SAP HANA Basics and technical concepts
SAP HANA Application Architectures
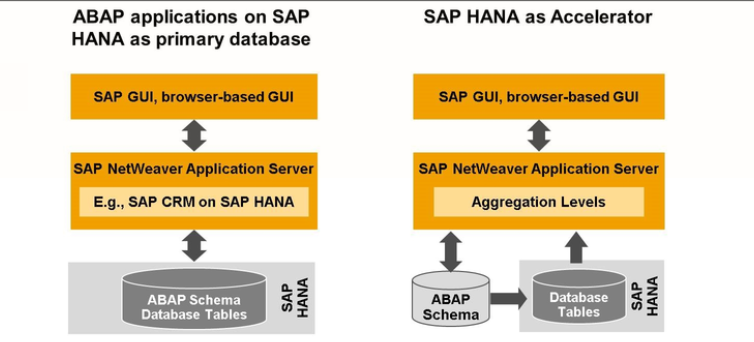
SAP HANA can be used in different architectural scenarios, which in turn provide the technological base for the different areas.

From an ABAP Programmers point of view, there are two group of scenarios, as follows :-
- SAP HANA functions as the database for an application Server ABAP
- Standalone SAP HANA Server
SAP HANA Innovations and Challenges
- In-Memory Computing and Shift of performance Bottleneck:-
- Avoid CPU Cache misses and expensive data transfer from main memory into the CPU- optimizing loading the data into the CPU
- Avoid idling the CPU cores- make use of parallelism by using all the cores of a CPU and several CPU’s
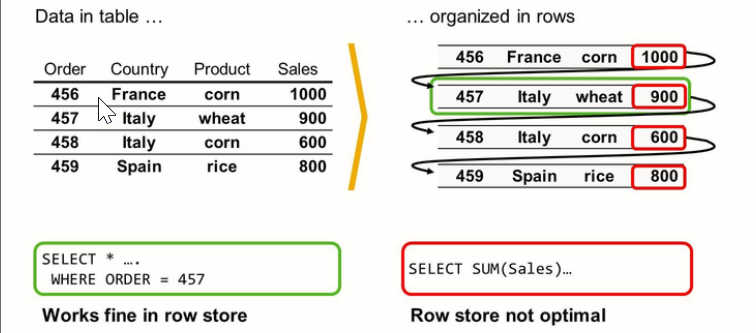
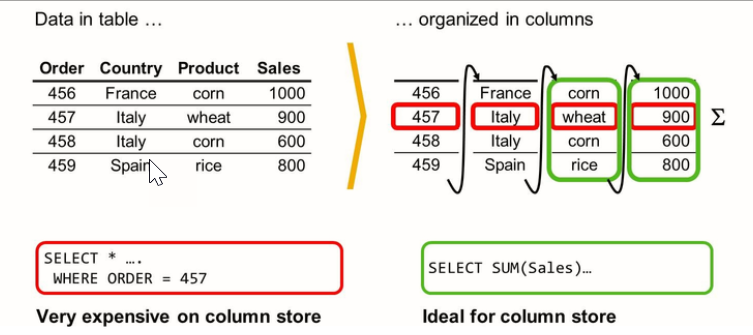
- Column Store Versus Row Store
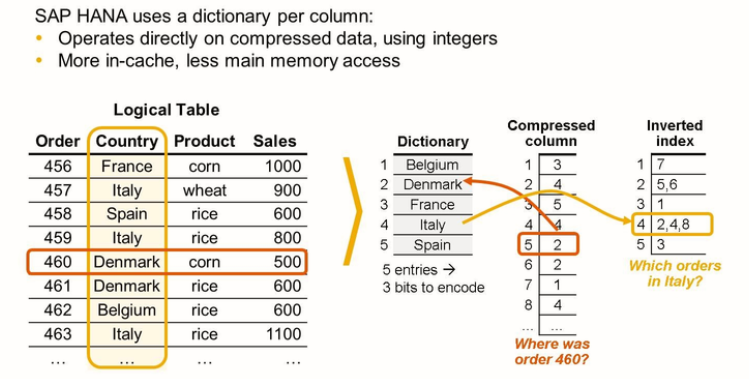
- Data Compression
- It reduces the amount of memory required.
- It speeds up operations on column because the columns can be loaded into the CPU caches faster and with fewer loading cycles
- It speeds up operations on columns because many comparisons become integer value comparisons.
- Partitioning and Parallel processing
With fast communication between processors cores enabling parallel processing. This shifts the performance bottleneck from disk I/O to the data transfer between CPU cache and main memory. To get the best performance, new bottleneck has to be avoided by addressing the challenges as follow:
By accessing data in column-store order, you benefit immensely from simplified table scan and data pre-caching. This can make all the difference in performance
 |
 |
|
Row Store
|
Column Store
|
SAP HANA uses different, efficient compression methods, such as dictionary encoding, run-length encoding, and more. This has the following benefits: -
On SAP HANA and with column storage, data is only partially blocked. This makes parallel processing possible. Even the same column can be split up and processed by different cores at the same time
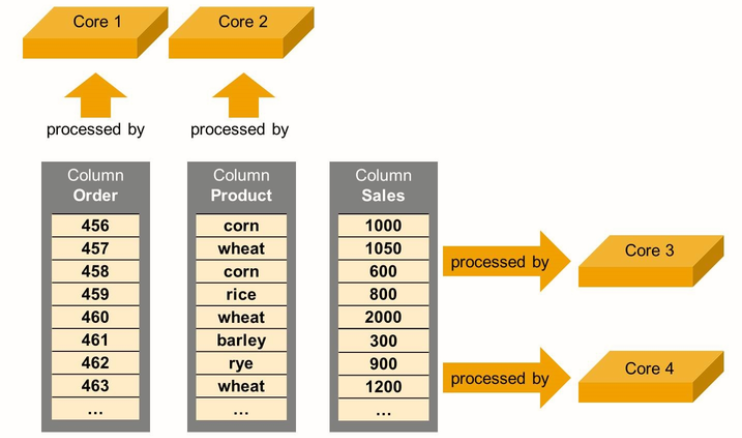 |
 |
|
Parallel Processing |
Using partitioning to further leverage parallelism |
The use of parallelism can be taken a step further by creating different partitions of the data to be stored and processed on different blades. This allows for the management and processing of huge amounts of data.