Developing Draft-Enabled Applications
Implementation Aspects of Draft
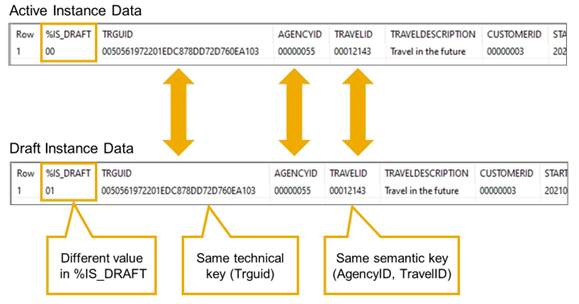
Key Component %IS_DRAFT
If a RAP Business Object is draft enabled, all derived types for its entities contain an additional component %IS_DRAFT that is used to distinguish between active instances and draft instances.
The example shows screenshots from the table display tool in the ABAP debugger.
The draft indicator %IS_DRAFT is typed with data element abp_behv_flag (technical type X(1)) and can assume two different values, which can be found in constant structure if_abap_behv=>mk. For a draft instance, %IS_DRAFT equals if_abap_behv=>mk-on (#01), and if_abap_behv=>mk-off(#00) for active instances.
In RAP, an edit-draft is created by copying all fields of an active instance. In particular, the primary key fields have identical values in a draft instance and the corresponding active instance. The only way to distinguish between draft and active data is the value of %IS_DRAFT.
Because of this, %IS_DRAFT must be treated like an additional key field that is mandatory when accessing data via EML and in RAP implementations. The framework supports this by automatically including component %IS_DRAFT in the component group %tky.
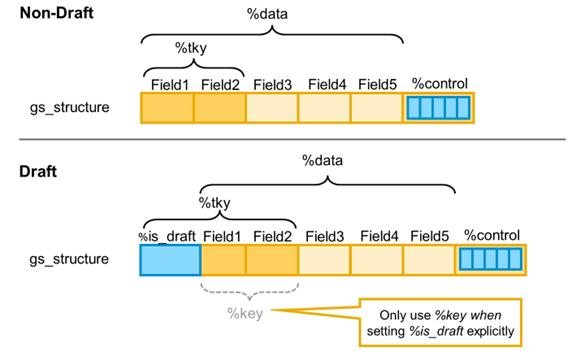
Component Groups %tky and %key
If you use %tky to address the primary key field of an entity, you do not have to change your business logic implementation when draft-enabling the business object. The business functionality runs smoothly without adapting your code after draft-enabling your business object.
If you used field group %key in your business logic implementation, or addressed the key fields directly via their individual component names, you have to revise the implementation when draft-enabling the business object.
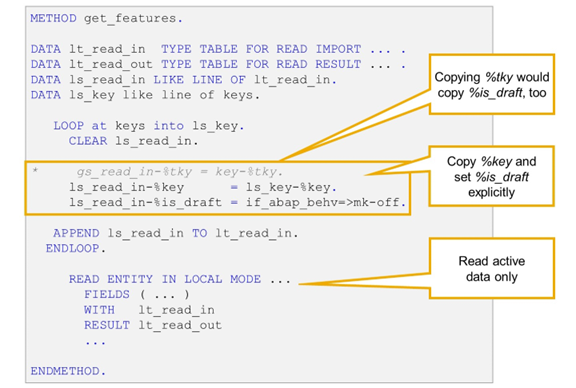
Example: Feature Control for Draft Instance
In the behavior implementation for a draft-enabled business object, import parameter keys always contains the technical key fields and the draft indicator %is_draft. When you use component group %tky to setup the input for a READ ENTITY statement, you read draft data for draft instances and active data for active instances.
There can be situations where it becomes necessary to read the active data for a draft instance and not the draft data itself. A good example is the implementation of instance feature control.
Let’s consider a sales order that becomes read-only when having a certain status (cancelled, delivered, and so on). When feature control is based on the draft data, the draft becomes read-only as soon as the user changes the status in the draft. If the status change was done accidentally, the user has no chance to undo it in the current edit process. The only remaining option is to cancel the draft and start editing again. But if feature control is based on the active instance, the draft data remain editable until the active data is updated.
To read the related active data for draft instance, use component group %key instead of %tky and set the draft indicator %is_draft explicitly.