Changing Data Stored in Tables
Modifying Data – Overview
The following list provides an overview of the statements used to modify data:
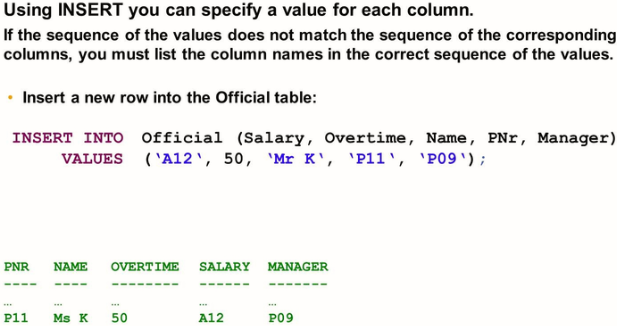
INSERT: The INSERT statement adds rows to a database table
UPDATE: The UPDATE statement changes values of existing rows in a table
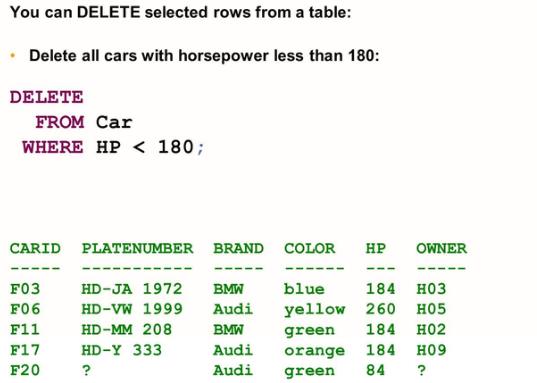
DELETE: The DELETE statement permanently removes existing rows from a table.
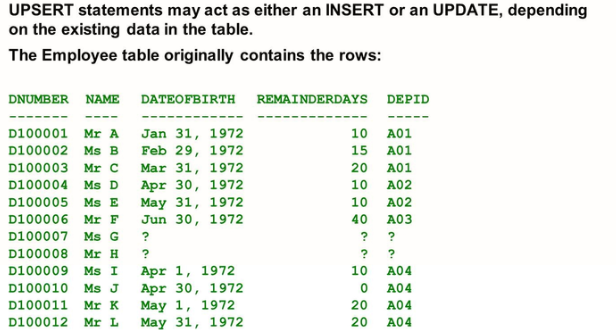
UPSERT: The UPSERT statement changes existing rows of a table if found, else it inserts the new rows. It is a combination of INSERT and UPDATE. REPLACE is a synonym for UPSERT.
Inserting Data
The INSERT statement is used to add new rows to a database table. If the table already contains a row with the same primary key values or if you try to add several rows with the same primary key values, the DBMS checks and, in such cases, raises an exception.


Updating Data
UPDATE <Table>
SET <column> = <value> [,
<column> = <value>, …]
[WHERE <condition>]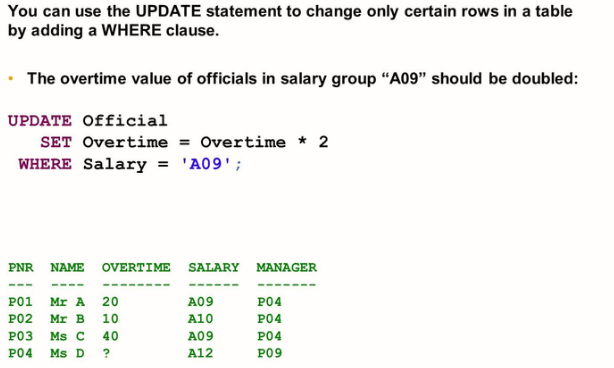
The UPSERT/REPLACE statement
Due to its support for inserting data, the UPSERT statement comes in three syntax variants similar to the INSERT syntax variants:
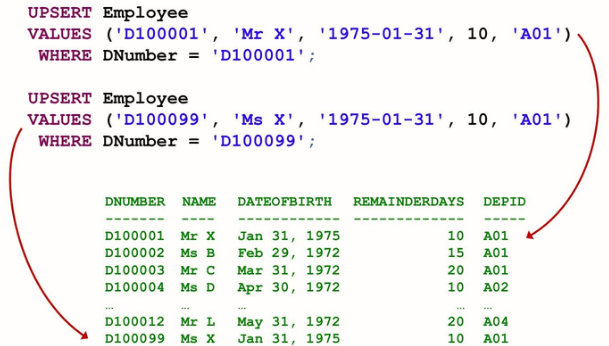
- UPSERT Table (Column List) Values (Value List) WHERE condition
If the condition evaluates to be true, the matching rows are updated. If not, a new row with the values provided is inserted.
- UPSERT Table (Column List) Values (Value List) WITH PRIMARY KEY
Updates the row with the primary key contained in the value list if present. If not, a new row with the values provided is inserted.
- UPSERT Table (Column List) SELECT ………FROM ……………WHERE…………
For each row returned by the subquery, checks if the table contains a row with the same primary key value. If yes, the existing row is updated with the row returned by the subquery. If not, a new row with the values provided is inserted.
Deleting Data
DELETE FROM <table>
[WHERE <condition>]