Using Generic Data Types
Generic typing enables the field symbol to refer to data objects with different types. As a result, you can address different data objects in the same operand position of an ABAP statement.
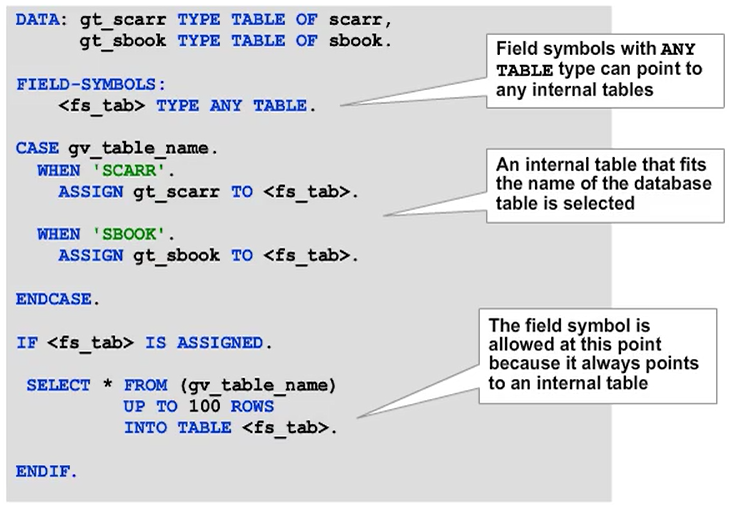
The figure shows an example of how to use a field symbol in a dynamic SELECT statement.
Type Casting With Field Symbols
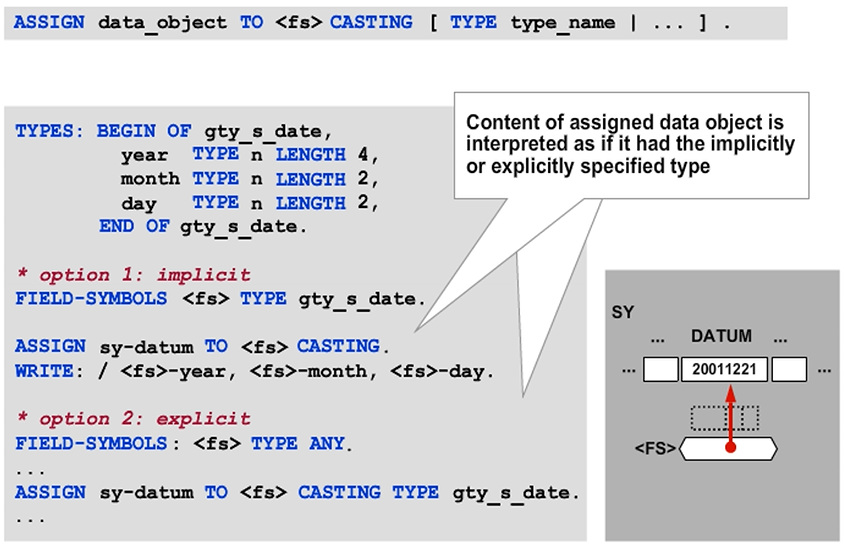
If the CASTING addition is used when a data object is assigned to a field symbol that has a different type, the restrictions of having to use the data objects original type are removed.
If the CASTING TYPE addition is used when assigning a data object to a field symbol that has a different type, the data object can be accessed using the field symbol as if it has that explicitly specified type.
In the figure, note that the system field SY-DATUM is an elementary character-type component of length 8.
Dynamic Access to Data Objects
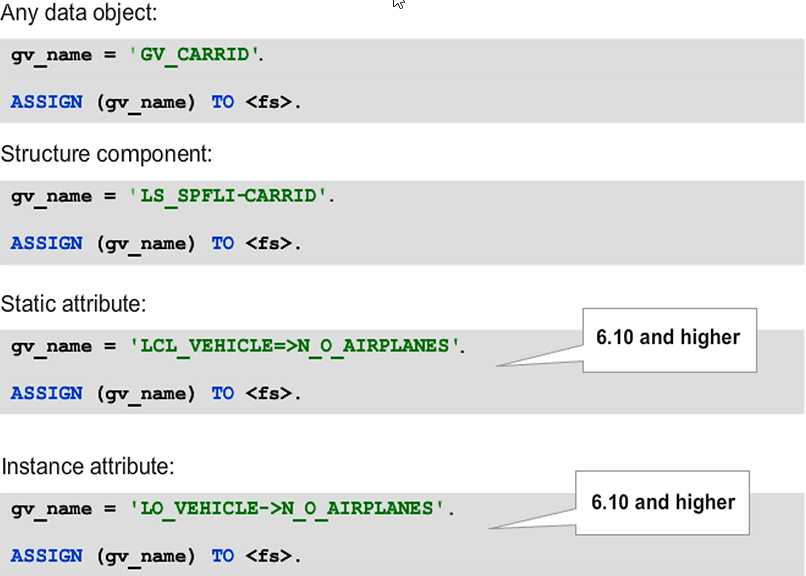
In most ABAP statements, you cannot replace data objects in operand positions directly with character-type data objects in parentheses. However, this option is available in the ASSIGN statement for the data object to which you assign the field symbol.
