Aggregating Data
Calculations Across Multiple Rows: Aggregation
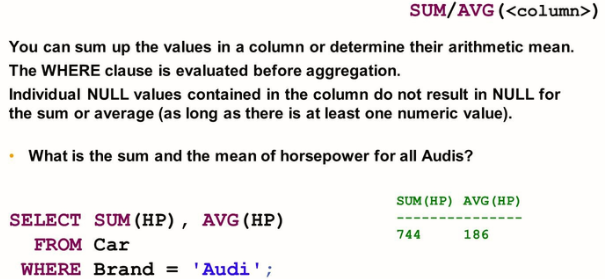
Function expressions allow the values of columns to be calculated based on the values of other columns on a row-by-row basis. But in many cases, you may want to calculate a single value across the values of multiple rows in one or more columns. You can use aggregate expressions for this purpose.




Difference between the COUNT expressions

The DISTINCT modifier may also be used with the SUM or AVERAGE aggregates, but not with the MAX or MIN aggregates.


Note that, in general, the order in which functions and aggregate expressions are nested matters. As an example, the following two SELECT statements lead to different results:
|
SELECT ABS ( MAX(0-HP) ) FROM CAR ; ------Result : 75 |
|
SELECT MAX( ABS(0-HP) ) FROM CAR; -------Result: 260 |

The GROUP BY Clause
You must explicitly include each column in the GROUP BY clause that is not used in an aggregate expression.



The HAVING Clause
When using grouping, you can discard some of the resulting groups in a way like how you exclude rows from a non-aggregated result set. The corresponding keyword is HAVING. The HAVING clause behaves like the WHERE clause but affects the resulting groups instead of the rows when calculating the aggregate values.

