Explaining the Functionality of Logical Databases
Logical Databases
Data that is to be output in a list or ALV can be read from the database using Open SQL or Native SQL statements.
If you use Native SQL, it will need to be recorded if you move from one Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) to another, so for portability reasons, it is best to avoid Native SQL restrictions or requirements. Open SQL is a platform-independent SQL variant used in ABAP. Open SQL statements are translated into the relevant Native SQL by the database interface.

Advantages of a Logical Database
A single logical database name can be the data source for various reports. In executable programs, the logical database name is entered in the program attributes. Other programs can call it using the LDB_PROCESS function module.
Advantages of logical databases over other methods of data retrieval are as follows:
- Predefined selection screen
- Flexibility with the use of selection screen versions, variants, or separate program extensions
- Developer not required to know the exact structure or relationships between the tables in the logical database
- Data is provided to the application program according to the hierarchy of the table
- Central location for performing all maintenance and enhancements
- Predefined authorization checks

Logical Database – Overview
A logical database is an ABAP program that reads data from the database and passes it to other programs.
The hierarchical structure of the logical database determines the order in which the data is supplied to programs. A logical database provides a selection screen and related logic that checks user entries and performs error dialogs. You can add your own parameters and selection options.
There are more than 250 logical databases in SAP ERP systems.

Logical Database – F1S Nodes
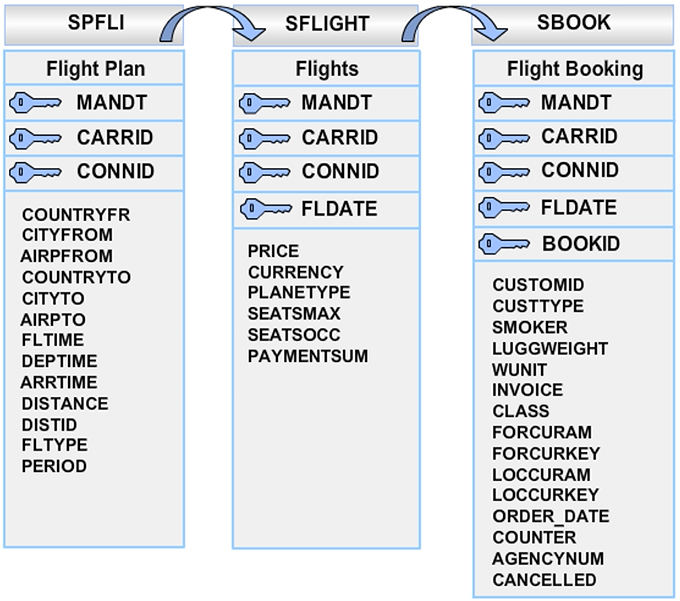
The demonstration programs and exercises for ABAP courses and ABAP documentation use the SAP BC_TRAVEL flight data model. This is found in package BC_DATAMODEL, which contains a logical database F1S.
The F1S logical database consists of the following tables:
- SPFLI (Flight connections)
- SFLIGHT (Flights)
- SBOOK (Bookings)