Implementing Authority Checks
When CDS views are built on top of each other, each CDS view needs its own access control. For example, an access control defined for an data model view does not also apply to the projection view built on top of this data model view. But it is not necessary to repeat the same conditions repeatedly. By using addition INHERITING CONDITIONS FROM ENTITY, one access control can inherit the conditions from another, typically an underlying CDS entity. In this way, a projection view can inherit its conditions from the underlying data model view.
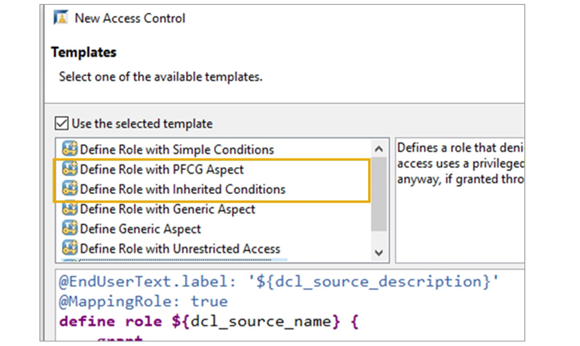
Templates for Creating Access Controls
When creating an Access Control, ADT offers a number of templates for the source code.
The Define Role with PFCG Aspect template is a blue print for an Access Control that defines conditions based on authorization objects.
The Define Role with Inherited Conditions template uses the addition INHERITING CONDITIONS FROM ENTITY instead.
Authority Check in Behavior Implementation
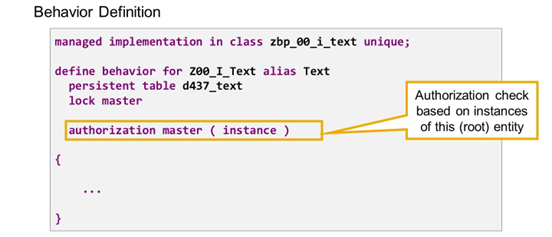
Activate Authorization Control in RAP BO
Authorization control in RAP protects your business object against unauthorized access to data. Authorization control is defined on entity level by adding authorization master ( instance ) or authorization dependent to the define behavior statement.
In the brackets after authorization master, the following variants are available:
global
- Limits access to data or the permission to perform certain operations for a complete RAP BO, independent of individual instances, for example, depending on user roles.
- Must be implemented in the RAP handler method FOR GLOBAL AUTHORIZATION.
instance
- Authorization check that is dependent on the state of an entity instance.
- Must be implemented in the RAP handler method FOR INSTANCE AUTHORIZATION. For compatibility reasons FOR AUTHORITY is also supported.
global, instance
- Combination of global and instance authorization control: Instance-based operations are checked in the global and in the instance authority check.
- Both RAP handler methods, FOR GLOBAL AUTHORIZATION and FOR INSTANCE AUTHORIZATION, must be implemented.
- The checks are executed at different points in time during runtime.
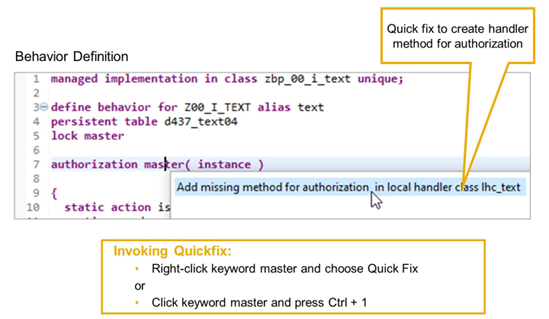
Creating the Authorization Handler Method
If the behavior definition contains the authorization addition when you create the behavior pool, the quick fix will automatically create the local handler class and the method or methods for authorization implementation.
If you add the authorization definition when the behavior pool already exists, you have to add the missing implementation method.
There is a quick fix for updating the behavior pool. To invoke this quick fix, place the cursor on the keyword master and press Ctrl + 1.
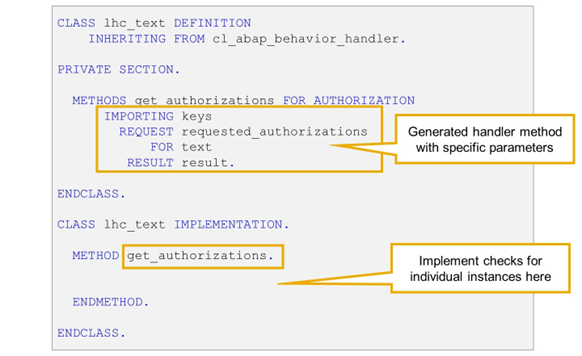
Implementing the Authorization Handler Method
Authorization handler methods are defined with addition FOR INSTANCE AUTHORIZATION or with addition FOR GLOBAL AUTHORIZATION. The methods that are required depend on the behavior definition.
Like all handler methods, authorization handler methods require specific parameters that are supplied or evaluated by the RAP runtime framework. The types of these parameters are derived from the CDS data definition and the CDS behavior definition.
