Using Dynamic Statements and Dynamic Calls
Dynamic Tokens in ABAP Statements
In many ABAP statements, parts of the statement are not defined until runtime. The parts of the statement that will be defined at runtime are replaced with a data object. The system evaluates the content of the data object at runtime and executes the statement accordingly. We differentiate between two cases with regard to syntax, depending on whether the developer uses the data object in place of a literal or an identifier.

Tokens – Replacing Identifiers
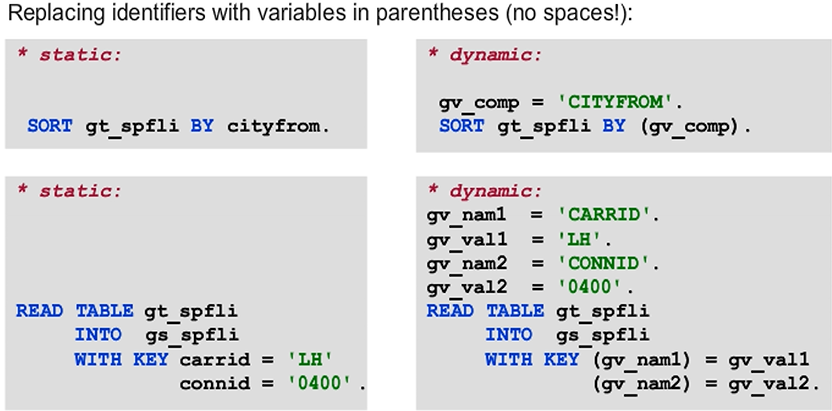
When you replace identifiers, you have to flag the data objects specifically to make it clear whether the contents of the data object should be used, or the data object itself. Therefore, to avoid ambiguity, specify the data object whose content appears in place of an identifier in parentheses.
No spaces are allowed within the parentheses when using data objects that replace identifiers.
Not all ABAP syntax supports the dynamic specification of certain components of an ABAP statement. For details, see the documentation for the respective statement.
Dynamic Open SQL
An important application for tokens is the flexible design of database accesses that use Open SQL. This is particularly relevant for read access with SELECT , but statements for write accesses also offer this option.
You can replace nearly all components of a SELECT statement with data objects, either as a character-type elementary data object or as an internal table with a character-type line type. The figure shows several examples.

Dynamic Calls
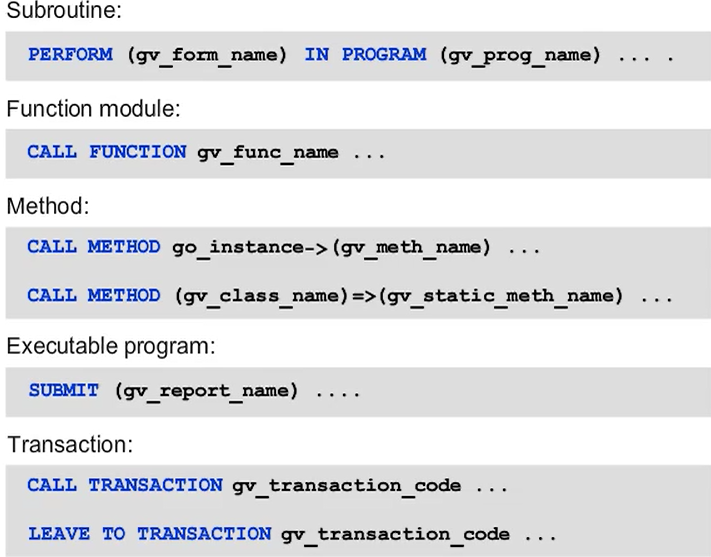
ABAP enables you to call modularization units and programs dynamically. With this approach, the developer replaces the name of the modularization unit, the transaction, or the program with a character-type data object in the call syntax.
When making dynamic calls, the following rules apply:
- Do not use parentheses for function modules or transaction codes because variables replace text literals.
- Use parentheses for subroutines, methods, and executable programs because here you replace an identifier not a literal.
