Implementing a Selection Screen
Selection Screens
Selection screens serve as an interface between the program and the user, and allow the amount of data to be read from the database to be limited.
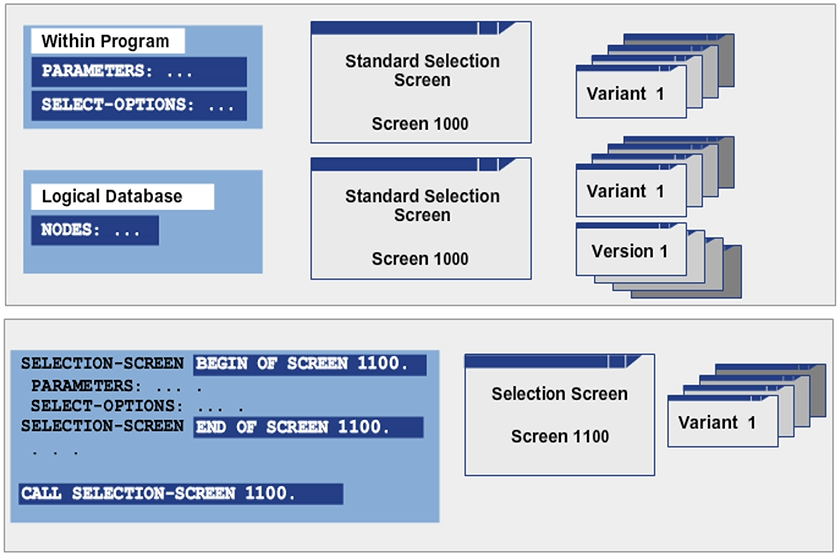
You can use the declarative statements PARAMETERS and SELECT-OPTIONS to generate a standard selection screen (screen 1000) with input fields.
Logical databases supply a selection screen whose appearance is dependent on the specified nodes (NODES <name>).
In addition to the standard selection screen, you can also use SELECTION-SCREEN BEGIN OF SCREEN... to create an additional selection screen and use CALL SELECTION-SCREEN statement to call it.
You can create variants to save selection screen values that you use frequently. You can use the variants at any time. If a report with a selection screen runs in the background, a variant is always required.
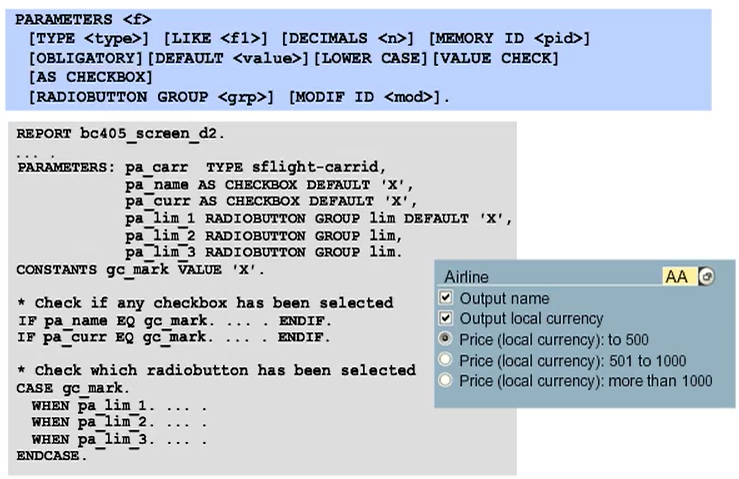
Declaration of Selection Screen Fields Using the PARAMETERS Statement
The PARAMETERS statement is a declarative language element. As in the case of the DATA statement, you can declare parameters with the TYPE or LIKE additions, and the system will then generate input fields on the selection screen.
You can maintain selection texts by choosing Goto → Text Elements → Selection Texts.
The names of PARAMETERS can have a maximum of eight characters.
With the DEFAULT <value> addition, you can set a default value for the input field. If you assign a MEMORY ID <pid>, the system retrieves the current value from SAP Memory and displays it on the screen automatically. SAP Memory is a user-specific memory area in which simple data values, for example, the key for an airline, are stored for SET/GET parameters. These data values are stored for the duration of a user session. SET/GET parameters are identified by a name, which can be maximum 20 characters long. A SET/GET parameter can be assigned to a data element. Fields based on this data element can then use the SAP Memory mechanism.
You can find out the name of a particular SET/GET parameter by placing the cursor on a field and choosing Help (F1) → Technical Information. In the Parameter ID field, you find the name of the SET/GET parameter.
If you declare mandatory fields using the OBLIGATORY addition, users cannot proceed without entering values in these fields.
Declaration of Selection Screen Fields Using the SELECT-OPTIONS Statement
SELECT-OPTIONS is a declarative language element with the same naming restriction of eight characters as PARAMETERS. SELECT-OPTIONS allows the use of a value range and complex selections instead of a single input field.
The SELECT-OPTIONS keyword generates an internal table <seltab> with a standard structure and a header line.
This internal table has the following columns:
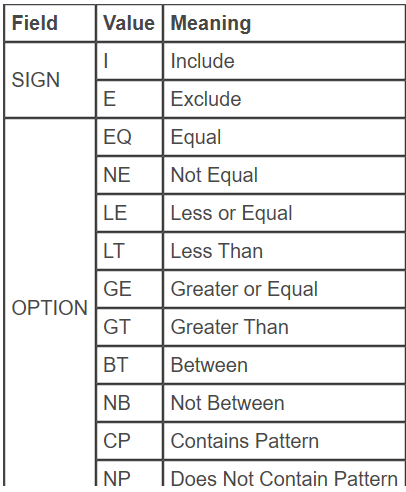
- Sign (indicator meaning including or excluding)
- Option (relational operator)
- Low (lower limit)
- High (upper limit)
You can maintain the selection text in the same way as with PARAMETERS by choosing Goto → Text Elements → Selection Texts.
Use the addition FOR to specify the type of the field. Use the name of a variable that you have already declared in a DATA or NODES statement.
Each line of the selection table <seltab> formulates a condition using one of the relational operators.

Possible Values for SIGN and OPTION
The selection set is a union of all includes (I1, ..., In) minus the union of all excludes (E1, ..., Em). If no values are entered into the SELECT-OPTION, the system returns all rows from the database.
SELECT-OPTIONS with Multiple Selection Criteria
If a user enters data in a SELECT-OPTIONS object, the system automatically fills the internal table.
To change the default values for the SIGN and OPTION table fields, choose Edit → Selection Options from the selection screen.