Creating OData V4 Services
Recap: OData V2 Service Development Options
The OData V2 Service Development options include:
- Code-based implementation
- Referenced and mapped data sources and classic APIs
- publish:true and referenced data sources using the BOPF framework
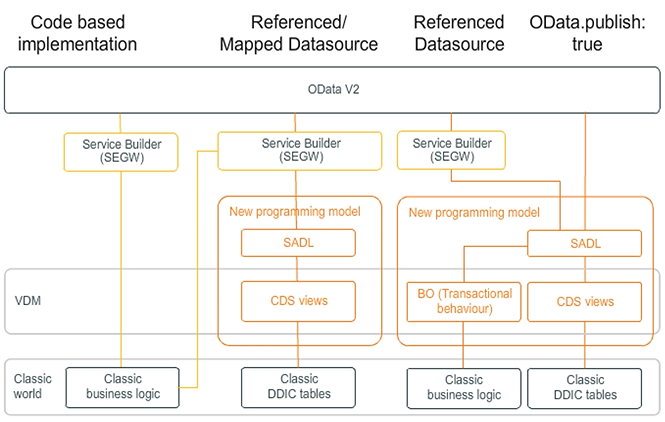
Definition: OData V2 Service Development Options
Code-based implementation
The first option to build OData services that was available, and which is still widely used, is using the Service Builder for OData V2 modeling and a code-based implementation of the data provider extension class that works as an adapter from business logic to protocol specifics. The implementation of the data provider extension class requires deep knowledge of the V2 OData protocol specifics, and the developer has to build everything from scratch. This development approach is described in Unit 3.
Referenced and mapped data sources and classic APIs
A first use of CDS views when developing OData services became available with AS ABAP 7.40. The read and query methods are generated using the mapped data sources, while the create, update, and delete methods have to be implemented using code-based implementation. The mapped data source approach is described in Unit 6, Lesson 2. This is where the Service Builder using the referenced data source approach comes into play.
Here, the data model is based on CDS views and read access is provided out of the box by the underlying CDS views. The Service Builder generates a model provider extension class and data provider extension class that can be used to implement extensions using code-based implementation while leveraging the generic support for read access. By implementing the create, update, and delete methods, it is possible, for example, to call a BAPI to update a business object as described in Unit 6 Lesson 3.
OData.publish:true and referenced data sources using the BOPF framework
When the new programming model became available it first only supported read access (AS ABAP 7.50 SPS01). Write access via BOPF became available with a later version (AS ABAP 7.50 SPS05) which allows you to build “Batch-input”-like SAP Fiori apps.
The BOPF implementation and CDS implementation are both OData protocol-agnostic and the OData protocol support is provided by the SAP Gateway framework. As a result, no deep knowledge of the OData protocol is required. In addition, there is only a minimal implementation effort needed to also support create, update, and delete functionality for your service.
If you are building an application using the new ABAP programming model for building state-of-the-art, intrinsically SAP HANA-optimized Fiori apps in SAP S/4HANA, you can leverage an out-of-the-box OData V2 support. By simply adding the annotation @OData.publish:true in your CDS consumption view, an OData V2 service is generated in the SAP Business Suite or SAP S/4HANA back end that can be published in the SAP Gateway server.
The use of referenced data sources is not limited to access data via classic APIs. It can also be used as an extension layer for applications that are based on the new programming model and that perform their updates via BOPF. Here, the ABAP layer can be used to add additional annotations to the metadata of a service that is not supported by CDS. It is also possible to implement additional business logic via ABAP code, though both extension options should be avoided if possible.
OData V4 Service Development Options
Code-based implementation of OData V4 services requires the implementation of an SAP Gateway data provider class that works as an adapter from business logic to protocol specifics. The service implementation requires a deep knowledge of the OData V4 protocol. The developer has to develop everything from scratch because no code reuse from existing V2 service implementations is possible.
It is planned to support OData V4 as a new type of service binding with the latest ABAP programming model for SAP S/4HANA. The first version of this programming model became available with the SAP Cloud Platform ABAP Environment.
