SAP HANA as Secondary Database – Access Via Open SQL
Secondary Database Connections
Each application Server ABAP is connected to a Database Management System(DBMS) that contains the ABAP Repository and the database tables and views defined in this system’s ABAP Dictionary. This DBMS is referred to as its Primary Database. Aside from this primary database connection, it is possible to establish connections to additional database management systems or secondary database connections. In the scenario, SAP HANA as Accelerator, where SAP HANA is used as secondary DBMS, it is necessary to establish such a secondary database connection to SAP HANA.
Secondary database connections, among other things, are created and maintained via transaction DBACOCKPIT. Each database connection is identified by a name that must be unique with the application server.
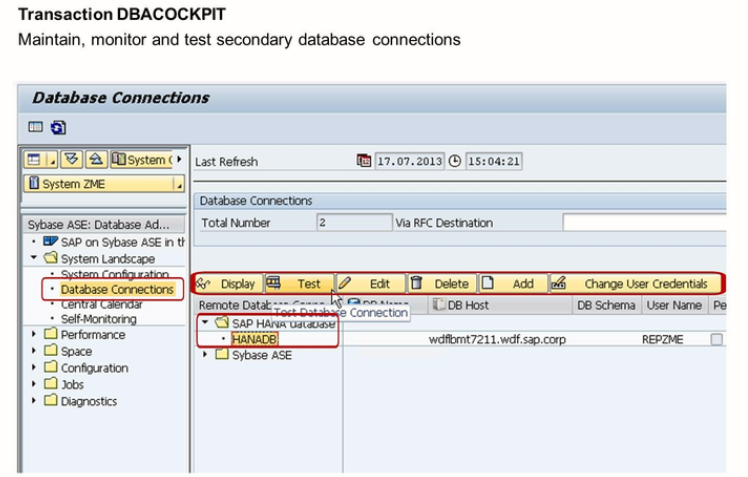
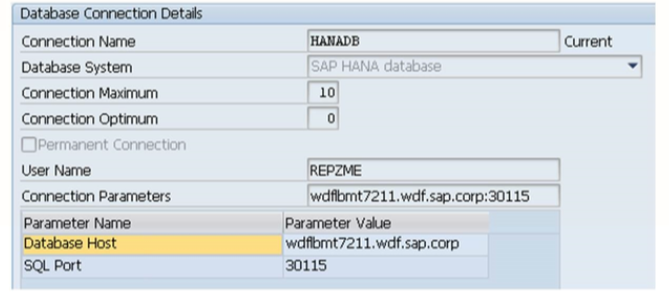
Inside the connection, the DBMS is identified by a hostname and an instance number, which related to an SQL port. Furthermore, a database user (with a password) must be implemented. Any access to the database via this secondary database connection is equivalent to a log on to the database with this user.
Access to Secondary Database with Open SQL
Once the secondary database connection is established, it is easy to use it in ABAP programs. Open SQL offers an additional CONNECTION, which has to be followed by the name of the secondary database connection.
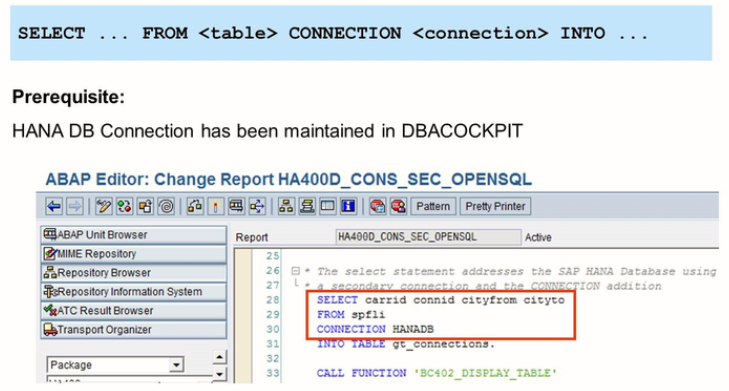
However, some restrictions apply when using Open SQL to access a secondary database. Due to the syntax check for Open SQL statements, the tables and fields the statement refers to must exist in the ABAP Dictionary of the application server. This implies that objects only known to SAP HANA( such as SAP HANA views or procedure) are not accessible by Open SQL. Also, Open SQL access to a secondary database is restricted to the default schema of the database user in the connection. Normally, the name of the schema is identical to the user name.