Implementing the Behavior for Composite RAP BOs
Read-by-Association Operations

Read by Association
When accessing a RAP business object via EML, you can use the associations defined in its behavior definition to read data from associated child entities that are part of the composition tree.
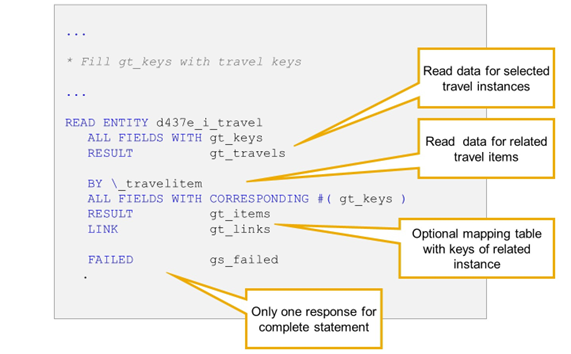
The read-by-association operation is implemented by adding BY \<association_name> between the entity name and the field specification in READ ENTITIES or READ ENTITY. In the example, the association name is _line.
The derived types for the read-by-association operation are defined by using <entity_name>\<association_name> instead of the entity name.
Example: Reading Parent Entity Data and Item Data
It is possible to read parent entity instances and the related child entity instances in the same EML statement, even when using the short form, READ ENTITY. In the example, gt_keys is filled with one or several keys for instances of root entity d437_i_travel. The first part of the READ ENTITY statement retrieves the data for the travel instances.
The second part reads data of all TravelItem instances that are related to the root entity instances via association _travelitem.
The addition LINK is only available in read-by-association operations and returns an internal table with keys of source entity instances and target entity instance. It can be used later to map the travels to the related items if more than one travel has been read.
Create-by-Association Operations
Create by Association
If an association is create-enabled in the behavior definition, you can use this association to create instances of the associated entity.
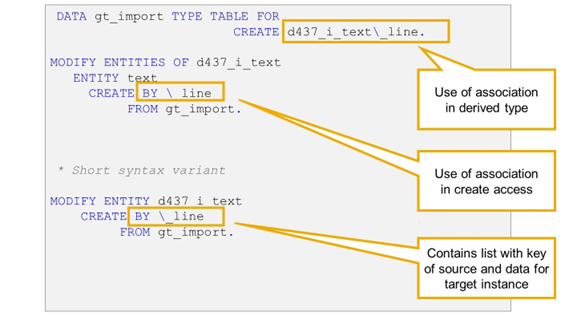
The create-by-association operation is implemented by adding BY \<association_name> after the keyword CREATE in MODIFY ENTITIES or MODIFY ENTITY. In the example, the association name is _line.
The derived type for the create-by-association operation is defined by using <entity_name>\<association_name> instead of the entity name alone.
Derived Type for Create-by-Association
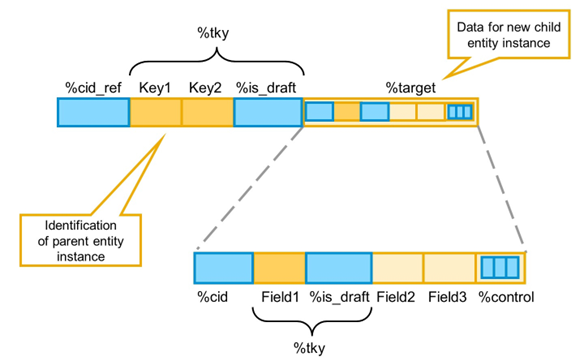
The line type of the internal table that serves as import for EML operation Create-By-Association consists of two parts:
- Elementary components to identify the instance of the parent entity. These fields are summarized in component group %tky.
- %target is a structured component to specify the data for the new child entity instance, including a %control structure to specify which components are supplied
The component %cid_ref is needed to identify the parent entity instance in situations where the actual key is not yet available. This is the case if, for example, internal numbering is used and the parent entity instance has just been created, or is created in the same EML statement.
Similarly, the component %cid in the sub-structure %target is used to set a temporary key for the new child entity instance, by which it can be identified until internal numbering provides the actual key.