Defining Actions and Messages
This quick fix creates the class pool and generates the required local class or classes and the required methods for all parts of the behavior definition that need implementation.

Creating the Action Handler Method
If the behavior definition contains the action definition, the quick fix will automatically create the local handler class and the action implementation method.
If the behavior pool already exists when you add an action (or anything else that needs implementation), you have to add the missing implementation method to the behavior pool yourself.
There is a quick fix for updating the behavior pool. To invoke this quick fix, place the cursor on the name of the action and choose Ctrl + 1.
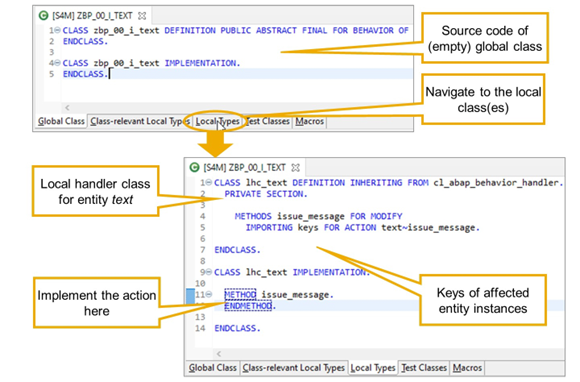
Navigating to the Action Handler Method
The implementation of an action is contained in a local handler class as part of the behavior pool. To navigate to the definition and implementation of the local class choose the Local Types tab.
The generated action handler method is located in the local handler class for the related RAP BO entity. This local class inherits from the base handler class CL_ABAP_BEHAVIOR_HANDLER. The name of the generated local handler class is lhc_, followed by the alias name of the entity. If there is no alias, the technical name of the entity is used instead.
Actions in OData Services
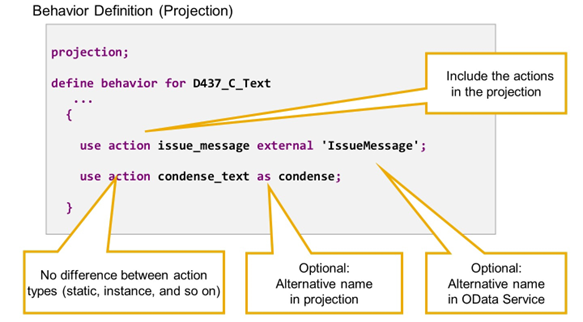
Example: Action Projection
The syntax element use action is used to add actions from the underlying base behavior definition to the projection. Only such actions can be reused that are defined in the underlying behavior definition.
Some additions existing to adjust or extend the action definition. Among those is addition as to define an alias for the action in the projection layer. Addition external defines an alias for external usage, for example in the OData Service. This external name can be much longer than the alias name in ABAP and needs to be used when defining the corresponding UI annotations.
Actions in SAP Fiori Elements
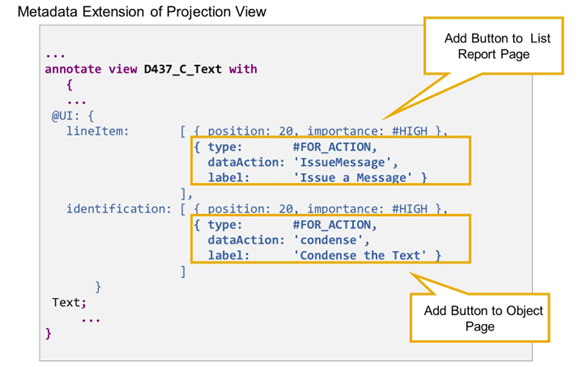
Action Buttons in UI Metadata
On the UI, actions are triggered by choosing an action button. This action button must be configured in the backend in the metadata of the related CDS view. Depending on where you want to use an action button on the UI (list report, or object page), use the annotation @UI.lineItem or @UI.identification to display an action button.
Messages in RAP
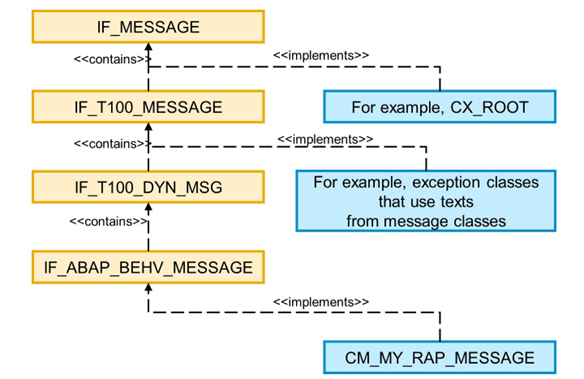
Messages in EML and RAP
Messages offer an important way to guide and validate consumer and user actions, and help to avoid and resolve problems. Messages are important to communicate problems to a consumer or user. Well-designed messages help to recognize, diagnose, and resolve issues.
The message concept of EML and RAP is based on the proven concept of class-based messages. At runtime, a message is represented by an instance of an ABAP class that implements global interface IF_MESSAGE.
For messages in EML and RAP, it is not sufficient to implement interface IF_MESSAGE. The relevant classes have to implement the specialized interface IF_ABAP_BEHV_MESSAGE.
ABAP Class for Class-based Messages
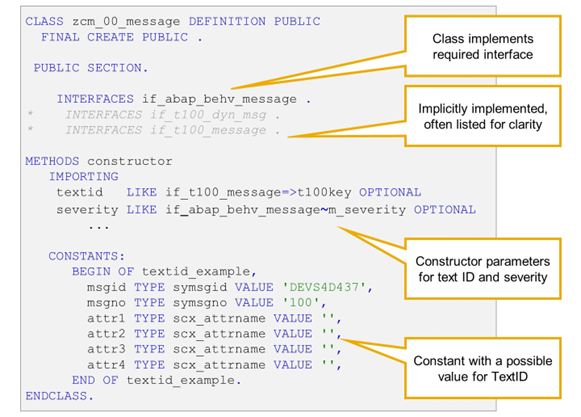
ABAP Class for Class-based Messages
Classes which implement interface IF_ABAP_BEHV_MESSAGE have the following important instance attributes:
- IF_ABAP_BEHV_MESSAGE~M_SEVERITY
Based on elementary type IF_ABAP_BEHV_MESSAGE~T_SEVERITY. Used to specify the message type (error, warning, information, success).