Actions
Actions
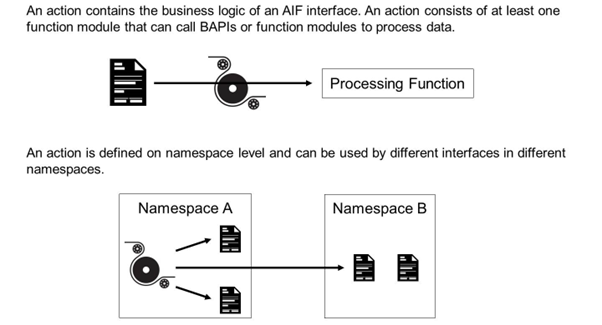
An action is an interface building block that contains the business logic of an SAP Application Interface Framework interface. It consists of at least one action function module that can, for example, call BAPIs or function modules to process data.
An action is defined by its name and the namespace it is assigned to. The action's main component type defines which data type the action handles. An action can be assigned to different interfaces across different namespaces.
Since actions in the SAP Application Interface Framework have a well-defined input (a data structure with the type defined as the action's main component type), they remain independent of the context in which they are called. As a result, actions can be reused easily by several interfaces in the SAP Application Interface Framework.
To Define an Action:
- In the first step of creating an action, you maintain general information:
- Name and description.
- Commit mode and commit level.
- (Optional) init function before processing.
-Main component type.
- In the second step, the function module containing the business logic is defined. You can define multiple function modules for one action. For every function module, you must maintain the following information:-
- Function number and function module name.
- Stop processing on error.
- Restart always.
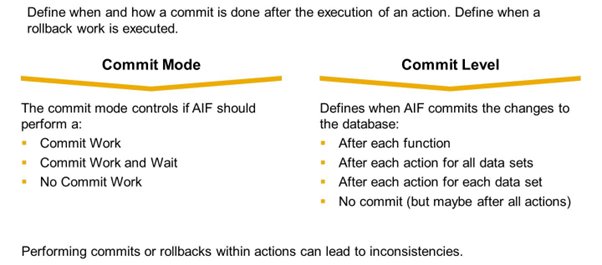
Commit Mode: The commit mode controls if AIF should perform a:
- Commit Work
- Commit Work and Wait
- No Commit Work
Commit Level: Defines when AIF commits the changes to the database:
- After each function: A commit is done after each separate function call of the action.
- After each action for all datasets: Leads to a commit after the action was executed for all datasets of a table the action was called with.
- After each action for each dataset: Leads to a commit after all functions of the action have been executed for a dataset (dataset = a line of a table).
- No commit (but maybe after all actions): Does not lead to a commit at the action level. However, at the interface level, there could be a commit (if it is customized accordingly).
Which commit level should be chosen depends on your requirements. You should also consider that AIF will perform a rollback in case of an error. If a message is restarted and a function was executed successfully before, AIF will not execute it again if AIF already performed a commit for this function.
Example
You have a table that contains customer data and an action that creates those customers. The commit level for the action is set to After each function. Your table contains two customers. The creation of the first customer is successful but the creation of the second customer fails. A user corrects the error and restarts the message. AIF will only try to create the second customer. For the first customer, the function module will not be executed again.
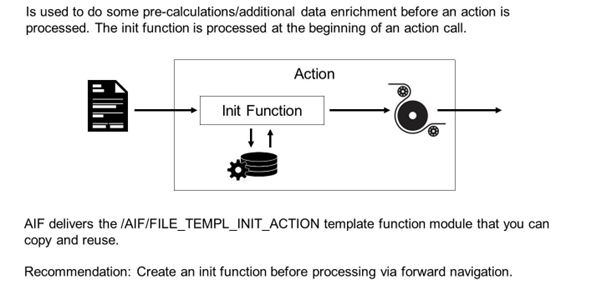
Defines a function module that is called by AIF at the beginning of the processing of the current action.
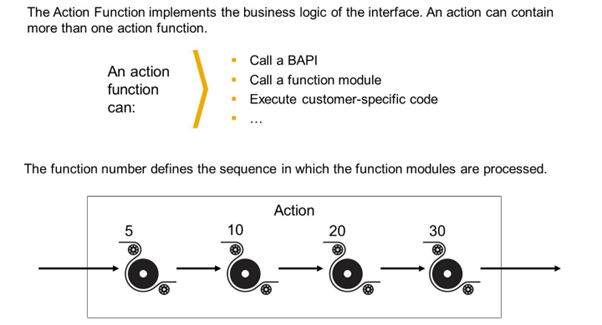
An action can have different function modules to be executed during the processing of the action. The function number defines in which sequence the function modules are processed.
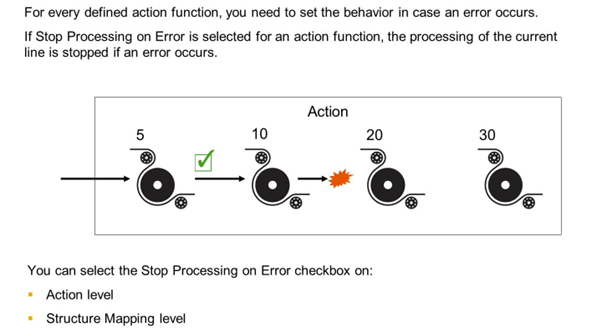
The Stop Processing on Error checkbox specifies if the message processing should be stopped if an error occurs.
Stop Processing on Error in Define Functions
An action has function numbers 5, 10, 20, and 30. For function number 10, the Stop Processing on Error checkbox is selected. If an error occurs while function number 10 is being executed, function numbers 20 and 30 are not executed for the current line.