Creating Local Class
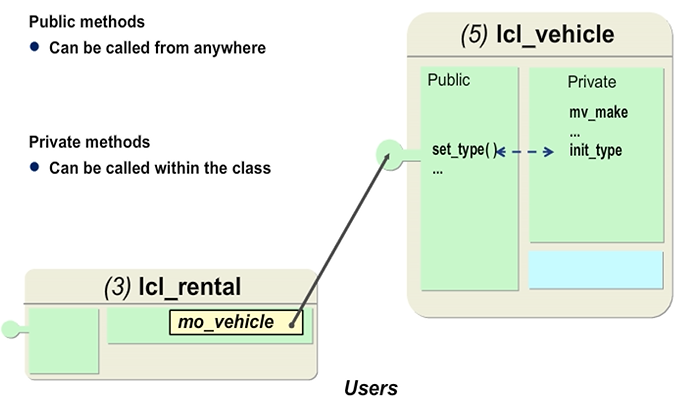
Access to Private Methods
You define private methods in the PRIVATE SECTION and public methods in the PUBLIC SECTION of a class.
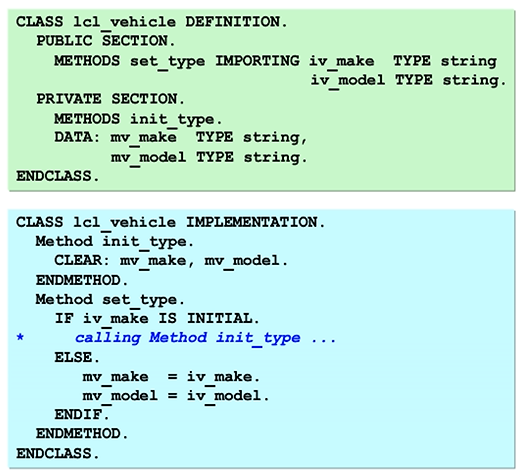
It is not possible to access private methods directly from outside. However, a private method can be called by a public method. In the figure, INIT_TYPE is a private method that is called by the SET_TYPE public method. Defining this private auxiliary method is useful because the instruction to initialize attributes may be used in other methods.
This is an introductory example. Later, you will learn more programming techniques for evaluating formal parameters.
In a class, declarations of attribute names, method names, event names, constant names, type names, and alias names share the same namespace. Additionally, there is a local namespace within methods. Local declarations within a method override declarations made in the class.
Static Methods and Instance Methods
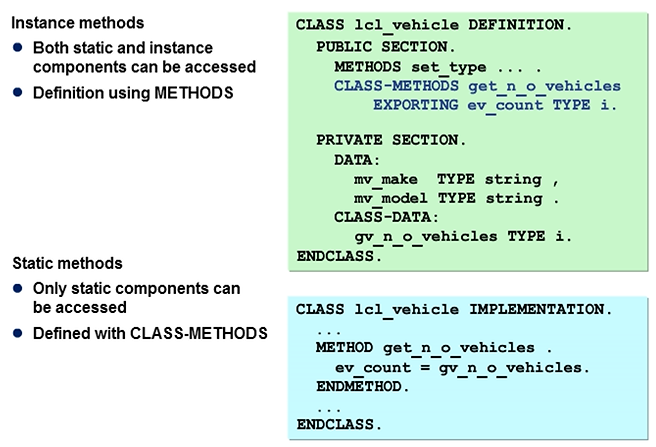
Different kinds of methods are as follows:
- Instance methods
You define instance methods using the METHODS syntax keyword.
- Static methods
You define static methods using the CLASS-METHODS syntax keyword.
You define static methods at the class level. In their implementation, you can only access static components. This means that static methods do not need instances and can be directly accessed through the class.
In the example shown in the figure, the static method GET_N_O_VEHICLES can only access the attribute GV_N_O_VEHICLES. The method set_type is an instance method and can access all the attributes, both static and instance.
You may see static methods referred to as class methods, in line with the CLASS-METHODS keyword.