Defining Composite RAP Business Objects
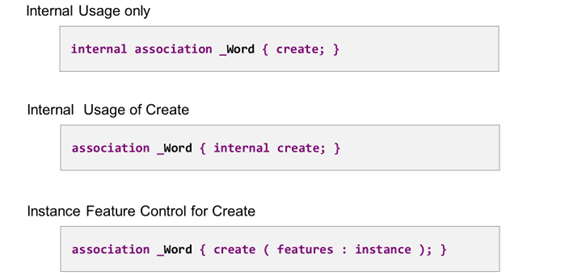
Some Variants of Statement Association
Several operation additions are available to restrict the usage of an association. If internal is placed before keyword association, read and create access are forbidden for an outside consumer of the business object. If it is placed within the curly brackets, before the keyword create, the create access is restricted, but read access is available for outside consumers.
As for the standard operations, update and delete, you can implement instance feature control for the create operation. To do so, add ( features : instance ) within the curly brackets, after keyword create.
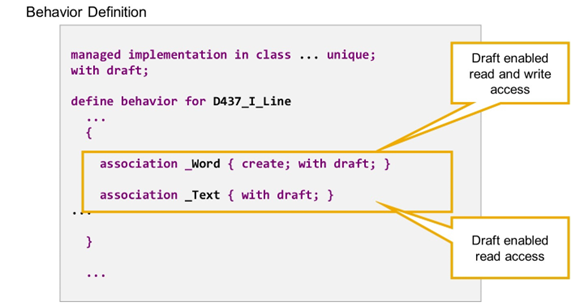
Draft Enabled Associations
By adding with draft; inside the curly brackets, you specify that the association is draft-enabled. A draft-enabled association retrieves active data if it is followed from an active instance and draft data if it is followed from a draft source instance (for details about the draft concept, see CDS BDL - managed, with draft).
If a business object is draft-enabled, then all associations should be draft-enabled, so that the associations always lead to the target instance with the same state (draft or active).
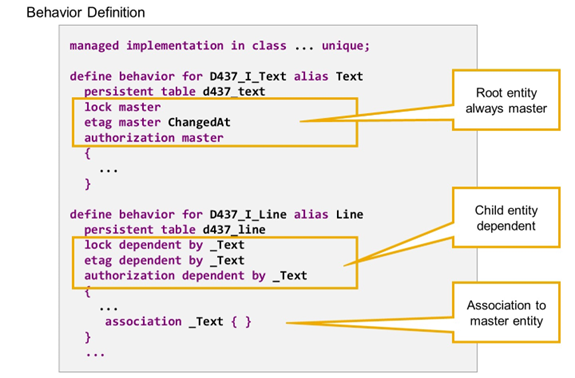
Locks, ETags, Authorizations and for Child Entities
The root entity of a business object is always defined as lock master and, if etag or authorization are specified, this is always with addition master.
For child entities, syntax options lock dependent by etag dependent by and authorization dependent by are available, each followed by the name of an association, that points to the related master entity.
The following rules apply:
lock:
- Currently, only root entities are allowed as lock master,
- Lock dependent is mandatory for child entities in managed scenarios,
- The association always points to root entity.
etag:
- Child entities can be dependent on master.
- Child entities with etag master have to define an own etag field.
- Association can point to non-root entity that is higher in the hierarchy.
Authorization:
- Currently, only root entities are allowed as authorization master.
- Association always points to root entity.