Understanding the background
The Limitations of classical Open SQL
Open SQL not only restrict itself to the DML part of the SQL. When we look at standard SQL, for example, the SQL-92 standard, many DML features described there are missing from Open SQL.


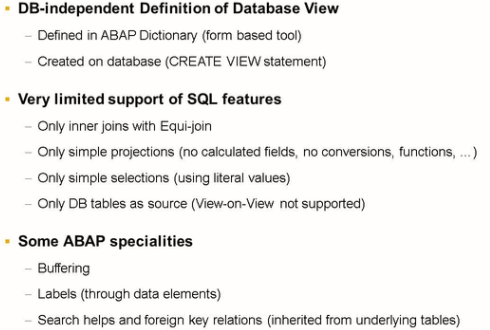
The limitations of ABAP Dictionary View
When it comes to the definition of views in the ABAP Dictionary, the gap between ABAP and standard SQL used to be even bigger.
SAP HANA and the need for Code-to-Data
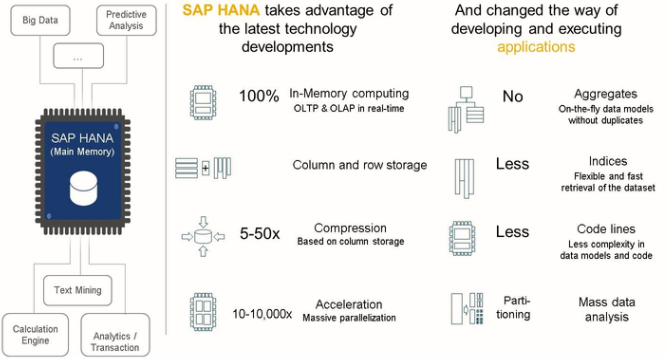
With SAP HANA, SAP combines the latest developments in hardware and software technology to provide a state-of-the-art-in-memory database.
The basic approach of classical ABAP Programming was:
- Keep load from database
- Get all the data you need on the application server, and
- Do your processing in ABAP

But to benefit the most from SAP HANA’s capabilities, especially from its use of parallelism and optimized data structure and transfer, it is better to do expensive calculations and aggregations on the database itself rather than transferring huge amounts of data onto the ABAP application layer. This is a fundamental change to the ABAP Programming paradigm. Now it becomes “logic to data”, or “code-to-data” as it is frequently coined, rather than “data to logic”.

SAP HANA Core Data Services

With the dawn of SAP HANA and the possibility to develop applications directly on the database, not using an application server any more, the need arose to create a meta model repository directly on the database. As with the ABAP Dictionary on the application server, there should be more in the box for you than using native SQL’s CREATE TABLE or CREATE VIEW. Especially regarding the need of enriching pure technical definitions with semantics. And that’s one of them main reasons for SAP’ Core Data Services.

There are many technologies that introduce higher-level models on top of SQL to add semantics and ease consumption – for example, OData EDM models, the semantic layer in the BI platform, JPA and enterprise objects in java, or the business objects frameworks in ABAP.
To address this, SAP HANA introduced a set of domain-specific languages (DSL) and services – called Core Data Services – for defining and consuming semantically rich data models.
Some of the enhancements are:
Expressions: Used for calculations and queries in the data model
Associations: replacing joins with simple path expressions in queries
Annotations: to enrich the data models with additional (domain specific) metadata.
ABAP Core Data Services

An ADT-based source code editor allows you to create DDL sources. On activation, the CDS entities defined in such a DDL source become full citizen ABAP Dictionary objects. They work as ABAP types that can be named after a TYPE addition and they can be accessed in open SQL.


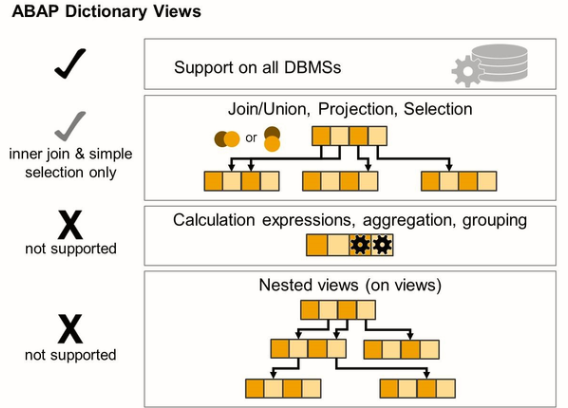
On a purely technical level, ABAP CDS view provide the following additional capabilities compared to ABAP Dictionary Views:
- Enhanced support for combining queries, such as UNION and OUTER joins.
- Support for calculations that use expressions in the column list and for selection
- Aggregating and grouping in the data model.
- Nester Views