Setting and Releasing Locks
SAP Locks
Depending on the lock mode, a lock module is either used to set a logical lock in the lock table or to check whether a lock can be set.
You can only set a lock if your lock does not collide with entries that already exist in the lock table for the respective table records. If there is an error, the lock module triggers appropriate exceptions. The application program can then determine the success or failure of the lock action on the basis of the return code delivered by the lock module and react accordingly. If there is an error, for example, the current user could receive an error message stating that he or she has been rejected by the system.
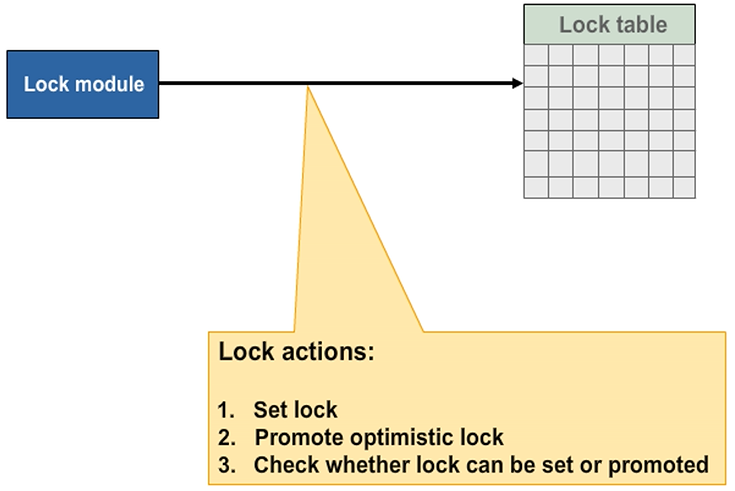
Lock Actions – Possible Results
Depending on the technique used for database updates, an application program may need to delete the lock entries it has created, or have them deleted automatically (if the SAP update technique is used).
If an application program that has created lock entries is terminated, the locks are released automatically.
Program termination takes place if any of the following statements are encountered:
- Execution of messages of the type A or X
- Execution of the LEAVE PROGRAM statement
- Execution of the LEAVE TO TRANSACTION statement
- If you enter /n in the command field
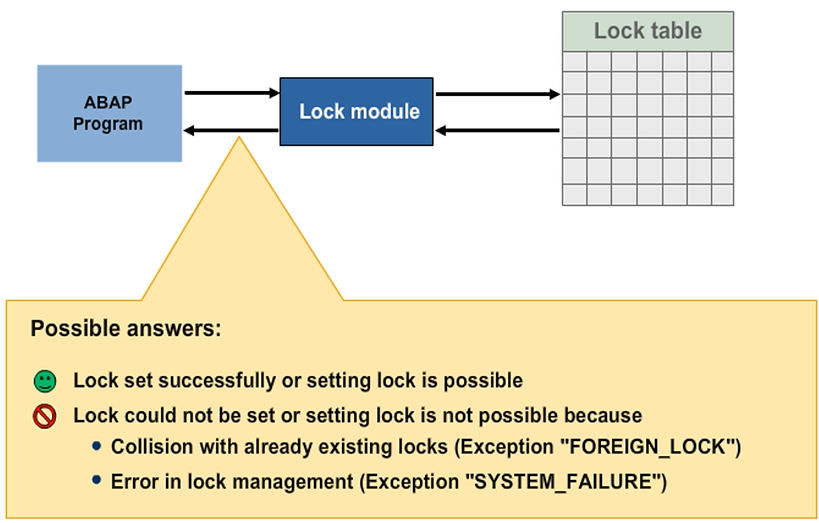
Set or Release Locks
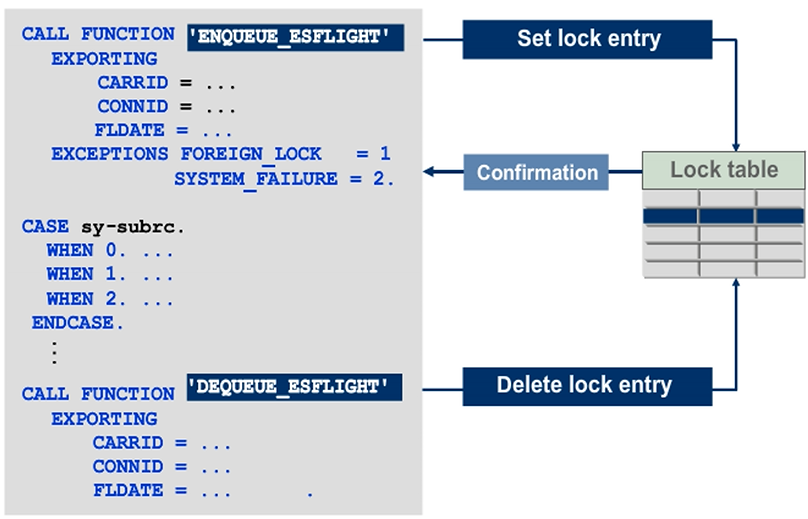
To specify which lock entry is to be created, use the import parameters of an ENQUEUE lock module that correspond to the key fields in the respective table. The import parameters are called lock parameters.
