Using data from a Table View
Returns the result of the first element of the list of <expressions> that does not evaluate to NULL.
The CASE Expression
A special way of calculating column values is using a CASE expression. This expression allows you to determine a column value based on conditions, in other words, to include an IF-THEN-ELSE type of logic in the projection list.

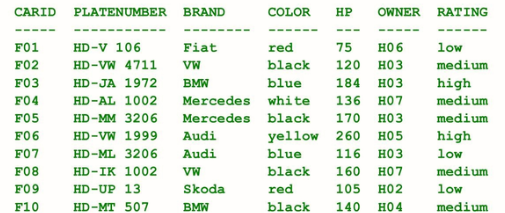



Eliminating Duplicates in Result Sets
If you project a table and don’t include the full primary key, duplicate entries can result. The duplicate entries can be removed explicitly using keyword DISTINCT.


If a projection list contains multiple columns, DISTINCT always refers to the combination of all these columns.
The TOP N Clause
You can use the TOP N clause as part of the SELECT clause to specify that the result set should contain at most N rows

- You can combine the TOP N clause with the keyword DISTINCT.
- No error is thrown if you request more rows than available. The result set will not be filled with additional, “artificial” rows.
- It is possible to request 0 result rows. In this case, the result set does not contain any row.
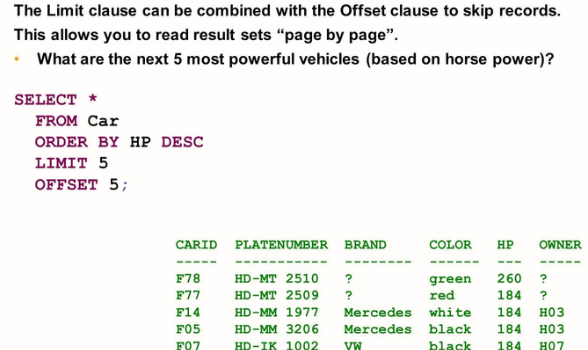
The LIMIT and OFFSET clause
To browse a result on a page-by-page, you can use the LIMIT and OFFSET clause.

The ORDER BY clause
You can use the ORDER BY clause to explicitly specify the sort order of the result set and this way get a reliable sort order.

- Use ORDER BY <fieldname> ASC – for sorting the field in ascending order (Optional).
- Use ORDER BY <fieldname> DESC – for sorting the field in descending order.
- The sorting can be applied using a column that doesn’t appear in the projection list.
- You can sort using a combination of columns
- Instead of the column names in the ORDER BY clause, the column numbers can be used.

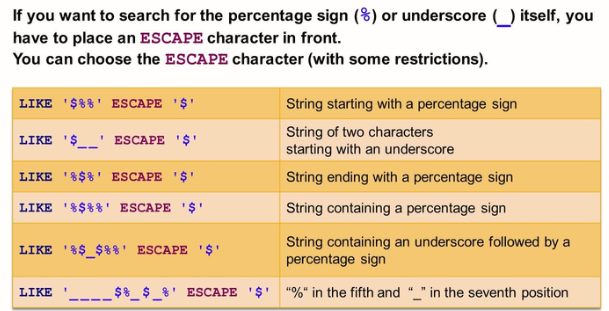
The WHERE Clause
The WHERE clause is used to select a subset of rows from the data source based on a specified condition. Only the rows matching the condition are returned.