Creating Lock Objects and Lock Modules
SAP Lock Concept
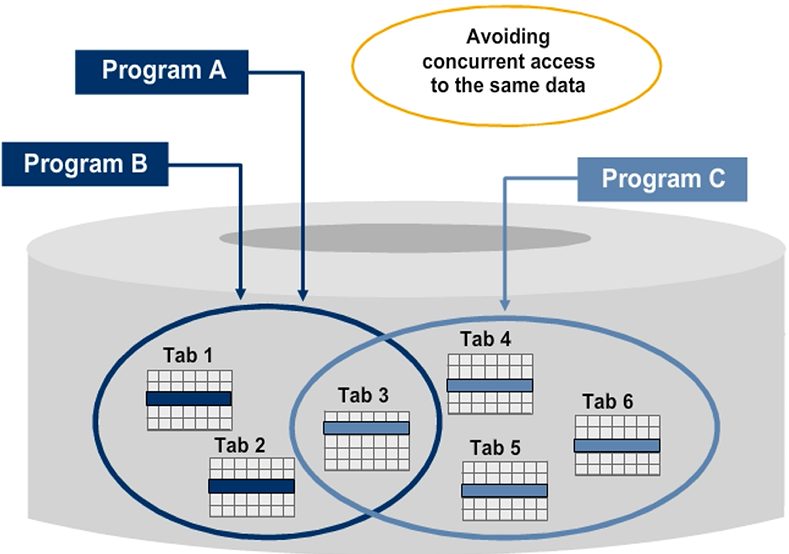
If multiple users are competing to access the same resource or resources, the access to data must be synchronized to protect data consistency.
For example, in a flight booking system, you must check whether seats are available. You must also guarantee that critical data (in this case, the number of available seats) cannot be changed while you are working with the program.
Locks are a method of coordinating competing accesses to a resource. Each user requests a lock before accessing critical data. When finished with the data resource, the user must release the lock to make the resource accessible for other users.
Database Locks
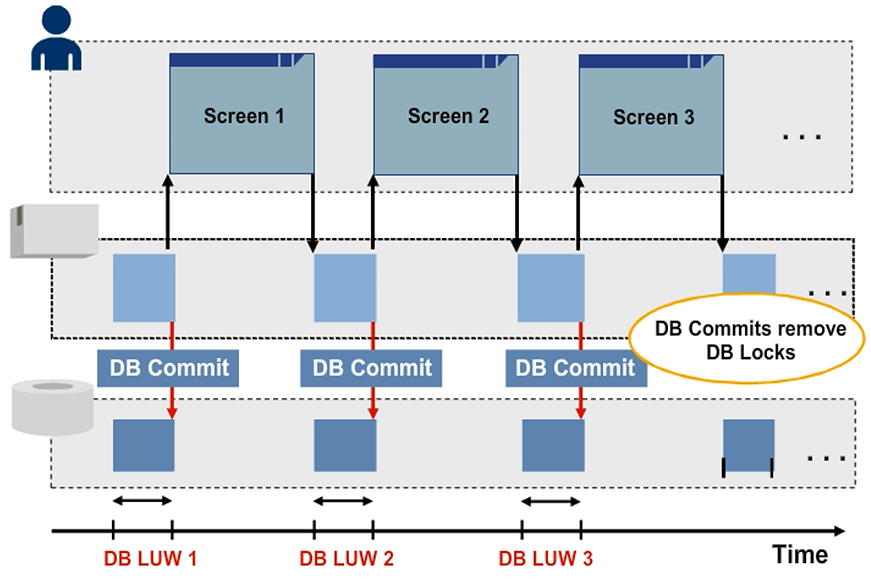
Database Management System (DBMS) physically locks the table lines read from the database for changing. Other users will not be able to access the locked record until the system releases the physical lock. In addition, database locks are automatically set if the database system receives change statements, such as INSERT, UPDATE, MODIFY, and DELETE from a program.
