Using Generic Data Types
Cast Assignment for Data References
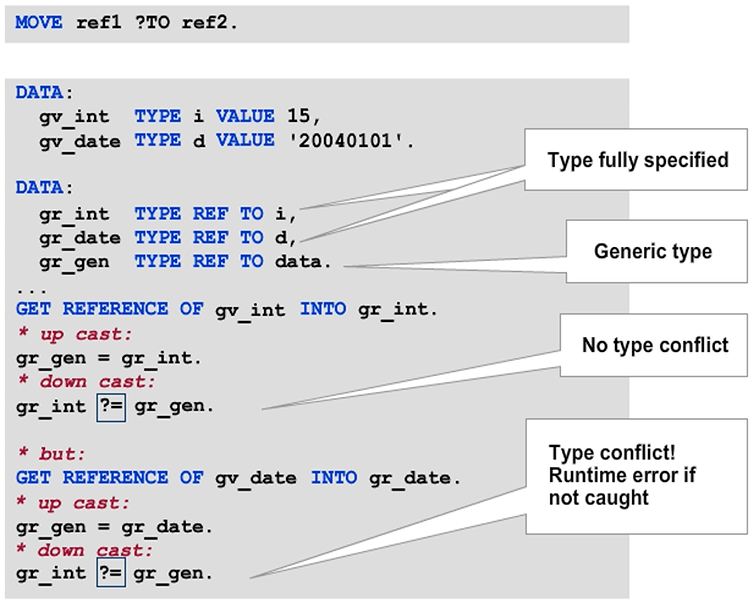
To address the content of referenced data objects, one option is to use a fully-typed data reference. The contents of the generic data reference are copied to the fully-typed data reference. The complete data reference can then be dereferenced in any operand item.
However, for this technique to work, the second reference variable needs to have the same type as the referenced data object.
When you assign values between two reference variables with different types, you perform a cast assignment. It is similar to cast assignment between object references in object-oriented programming.
As with object references, an upcast occurs when the target variable has a more general definition, and a downcast occurs when the target variable has a more specific type than the source variable. Accordingly, assignment from a generic data reference to a fully typed reference is a downcast.
While upcasts to type TYPE REF TO DATA always work, the downcast must have the ?= cast operator to pass the syntax check. The system checks compatibility at runtime in this case.
Caution: If the type of the new reference variable does not match the exact type of the referenced data object, a runtime error occurs. Class-based exception CX_SY_MOVE_CAST_ERROR is the exception that occurs.
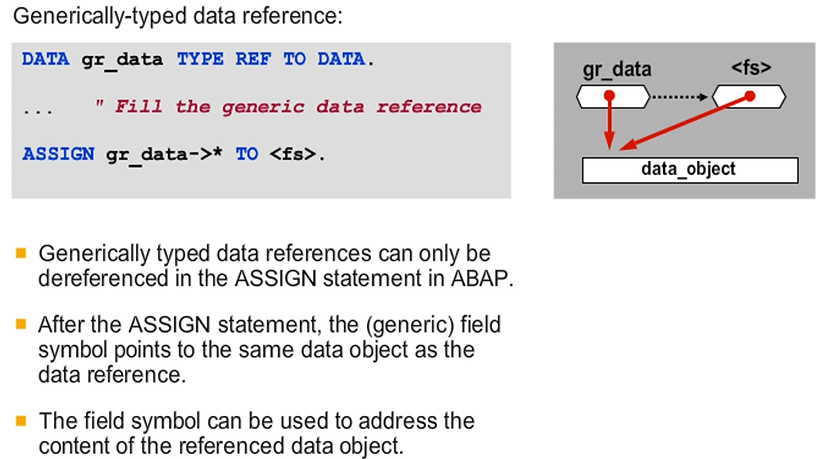
Dereferenced Generic Data References
The only ABAP statement in which you can dereference a generically typed reference variable is the ASSIGN statement.
The ASSIGN statement assigns a (generic) field symbol to the data object to which the generic reference variable points. You then address and further process the contents of the referenced object using this field symbol.