The Form Interface
The Form Interface
To access the form interface maintenance, use transaction SFP.
Alternatively, use transaction SE80 and choose Other Object. Select the More tab page and choose Interface.
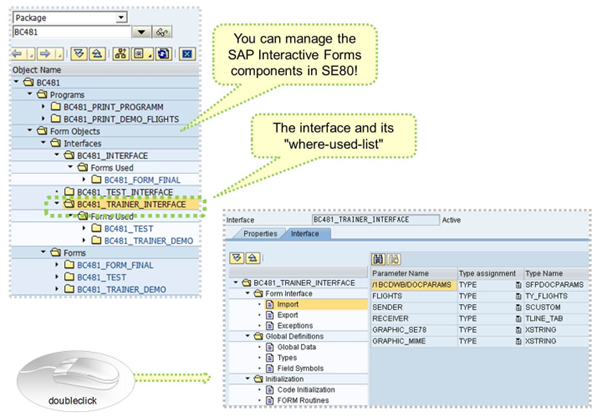
In SE80 navigation, using the package BC481 leads directly to the relevant interfaces, forms, and printing programs of the BC481 class.
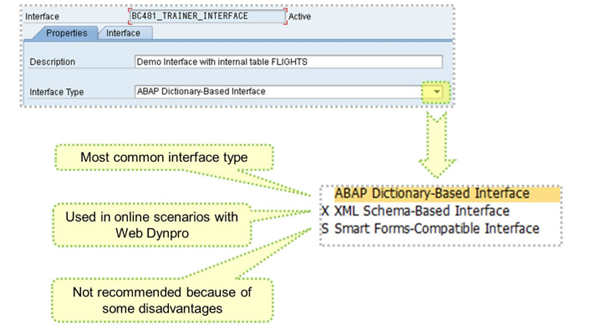
On the Properties tab page, you determine the type of the interface. These types differ in the number and types of parameters and other elements they have.
The type “ABAP-Dictionary-Based Interface” is the most common Interface type and is used for print/interactive scenarios.
The type “Smart-Forms-Compatible” is used for print scenarios, but only for the sake of keeping an old print program without changes. It is not recommended because of some disadvantages.
The type “XML-Schema-Based Interface” is used/will be generated automatically when a form is integrated in Web Dynpro.
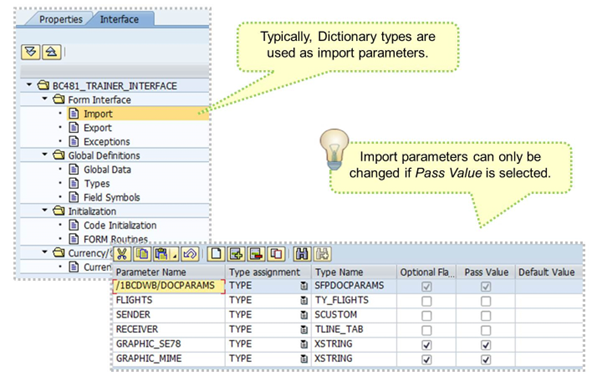
The import parameters defined in the interface can be passed from the application program to the form at runtime, and vice versa for export parameters.
The default export parameter /1BCDWB/FORMOUTPUT has to be evaluated in the calling program if the resulting document needs to be handled by the program itself. Export parameters can be added only for those interfaces that are compatible with Smart Forms.
Exceptions can be declared and, afterward, can be raised in the coding initialization.
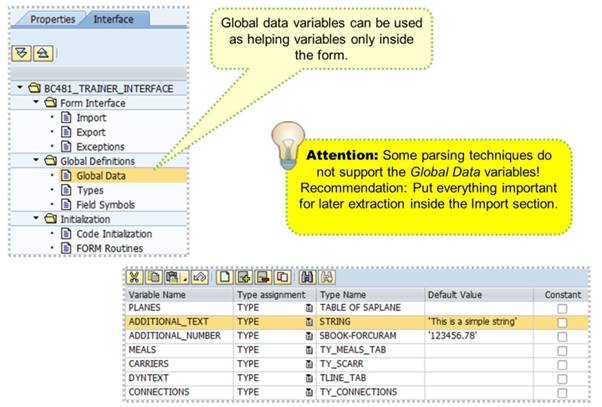
Global data can be used to create “helping” variables or additional variables needed in the form. These may include intermediate variables for calculations, flags, and so on.