However, at the end of a database logical unit of work (LUW), with every database commit, the database system releases all the locks that were set during the database LUW.
For Application Server (AS) ABAP, the database system releases each database lock if an implicit database commit is triggered. The release happens at the end of each dialog step (if the system displays a new screen) or if a wait situation occurs (for example, a function module is called using remote function calls (RFC). Therefore, database locks are not sufficient if data is collected throughout several screens and the respective data records are to be kept locked during the LUW time frame.
SAP Lock Concept – Logical Locks
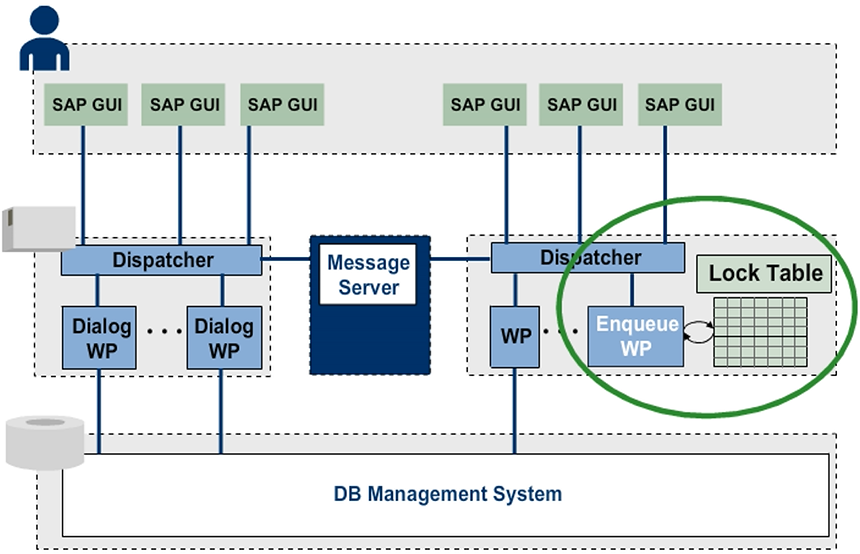
To maintain a lock through a series of screens (from the dialog program to the update program), AS ABAP offers a global lock table at application server level, which you can use to set logical locks for table entries.
The lock table and the enqueue work process that manages the lock table are on a uniquely defined AS ABAP application server (lock server, also known as enqueue server). All logical lock requirements of AS ABAP run on the basis of this system-wide work process.
The lock table is kept in the memory of the lock server. SAP recommends that you use a stand-alone lock server so that it is not necessary to implement high availability for the entire central instance. The stand-alone lock server, together with the lock replication server that runs on another machine, is a high availability solution. Then, your SAP system no longer has a central instance.
You can also use logical locks to lock table entries that do not exist on the database. This is appropriate, for example, when you enter new table lines, and it is not possible to lock the entries using database locks.
For further information, refer to the ABAP Editor keyword documentation for the term SAP lock concept.
Lock Objects and Lock Modules
A logical lock is set in the lock table by calling a lock module. A lock module is a special, table-related function module that is created automatically when a table-related lock object is activated. When the lock module is called, logical locks are set for entries in the respective table(s).
Lock objects are maintained in the ABAP Dictionary. Customer lock objects must begin with EY or EZ. When a lock object is created, the table whose entries are to be locked (primary or basis table) needs to be specified. Tables with a foreign-key relationship to the primary table are referred to as secondary tables, and can also be specified. By doing so, a combination of table entries that are related through the lock module can be locked. For example, a lock object that contains the tables SFLIGHT (primary) and SBOOK (secondary) enables you to lock a flight together with its bookings.
The lock module that the system automatically creates contains, as input parameters, the lock parameters contained in the lock object. Lock parameters are used to communicate to the lock module which records are to have a logical lock set in the locking table. The system automatically proposes names for the lock parameters for the names contained in the table key fields. The system-proposed names can be overwritten.