Creating User-defined Functions
SQL Script Basics
Applications benefit most from the potential of SAP HANA if they perform as many data-intensive computations in the database as possible. This avoids loading large amounts of data into an application server separate from SAP HANA, and leverages fast column operations, query optimization, and parallel execution. This can be achieved to a certain extent if the applications use advanced SQL statements, but sometimes you may want to push more logic into the database than possible using individual SQL statements, or make the logic more readable and maintainable.
SQL script has been introduced to assist with this task.
SQL Script Definition and Goal
- SQL Script is defined as follows:
- The language to write stored procedures and user-defined functions in SAP HANA .
- An extension of ANSI SQL.
- The main goal is to allow the execution of data-intensive calculations inside SAP HANA.
- Eliminate data transfer between database and application tiers.
- Execute calculations in the database layer to benefit from fast column operations, query optimization, and parallel execution.
This is helpful for the following reasons:
SQL Script Advantages
Compared to plain SQL, SQL Scripts provides the following advantages:
- Using SQL Script, complex logic can be broken down into smaller chunks of code. This enables modular programming, reuse and a better understandability by functional abstraction. SQL only allows the definition of SQL views to structure complex queries, and SQL views have no parameters.
- SQL Script supports local variables for intermediate results with implicitly-defined types. With standard SQL, it would be required to define globally visible views even for intermediate steps.
- SQL Script has flow control logic such as if-then-else clauses that are not available in SQL.
- Stored procedures can return multiple results, while an SQL query returns only one result set.
SQL User-Defined Functions
The simplest database objects for which you can make use of SQL Scripts are scalar user-defined functions (Scalar UDFs).
Scalar UDFs allow you to define functions that take several input parameters and return scalar values. Only expressions are allowed in the body of the UDFs, so no table operations, CE functions or array operations.
Scalar UDFs support the following:
- They can have any number of scalar input parameter
- They can return multiple scalar values.
- They can contain expressions within their body. Table and array operations are not supported.
- They can be used in the field list or the WHERE clause of SELECT statements – like built-in functions
- They are callable via direct assignment in other user-defined functions or stored procedures.
- They must be free of side-effects and do not support any type of SQL statement in their body.
Options Used to Define UDFs in SAP HANA
The following are some options used to define UDFs in SAP HANA:
- Executing direct SQL statements in the SQL Console of Web IDE to generate the run time object - this is not recommended as this approach provide no support for managing the lifecycle of functions, for example, for adjusting the function code of an existing function. It also means the functions is not considered as part of a complete sets of development files that should be built together as complete unit.
- Defining the UDF in a development source file of the type _hdbfuncion in the Web IDE development view, then building it to generate the runtime object- this is the recommended.
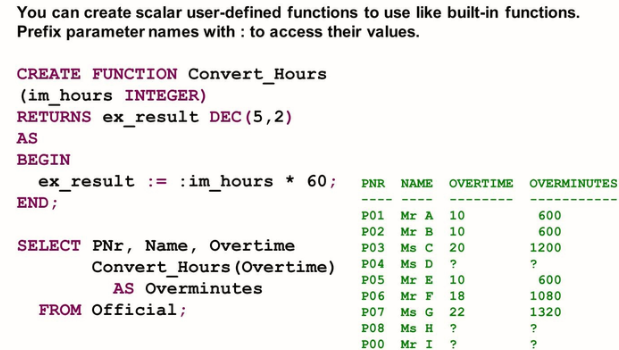
The SQL statement to define UDFs is CREATE FUNCTION. The basic syntax to define a scalar UDF using the direct SQL method is as follows:
Basic Syntax to define a scalar UDF
CREATE FUNCTION <function name>
(< List of input parameters with type>)
RETURNS <scalar result parameter name and type>
AS
BEGIN
<function body>
END;
Deleting UDFs
DROP FUNCTION <function name>