Advanced Structure and Field Mapping
After all mappings are done, the data is mapped from the source to the destination structure.

Further Explanations about objects, displayed in the figure:
Selection Field
Defines a field of the sub-table that is used for filtering the table rows for the hierarchical mapping. The field is part of the selected sub-structure of the raw structure.
Operator
Defines the comparison operator for comparison between the input value of the Selection Field and the Comparison Field.
Comparison Field
Defines a field from the source structure. The value of this field is compared using the operator defined in the Operator field and the field defined in the Selection Field.
Example
Flights belonging to a specific customer are identified by the customer ID. On the destinations side, you need the flight bookings belonging to the current customer. Therefore, you have to specify the Comparison Field and the Selection Field. At runtime, the customer with ID = 7411 is mapped. AIF then checks which flight bookings on the source side belong to customer 7411 and map those flights to the customer's flight bookings on the destination side.
Value Conversion

Data Element for Conversion: Defines the data element for conversion. In addition to the Data Element for Conversion, the Direction of Conversion Exit also needs to be maintained. If the direction is not maintained, the conversion is ignored.
Example: The source field is defined as STRING containing a date. The destination field is defined as DATS. The conversion element in this case would be DATS.
Conversion Routine: Converts data from display format to internal format and vice versa. If a standard conversion is not suitable, it can be overridden by a conversion routine in the underlying domain.
A conversion routine is identified by its five-place name and is stored as a group of two function modules. The function modules have a fixed naming convention. The following function modules are assigned to conversion routine xxxxx:
- CONVERSION_EXIT_xxxxx_INPUT
- CONVERSION_EXIT_xxxxx_OUTPUT
The input module performs the conversion from display format to internal format. The output module performs the conversion from internal format to display format.
Example for Conversion Routine: ALPHA, MATN1
Direction of Conversion Exit: Defines the conversion direction for the input data defined in the Conversion Exit field. Direction can be External to Internal or Internal to External. The Conversion Exit and the Direction of Conversion fields are required to be used in combination.
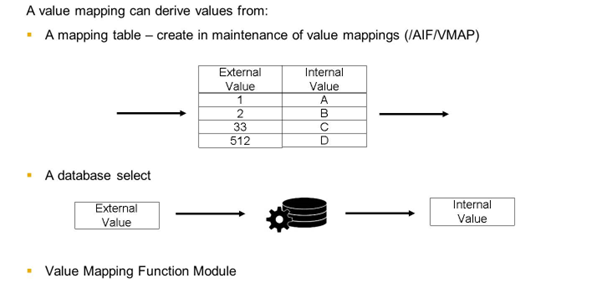
Value Mapping

A value mapping can be used to derive one or multiple values of a source structure to the corresponding values in the destination structure.
Value mappings are assigned to field mappings.

A value mapping is created in the AIF Customizing in the Define Value Mappings activity.
A value mapping has a well-defined input (up to five field values) and a well-defined output (one field value) and remains independent of the context in which they are called. Therefore, value mappings can be reused by several interfaces in several namespaces.
Value Mapping Creation