If the system does not set the lock successfully (sy-subrc <> 0), issue a corresponding dialog message to the current user.
At the end of the dialog program, use the corresponding DEQUEUE lock module to delete the entries from the lock table. DEQUEUE lock modules do not trigger any exceptions. An attempt to release an entry that is not locked has no effect. To release all locks that have been set by the current program execution at the end of your dialog program, use the DEQUEUE_ALL function module. Locks are released automatically at the end of the program and are passed over to update techniques. Therefore, DEQUE modules are hardly used.
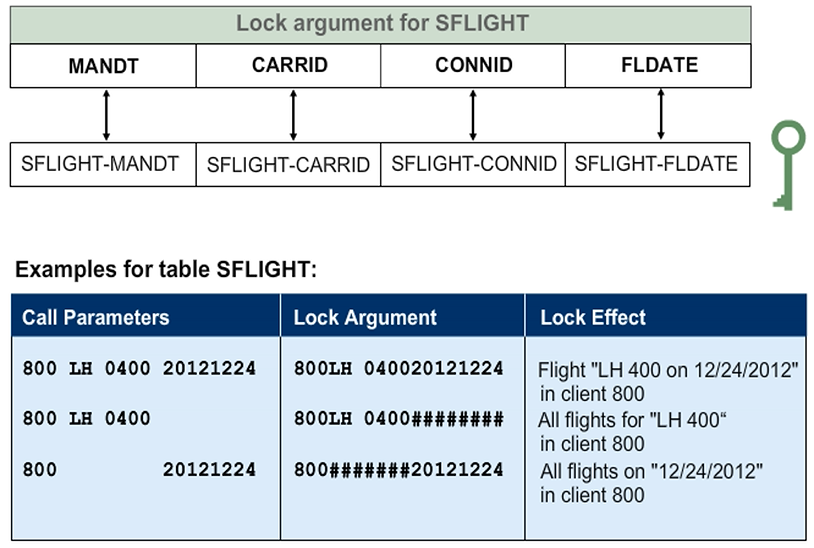
Lock Argument
The lock argument is constructed from the values of all lock parameters (key fields of the respective table). The core part of a lock entry, the lock argument defines which table lines are to be locked.
When calling a lock module, a lock parameter may be set to its initial value, or may not be specified at all. The system interprets a lock parameter that is not specified as a generic value, interpreting the lock as referring to all table lines to which the other parameter variants apply. An exception to this rule is the client parameter.
The following conditions apply to the use of SY-MANDT on a lock module call:
- If the client parameter is not specified, then the lock applies only to the current execution client (SY-MANDT).
- If the client parameter is specified with a specified client, then the call applies only to that client.
- If the client parameter is specified with SPACE, then the lock applies to all clients.
Use SM12 to Set and Manage the Lock Table
Parameters in ENQUEUE Module
The mode_<table name> parameter overrides the default lock mode of the lock module that is in the lock object.
Use the x_<> to specify lock entries where the <lock_parameter> has an initial value. Otherwise, the initial <lock_parameter> is regarded as a generic parameter.
The _scope parameter defines the validity range of the lock.
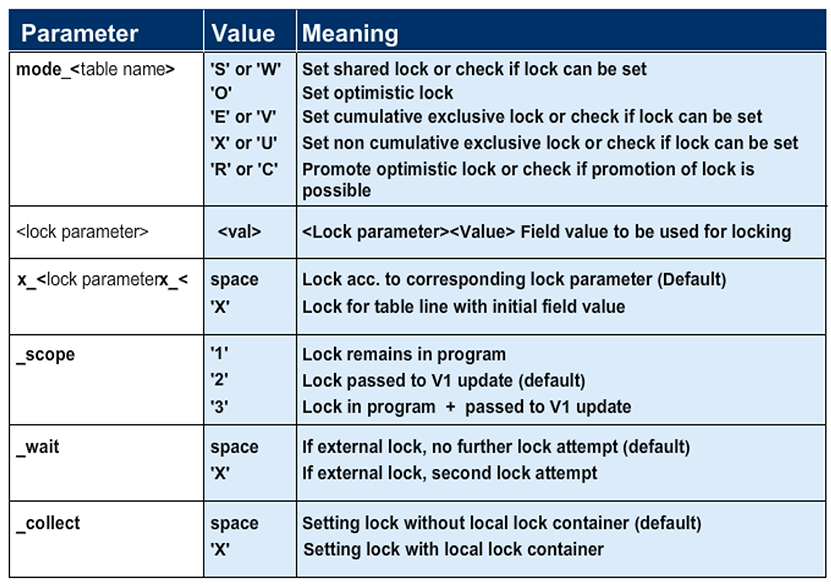
The _SCOPE Parameter
Using the Lock Container