Implementing Advanced Object-Oriented Techniques
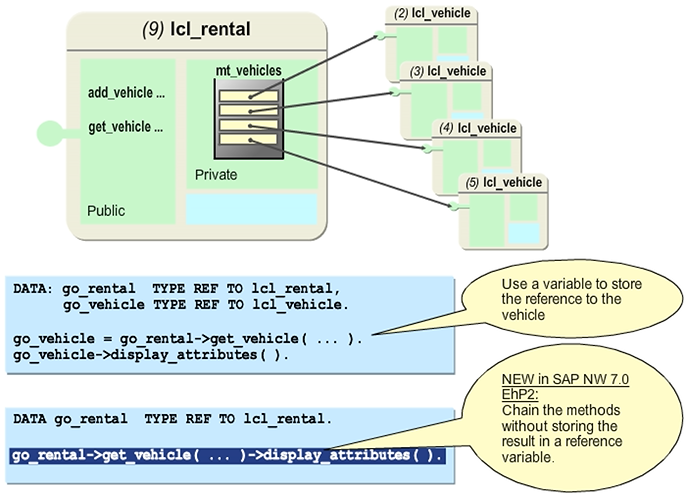
Creating Objects with the NEW Operator
The NEW operator creates a new instance of a class, thus replacing CREATE OBJECT. After NEW, you must specify the class that you want to instantiate. In the example in the figure, the pound sign (#) denotes that the class to be instantiated should be derived from the definition of the reference variable, so go_vehicle will hold a reference to an instance of the class lcl_vehicle. In the second example a subclass instance is created, therefore explicit typing with the desired subclass is necessary.
Note that the NEW operator can only accept the importing parameters of the constructor, and that it is not possible to handle conventional sy-subrc-based exceptions. You handle class-based exceptions by enclosing the statement containing the NEW operator in a TRY... CATCH... ENDTRY block as normal.
The NEW operator is available since Release 7.40.
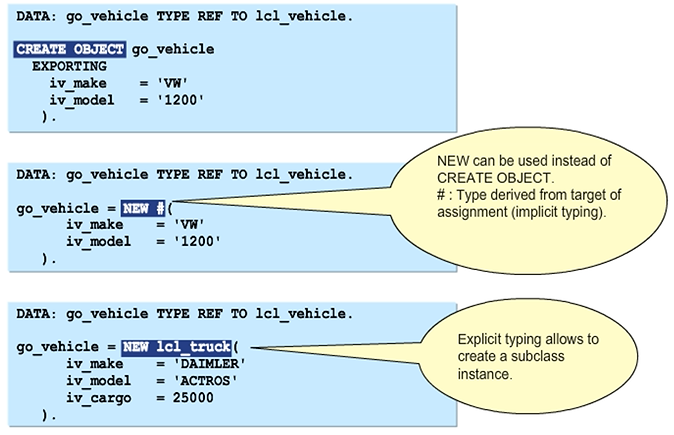
Using NEW at Expression Position
It is possible to use the NEW operator at many expression positions, especially as an actual parameter of a method.
In the first example in the figure, an object is created just before it is needed as input for an APPEND statement.
In the second example, immediately before a method call, we create a vehicle instance to use it as actual value for a method parameter.
In the third example, we create the ALV instance using NEW, and, instead of passing a reference variable to the i_parent parameter, we create an instance of the container control on the fly. The inner NEW operator cannot use the pound sign to derive the type of the new variable implicitly, since the formal parameter i_parent of the ALV constructor has the type REF TO cl_gui_container, which is a superclass that may not be used as a container.
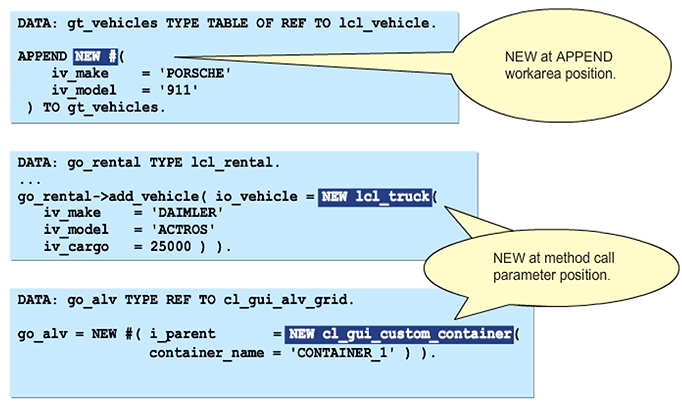
Conditions on Dynamic Type of Object Reference
From Release AS ABAP 7.50, you can use the expression IS INSTANCE OF to find out whether an object reference points to an instance of a particular class. IS INSTANCE OF is true if the object in question is an instance of either the specified class or one of its subclasses.
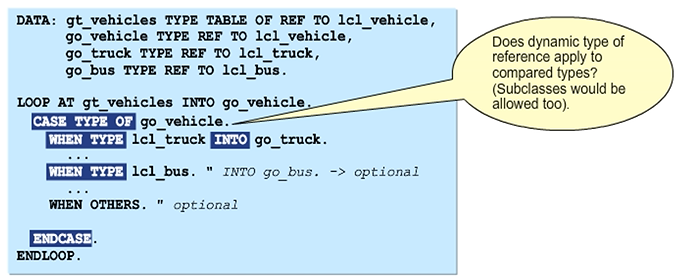
Special Case Distinction CASE TYPE OF for Object Reference Variables
Available from Release 7.50, the control structure CASE TYPE OF allows you to distinguish between different possible types of an object reference. The corresponding WHEN TYPE block is processed if the dynamic type of the object reference variable corresponds to the given class. The optional addition INTO allows you to perform a down cast directly by specifying a reference variable
Visibility of the Instance Constructor
In ABAP Objects, we can restrict the visibility of the instance constructor. If the visibility of the instance constructor is restricted, the CREATE OBJECT statements to instantiate this class is only allowed in certain parts of the coding.
The types of visibilities for the instance constructor are as follows:
- PRIVATE
If a class has a private instance constructor, it can only be instantiated from within the class itself, typically in static methods defined for that purpose. These methods are sometimes called Factory-Methods.
- PROTECTED
If the instance constructor is protected, the visibility is extended to all of its subclasses, that is, the subclasses can also create instances of the class.
- PUBLIC
A public instance constructor is the default visibility setting: Instances of the class can be created anywhere, inside the class itself, inside other classes, or, even in a non-object-oriented part of the program (for example, the main program).
Set the visibility by using the CREATE addition with the CLASS statement.
The relevant indicator is in the Class Builder on the Attributes tab page for the relevant class.