In the Initialization section, you can initialize global data before you start to process the form, for example, to convert selected application data. You can also select additional data without having to make changes in the application program. Always keep performance issues in mind when coding in the form interface.
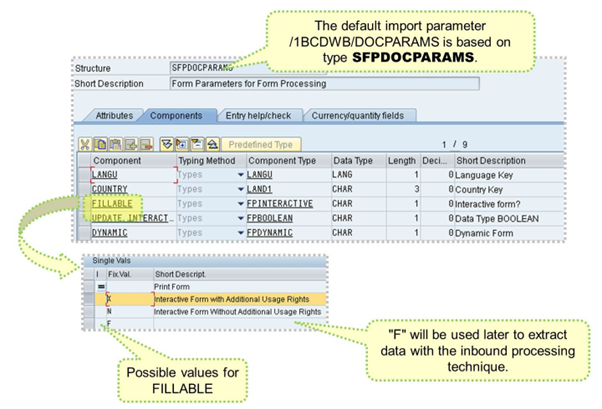
The default import parameter /1BCDWB/DOCPARAMS is used to determine form's locale (language and country) and whether the form allows interactive functions.
FILLABLE and DYNAMIC are the most interesting parameters for interactive scenarios.
- Fillable set to blank would result in a typical print form.
- Fillable set to “X” would resolve in an interactive form that can be saved on the file system.
- Fillable set to “N” would be the same as “X,” but saving the changed data is no longer possible.
- Fillable set to “F” is new as of SAP NetWeaver 7.0 EHP 1 and will be explained in the section on inbound handling of offline forms.
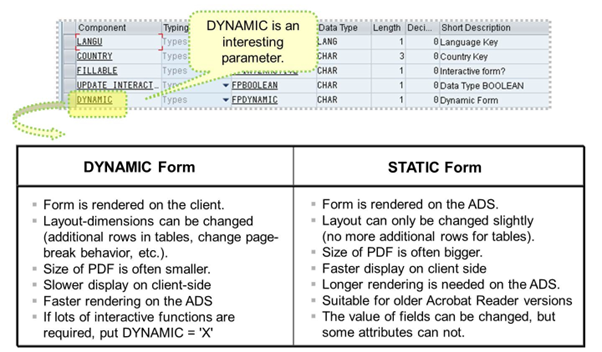
The figure above shows the main differences between static forms and dynamic forms.
To prove the result just create the same form twice, one with DYNAMIC = 'X' and the other with DYNAMIC = ' ' and try interactive functions!
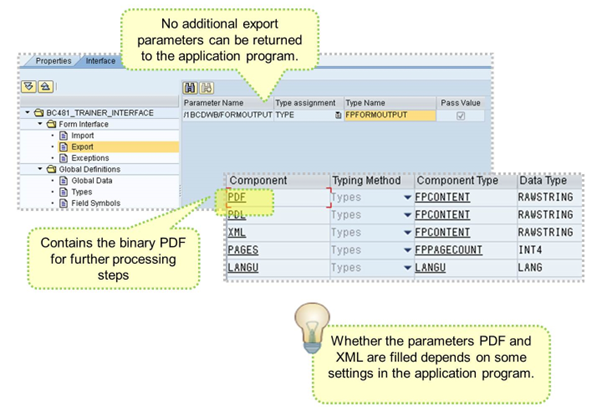
In the EXPORT section, there is just one default parameter of type FPFORMOUTPUT.
The component PDF is the most important and holds the binary content of the created PDF. It is used for further processing steps in interactive scenarios.
To receive the PDF inside this parameter, set GETPDF of the FP_FOB_OPEN function call to 'X'.
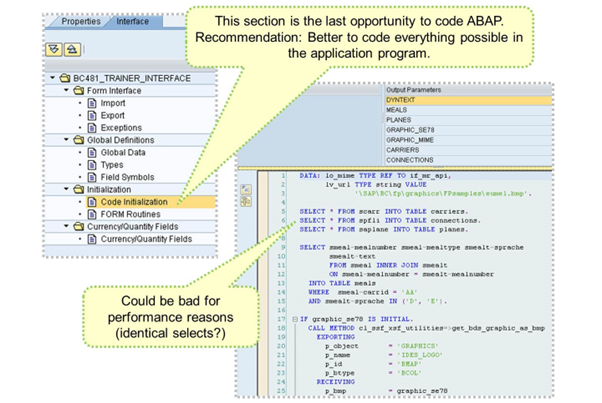
Code initialization is the last chance to code ABAP.