Using SAP HANA Full Text Search

SAP HANA uses an algorithm that calculates the closeness of the match to the original search string and represents it as a score 0 and 1, where 1 is a perfect match. In the fuzzy search itself, you can specify the lower threshold, below which hits are no longer displayed, or you can use the default setting of 0.8.
To use to Fuzzy search with good performance, full-text indexes are required for the relevant table and columns.
To create a full-text index, the table in question must be column-stored. The most common data type for which you will want to create such an index in NVARCHAR.
Creation of a Full-Text Index for Fuzzy search

The full-text index is a hidden column attached to the table that SAP HANA uses to perform the search SAP HANA can keep full-text indexes up to date either synchronously or asynchronously. Asynchronous means that the index is only updated after a certain time elapsed. Synchronous means that the index is updated immediately when inserting, updating, or deleting records, which also means that the insert, update and delete statement execution takes longer.

The most common data types for which you will want to create a full-text index is NVARCHAR (CHAR, STRING OR SSTRING in ABAP). In this case, you can create the full-text index as follow: -
- In an ABAP release 7.4 SP03 or higher using SAP HANA as its primary database, you can create the full-text index using the ABAP Dictionary. Create an index as usual. Then choose menu item GOTO-> Full-text index. Select Full-Text index. Choose a fuzzy search on if you create the index to enable the fuzzy search.
- When using SAP HANA as a secondary database, you cannot create a full-text index in the ABAP Dictionary, but must create it in the SAP HANA studio or using Native SQL. To use the SAP HANA studio, open the table definition in the SAP HANA studio. On the indexes tab, create a new index of type FULL-Text. In the pane below, you can select whether the index should be updated synchronously or asynchronously. Select the column that you want to index and select the fuzzy search checkbox. You then need to deploy the index by choose Execute.
Once the index has been created in the database, you can use it to perform a fuzzy search in the SELECT statement.
Fuzzy Search Usage
You implement a fuzzy search using the CONTAINS () function in the where clause of your select statement.
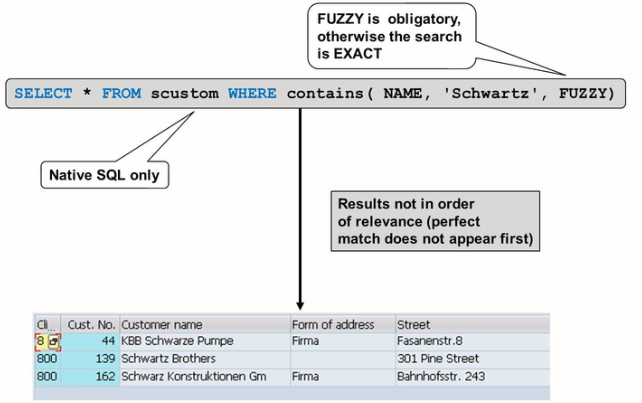
The argument of the function is the name of the column in which you want to search, the search string itself, and the search type FUZZY. The search type itself may also take an argument – a decimal value between 0 and 1 denoting the minimum tolerance allowed.
A further function that can be useful in the fuzzy search is a score ().
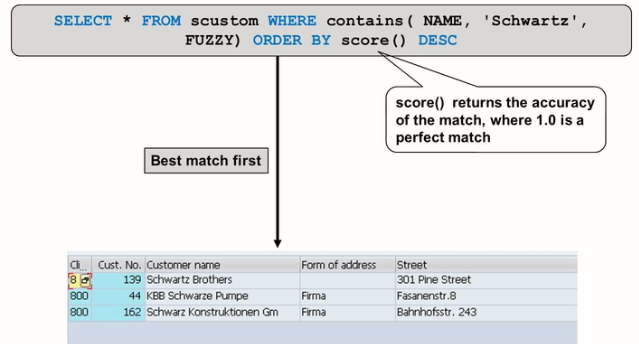
Score () is the ranking of each result in the result set. You can select the value into the result set to display on the screen or use it in the background in the ORDER BY clause to ensure that the best hits appear at the top of the list.
Linguistic Search

While the fuzzy search is very useful for entities such as names, it is sometimes more useful to perform a linguistic search, for example, when you want a string such as go to be considered more closely related to going or event went than to goat. In this case, you can index a column according to linguistic criteria. Words are then separated and reduced to their stems or basic forms.
Creation of FULL-Text Index for linguistic search
In an ABAP 7.4 system using SAP HANA as its primary database, you can create a full-text index for linguistic search as explained before and set TextAnalysis to on in the index definition.
In all other cases, you have to create the full-text index using SAP HANA studio or Native SQL.