Using Built-In SQL Functions in CDS Views
Arithmetic Functions
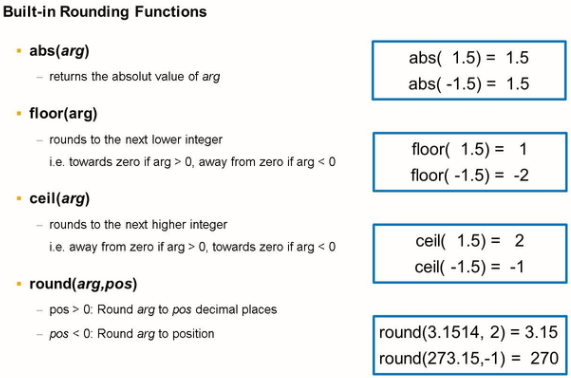
ABAP CDS offers a variety of built-in functions that supplement calculations with arithmetic expressions.
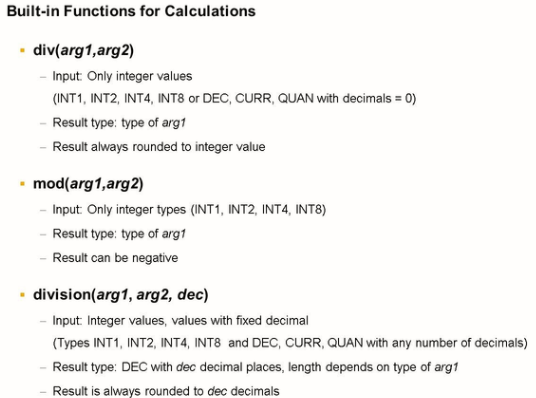
The main differences between function div () and division () are as follows:
Input: Div () only allows integer values as input. Division () only excludes floating-point numbers.
Result: Div () always returns an integer value as a result. Division () allows you to specify the precision of the result.
String Functions
ABAP CDS offers a variety of built-in functions for string processing. Some of them were already available in release NW 7.40, some others are new in NW 7.50.
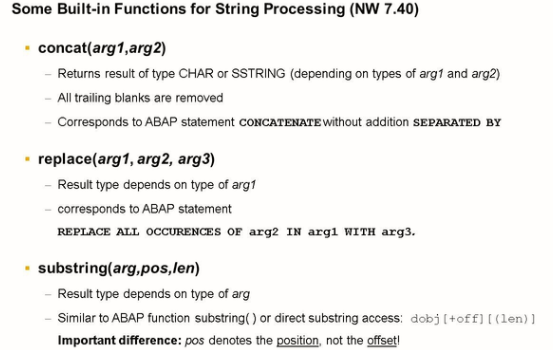
The figure shows some important string functions available as off NW 7.40. A complete list can be found in the ABAP language help.
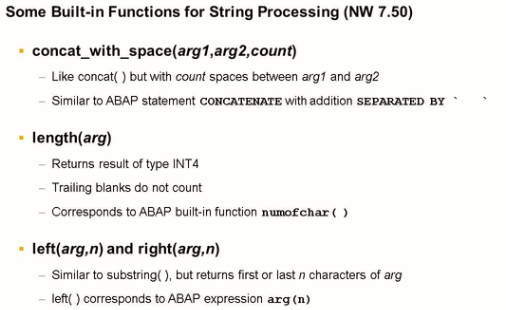
In NW 7.50 the existing functions for string processing were supplemented to fill gaps and to cover special cases.
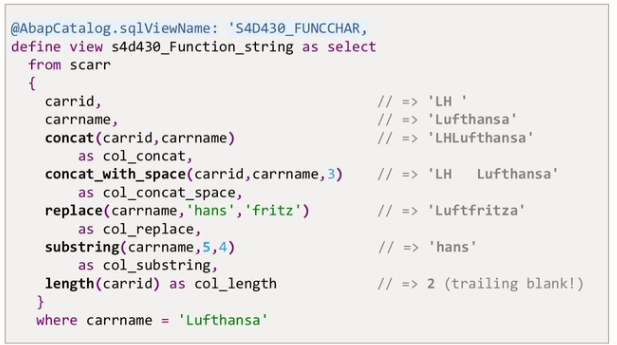
The figure above gives some examples of string processing in CDS views.
Currency and Unit Conversion
Amounts and measurements are usually stored on the database in a source unit and source currency. To make values in different units or currencies comparable with each other, they need to be converted.
Traditionally, we do these conversions with standard functions modules provided by SAP.

The function modules make use of conversion rules that are maintained in standard transactions and stored in tables.
ABAP CDS allows you to move the conversions from the ABAP stack onto the database level. Two built-in functions are available to implement conversions in the DDL source.

Database table SPFLI contains a field DISTANCE in which the flight distance is stored for each flight connection. The corresponding unit of measure is found in field DISTID.
In the CDS view definition above, the value in table field DISTANCE is converted into miles (“MI”) and returned as view field DISTANCE. Literal “MI” is returned as view field DISTID.
Semantics annotations are used to link the two view fields to each other.

Database table SFLIGHT contains a field PRICE in which the standard ticket price is stored for each flight. The corresponding currency code is found in field CURRENCY.
In the CDS view definition above, the value in table field PRICE is converted into US dollar (“USD”) and returned as view field PRICE. Literal “USD” is returned as view field CURRENCY.
Semantics annotations are used to link the two fields to each other.
Calculations with dates
As ABAP developers, we are used to doing calculations with data objects of type D: Subtract a date field from another date field to calculate the number of days that lie between them or add an integer value to date field to calculate the date that lies a certain number of days in the future. This is possible because ABAP automatically translates values of type D into integer values.
A similar mechanism does not exist on the database level. Here, date fields are not recognizable as date fields. Normally, they are created as ordinary character fields of length 8. Using these character fields in arithmetic expressions will lead to syntax errors and typecasting with CAST will lead to wrong results.

In order to make calculations with dates, four built-in functions are available in CDS as off NW 7.50.
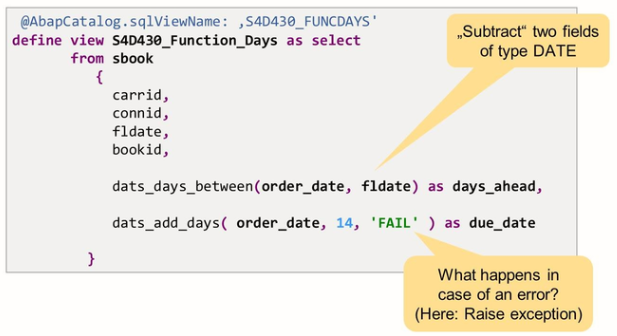
The figure above gives two examples:
- Field days_ahead returns the number of days that lie between the order date of the booking and the actual flight date.