the entity set.