Dynamic Function Module Calls
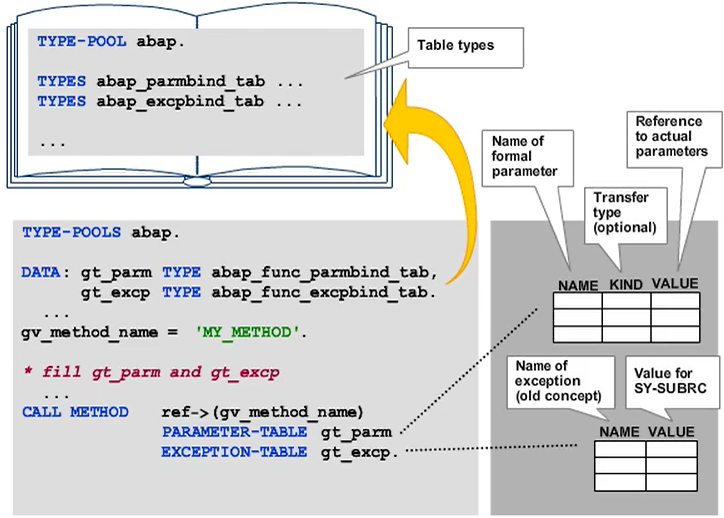
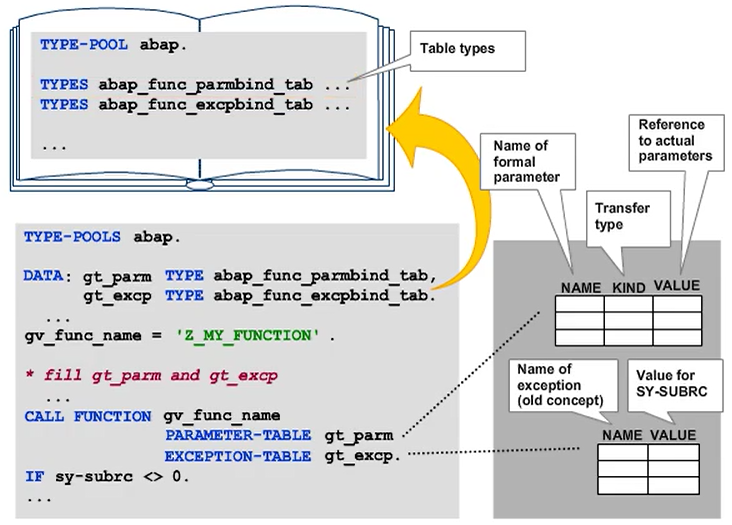
When dynamically calling function modules, the actual parameters are assigned to the formal parameters dynamically by specifying an appropriately typed internal table after the PARAMETER-TABLE addition. You cannot combine the PARAMETER-TABLE addition with IMPORTING, EXPORTING, CHANGING, or TABLES.
The internal table must have table type ABAP_FUNC_PARMBIND_TAB from type group ABAP.
The line type includes the following components:
- NAME
This is the name of the formal parameter.
Specify NAME in uppercase. - KIND
This is the type of parameter transfer (exporting, importing, changing, or tables). This is an integer type field. The ABAP type group provides the constants abap_func_exporting, abap_func_importing, and so on, to fill it. Note that a parameter defined as an export parameter in the function module must be assigned the constant abap_func_importing, just like if the function module is not called dynamically. - VALUE
This is the data reference to the value supplied for the parameter.
This field has the generic type TYPE REF TO DATA, which means that it can point to any type of data object. It is easy to fill the field with a GET REFERENCE OF act_par INTO gs_partab-value statement. In this statement, act_par stands for the actual parameter and gs_partab stands for the work area of the parameter table.
Caution: Table type ABAP_FUNC_PARMBIND_TAB defines a sorted table. Avoid using the APPEND statement to fill it. Instead, use key access with INSERT ... INTO TABLE.
Dynamic Method Calls
In method calls, the dynamic passing of parameters and the handling of conventional exceptions are similar to the procedure for function modules. There are a number of minor differences.