OData Fundamentals
Entity Data Model Overview
An EDM describes the organization and relationship of the data resources that are modeled as entity types within a particular business scenario. Entity sets are collections of entities, which are instances of entity types and can be accessed as follows:
- http://<host>/<ServiceRoot>/SalesOrderItems
- http://<host>/<ServiceRoot>/<Products
Entities are grouped into entity sets. For example, the SalesOrderSet entity set is a set of SalesOrder instances. All entities of one entity set are of the same entity type.
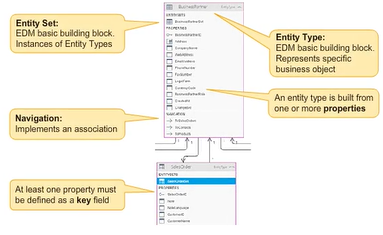
Entity Types
Entities are instances of entity types, which are richly structured records with a key. The structure of an entity type is provided by its properties. An entity key is formed from a subset of the properties of the entity type. The key (for example, SalesOrderID or BusinessPartnerID) is a fundamental concept used to uniquely identify and persist entity instances and to allow entity instances to participate in associations. The key of an entity is defined by one or many properties. Entities can be addressed individually by means of key values, or as collections by means of query options.
An association is a named relationship between two entity types. Every association includes two association ends, which specify the entity types that are related, and the cardinality rules for each end of the association. (Associations between two entity types can be compared to foreign key relationships between two tables.)
Entity types may include one or more navigation properties. The navigation property derives its name from the fact that it allows navigation from one entity to another. A navigation property is tied to an association and allows navigation from one end of an association, the entity type that declares the navigation property, to the other related end, which can be anything from 0 or more related entities. The BusinessPartner entity type has exactly one navigation property named ToSalesOrders. The navigation property makes it possible to navigate from a Business Partner instance to all the SalesOrders of that Business Partner.
All the properties of the Business Partner are listed as XML elements named property. All key properties can be found as propertyref elements in the key element. The BusinessPartner is identified by exactly one key field, the BusinessPartnerID.
Similar to properties, the navigation properties are specified in a separate element called NavigationProperty, which defines the navigation property name, the target entity type, and the cardinality.