Implementing a Gateway Service
SAP Gateway Service Builder
The SAP Gateway Service Builder caters for the needs of both experienced and less experienced developers who want to expose data for easy consumption using a variety of platforms, frameworks, and devices.
While experienced developers have maximum flexibility to define a new service from scratch and integrate their own source code, less experienced developers can reduce the time and effort involved in creating services by generating services based on existing business objects, such as BW Easy Queries or CDS views (as of NW 7.40), or interfaces such as Remote Function Call (RFC) function modules or F4 Search Help topics
Service Creation
The development of services using the Service Builder takes place in the SAP backend system.
The Service Builder supports all phases in the development of OData services. They are as follows
- Project Creation
The process starts when you create a project in the Gateway backend system.
- Data Model Definition
In this phase, you define the model your service is to be based on. That is, you define the entity types, entity sets, associations, and so on, that underlie your service.
- Service Implementation
In this phase, you implement the operations that are supported by the service. Here, the runtime objects (ABAP classes and other repository objects) that make up a Gateway service are generated. The actual implementation of the service can be done either by writing code or by mapping the methods of an OData service to the methods of a data source. In this phase, you also register the service in the backend.
- Service Maintenance
In this phase, you activate (or publish) the service on the SAP Gateway hub system that has been registered in the SAP backend system.

Project Creation
To develop a service using SAP Gateway Service Builder, you first need to create a project. You open the SAP Gateway Service Builder by using the transaction code SEGW.
The Service Builder uses projects to bundle all the artifacts you need to develop a service in one central location, helping you to organize the service development and modeling process. Since projects consolidate all related data, you can easily work on multiple projects in parallel and reuse data between projects before generating and activating the actual service.
In addition, you can use projects to organize the movement of objects from one system environment to another ensuring that all artifacts remain together at all times.

Data Model Definition
There are two types of documents associated with each OData service:
- Service document
- Service metadata document
Both document types can be retrieved from a server by means of an HTTP GET call. The service document is available at the Service Root URI and is formatted in Atom or JSON. If you click on the hyperlink, you send an HTTP GET call to the server and the server responds with the service document.
Service Builder Tree Structure
The Service Builder provides a nice tree view folder structure to organize the different components of a data model. This structure provides one folder for each of the following:
- Entity Types
- Complex Types
- Associations
- Entity Sets
- Association Sets
- Function Imports

Data Model in Service Builder
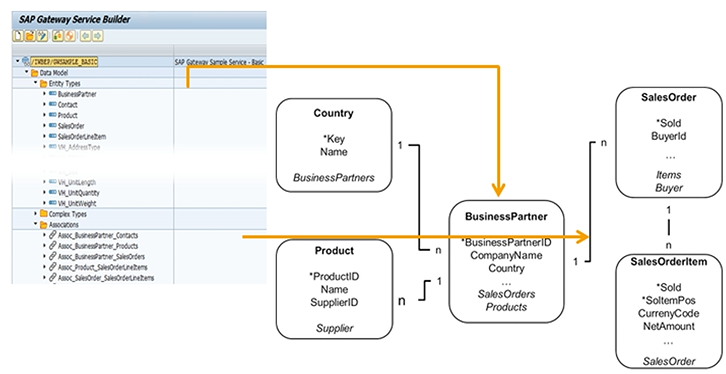
In the figure, the example entity data model consists of the five entity types: Product, BusinessPartner, SalesOrder, SalesOrderItem, and Country (not yet modeled in the Service Builder). The data model has the following characteristics:
- The entity type SalesOrder has the properties SoId, BuyerId, NetAmount, TaxAmount, and LifecycleStatus, where SoId is the key field.
- The entity type SalesOrderItem is built from the properties SoId, SoItemPos, CurrencyCode, and NetAmount. The key fields are SoId and SoItemPos.
- The entity types SalesOrder and SalesOrderItem are related using an association. This association describes the fact that at least one sales order item exists for a single sales order.