Defining a Data model
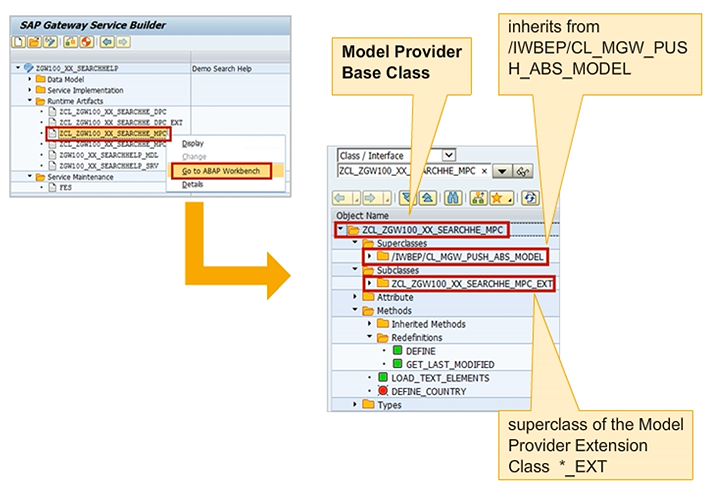
The Model Provider Base Class is a superclass of the Model Provider Extension Class. The extension class can be used to perform any manual changes required to the Model Provider Base Class, rather than changing the data model in the Service Builder.
By virtue of having /IWBEP/CL_MGW_PUSH_ABS_MODEL as the superclass, the Model Provider Base Class inherits a method called DEFINE. The base class overwrites the DEFINE method to implement all the model and metadata information for the service.
Model Provider Class
The implementation of the DEFINE method depends on the data model elements which were created in the Service Builder, such as entity types, associations, function imports, and complex types. For each of the artifacts created in the Service Builder, a private method is generated to create the corresponding data model element. This method is then called inside the DEFINE method.
Generated Data Provider Extension Class
You can access the code of the Data Provider Extension Class easily from within the Service Builder by clicking on the context menu of a class listed in the Runtime Artifacts folder.
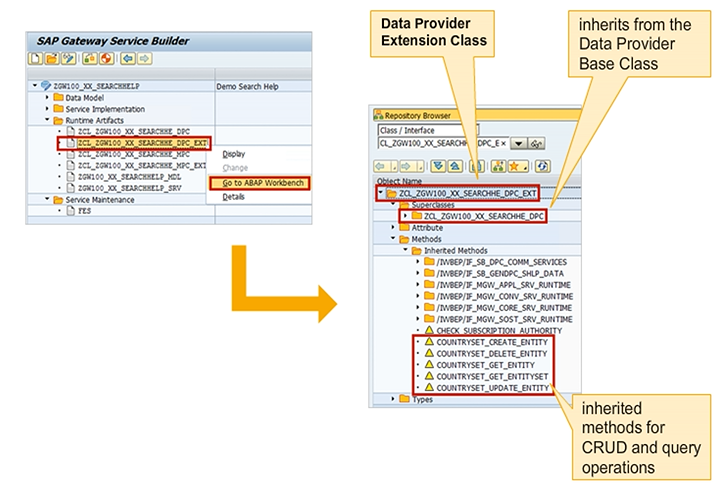
The Data Provider Extension Class inherits from the Data Provider Base Class, which is also generated.
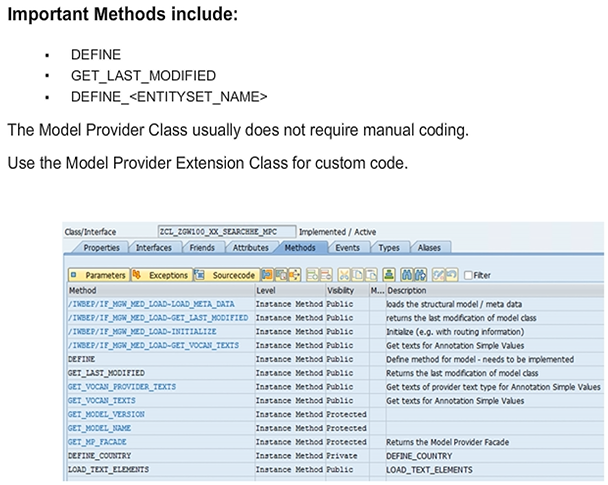
For each entity set in the data model, the Service Builder generates specific methods in the base class to reflect the entity set’s CRUD and query operations. For example, for an entity set called PRODUCTSET, the following methods are created in the base class:
- PRODUCTSET_CREATE_ENTITY
- PRODUCTSET_GET_ENTITY
- PRODUCTSET_UPDATE_ENTITY
- PRODUCTSET_DELETE_ENTITY
- PRODUCTSET_GET_ENTITYSET
In the base class, all these generated methods raise an exception indicating that the respective OData operation is not yet implemented.
The Data Provider Extension Class inherits these methods from the superclass and has to redefine them to program the data provisioning for the different request types. That is, to implement the service, you have to overwrite the appropriate methods from the base class in the extension class.
Registration and Activation
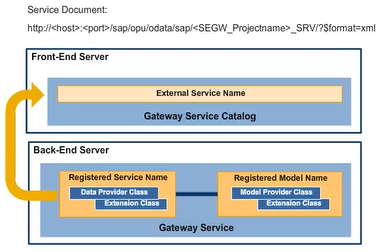
You have learned that to expose your Gateway Service to the outside world, you must activate the service on whichever server is acting as the Gateway hub system, that is, you must create an entry in the Service Catalog of the SAP Gateway hub system.
Publish the Service on the Hub
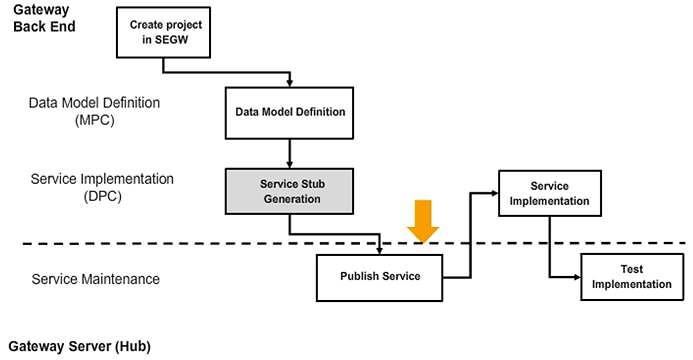
We have seen so far that the Service Builder generated four ABAP classes for our service: a Model Provider and a Data Provider Base class, as well as a Model Provider and a Data Provider Extension class. Both, the Model Provider classes and the Data Provider classes are hosted on an SAP Business Suite system, which is a backend system where the SAP Gateway backend add-ons are installed.
Using the Service Builder, we registered the service in the backend system and defined an external name of the Gateway Service, which is the name that is seen by the end user. So far, this Gateway Service is registered in the backend system where it would retrieve its data if being called from the outside world.
In order to expose our Gateway Service to the outside world, we must now activate the service on whichever server is acting as the Gateway hub system. That is, we have to create an entry in the Service Catalog of the SAP Gateway hub system. After that, the service is accessible from outside the SAP system. An entry in the service catalog is created by using the transaction /IWFND/MAINT_SERVICE.
Service Maintenance
By pressing the AddService button, you can choose to activate a service on the hub that is searched for by providing the system alias entry of the respective backend system.