Grouping Database Changes
SAP Logical Unit of Work
An SAP LUW consists of a set of dialog steps from Application Server (AS) ABAP that logically belong together. Database changes from these steps are bundled within one database LUW. These changes are either fully implemented or not implemented (“all or nothing principle”).
In general, a business transaction is not represented only by a single SAP LUW. The entire process, for example, from receipt of a customer order to the issue of an invoice, is split into logical parts, each corresponding to an SAP LUW. The definition of SAP LUWs depends on the entire process and its modeling.
For further information, refer to the ABAP Editor keyword documentation for the term transactions and logical units of work.
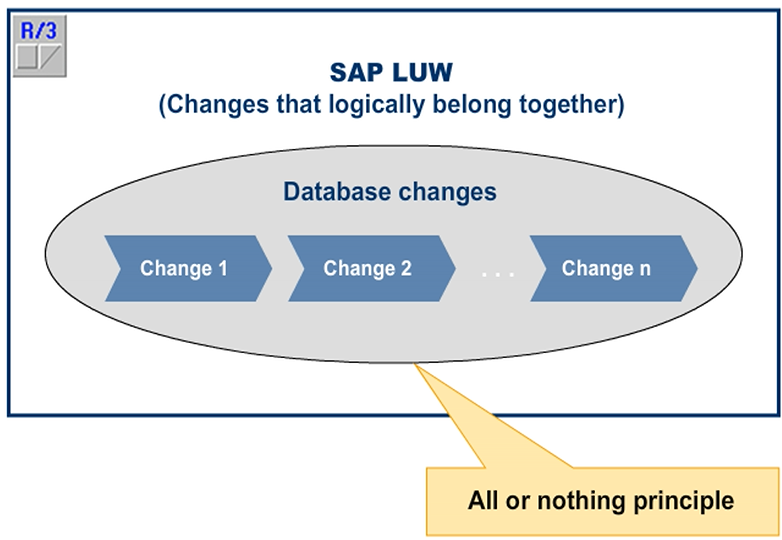
Database Logical Unit of Work
A database LUW consists of changes that are executed until the database status is sealed (database commit).
Within a database LUW, you can discard all changes that have taken place up to a specific point in the database (database rollback). When changes are discarded, the database is reset to its original status. The DB ROLLBACK function can be used to restore the previous (consistent) database status if an error occurs.
The current database status is sealed by a database commit. After the database commit, the current database LUW cannot be discarded.
A database rollback and database commit can be triggered explicitly or implicitly when processing a program.
An explicit database commit is executed if the following conditions occur:
- The ABAP statement COMMIT WORK is processed.
- The function module DB_COMMIT is called.
Wait situations lead to an implicit database commit if the following conditions occur:
- A dialog step is completed.
- A function module is called via Remote Function Calls (RFCs) synchronously or asynchronously, or the called function ends.
- A WAIT statement interrupts the work process.
- Dialogs (information, warning, or error messages) that occur during the messages of certain quality, which are processed in between the ABAP Open SQL statements of one LUW are sent in a dialog step.
- A transaction is called (CALL TRANSACTION ..., LEAVE TO TRANSACTION...), or the called transaction ends.
- A program is called (SUBMIT ...), or the called program ends.

Explicit and Implicit Database Rollback
Explicit Database Rollback
- An explicit database rollback is executed if the ABAP statement ROLLBACK WORK is processed
Implicit Database Rollback
- A runtime error occurs in a program performing the database changes( for example, division by zero)
- A termination message is sent by the system in a dialog step. This is typically an A or X message type. However, in certain cases, termination message are also generated with I,W and E messages
Processing an SAP LUW
If there is an error during the processing of an SAP LUW, it is possible to restore the consistent database status that existed before the SAP LUW started. To restore the database status, the SAP LUW must be processed within a single database LUW.
A transaction usually has several screens for entering change data because AS ABAP has a client/server architecture. Whenever there is a screen change, the system automatically triggers an implicit database commit. Within a transaction, you can bundle the user entries that form an SAP LUW within a database LUW, and write the entries to the database.

Changes to Database Bundles
AS ABAP is based on a client/server architecture with three levels: database server, application server, and presentation server. This architecture, along with the distribution of user requests (user dispatching), leads to an efficient and cost-effective multiuser system.
Majority of users with minimum configuration desktop computers can be mapped to a few high-performance work processes on application servers. Each work process on an application server is assigned a work process on a high-performance database server.