This approach indirectly makes it possible to call the data object dynamically by its name. You have to assign a generically typed field symbol to the data object using the syntax in the figure. Then use that field symbol in the ABAP statement. There are easier and less error-prone alternatives to specifically access attributes and structure components.
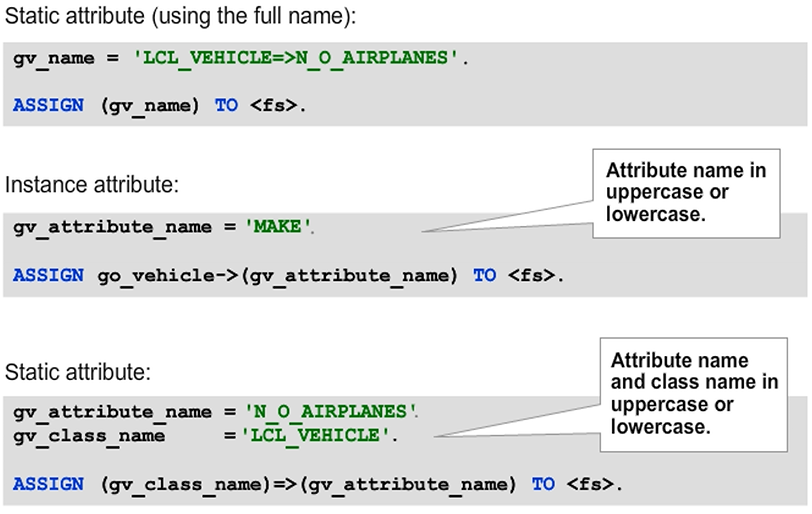
Dynamic Access to Instance Attributes and Class Attributes
In addition to using the full identifier for dynamic access to attributes of classes and objects, you can also specify only the attribute name with a character-type data object. The object reference and component selector are specified statically. You can also dynamically specify the class name for static attributes, if necessary. This syntax is similar to that used for dynamic method calls.
Hint: Because the syntax check supports the static part of the statement, these variants are less error-prone and are therefore preferred.
Dynamic Access to Structure Components
A special variant of the ASSIGN statement provides access to structure components dynamically. You specify the structure statically or through a separate field symbol in the ASSIGN COMPONENT ... OF STRUCTURE ... statement. Address the components either by name or by position (number) within the structure.
Because the syntax check supports the static part of the statement, these variants are less error-prone and are therefore preferred.
Because the system addresses the components of a structure by their positions in sequence, you can process any structure completely, component by component.

Full Processing of Any Non-Nested, Flat Structure
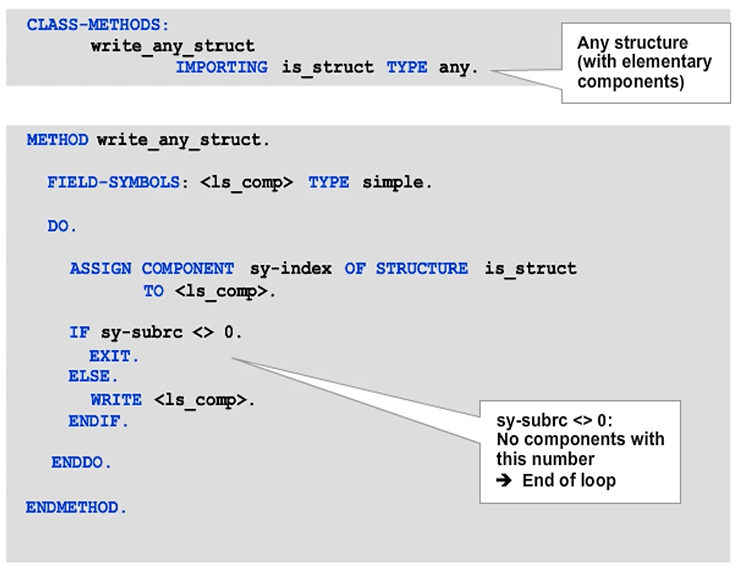
In the figure, an uncatchable ASSIGN_TYPE_CONFLICT runtime error occurs if the transferred structure contains a component that is incompatible with the generic SIMPLE type of the field symbol. Similarly, a runtime error occurs during the WRITE statement if you type the field symbol with ANY.
Generically Typed Data References
The use of generically typed reference variables is restricted in ABAP. With the exception of the ASSIGN statement, generically typed reference variables cannot be dereferenced directly in operand positions. The statement WRITE ref->* causes a syntax error, for example, if the data reference has type TYPE REF TO DATA.
Due to these restrictions, only use generic data references where generic field symbols do not work.
Common Use cases for references with TYPE REF TO DATA
- In internal tables