Using SQL Expression in CDS Views
Literals

ABAP CDS syntax offers the following types of literals:
Character Literals:
- Series of characters enclosed in single quotes
- Type NUMC if it consists only of digits
- Type CHAR otherwise
Numeric Literals:
- Series of digits without quotes
- May contain a decimal point, but not before the first digit
- Type FLTP if it contains a decimal point
- Type INT1, INT2 or INT4 otherwise, depending on the size
Domain prefixes for literals
In certain operand positions, a literal can have a domain prefix. A domain prefix consists of the name of a repository object of type DOMAIN, introduced with character “#” or ”:” and separated by a period(“.”).
For most of the text literals, the quotes can be omitted when they are prefixed with a domain. If a literal is prefixed with a domain, the syntax check will issue a warning in case the literals do not match the fixed values of the domain or do not lie in the value range specified by the domain.
CASE Distinction

ABAP CDS offers case distinctions that can be used in the element list of a SELECT statement and as operands for other expressions.
A case distinction returns exactly one value. This value depends on a series of conditions.
A case distinction always starts with key work CASE and ends with key word END. The rest depends on the type of case distinction:
Simple Case Distinction
The result depends on the values of several operands. The simple case distinction is comparable to the CASE statement in ABAP.
Complex Case Distinction
Also known as the searched distinction. The result depends on a sequence of logical expressions. The complex case distinction is comparable to the IF statement in ABAP.

Field CLASS of table SBOOK is of type CHAR length 1 and can have three different values. To make this more readable, the case distinction replaces the technical one-character key with a longer text.

Customers with a luggage weight larger than 20 kilograms or 44 pounds will be classified as having excess language. First-class passengers, however, are always excluded from this classification.
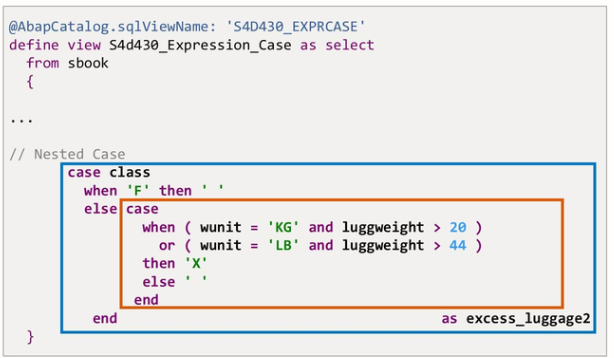
The outer CASE expression checks whether this is a first-class booking. The result in the ELSE branch of the outer CASE expression is not literal but it consists of another case expression based on the luggage weight and unit. Of course, also the result after a WHEN…THEN branch could be a case expression.
Arithmetic Expressions

In ABAP CDS, arithmetic expressions can be used as elements of the field list. ABAP CDS supports four operators, brackets and three different arithmetic’s. The value range and precision of intermediate results highly depends on the arithmetic that is used.

Type Conversions

Unlike ABAP, ABAP CDS does not know implicit type conversions. On the contrary, CDS inspects very strict type compatibility rules. The CAST expression of CDS allows you to implement explicit type conversions.
In NW 7.50, any data element from the Dictionary can be the target type of a type conversion with CAST.
