Describing Data Types, Data Objects, and Objects at Runtime
RTTI Class Hierarchy
As of SAP Web AS 6.10, ABAP developers can use a class-based concept, RTTI, to determine type properties, such as data types and object types, at runtime.
Before RTTI, ABAP contained only the DESCRIBE FIELD and DESCRIBE TABLE statements. However, these statements are limited to properties of data objects, and do not determine as many properties as RTTI.
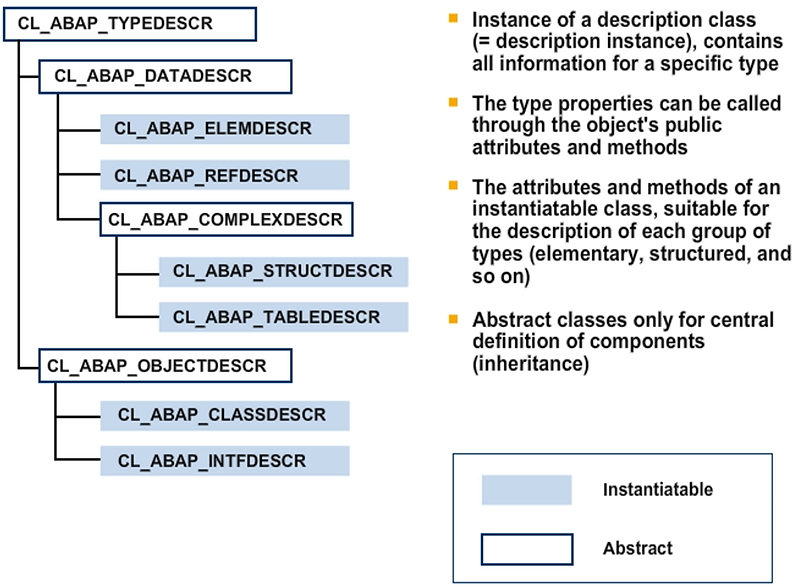
RTTI consists of a hierarchy of ten global classes that developers use.
The description of a type at runtime is realized as an instance of one of these classes. The properties of the type are saved in the instance attributes and can be queried directly or using appropriate methods. At runtime, only one description object exists for each type.
All classes inherit properties from a shared superclass, either directly or indirectly, and their names all follow the pattern CL_ABAP_xxxDESCR, where xxx stands for the category of the type used to describe the respective class.
Different classes are needed because the attributes and methods of each class relate to a specific category of types. For example, you use class CL_ABAP_TABLEDESCR to describe table types. Therefore, the class contains attributes for the table category and the structure of the table key, among other information. These attributes are specific to class CL_ABAP_TABLEDESCR. No other RTTI classes contain them.
RTTI Classes – Purpose
RTTI classes can be instantiated:
|
RTTI Class |
Purpose |
|
CL_ABAP_ELEMDESCR |
To describe elementary data types |
|
CL_ABAP_REFDESCR |
To describe references types |
|
CL_ABAP_STRUCTDESCR |
To describe structure types |
|
CL_ABAP_TABLEDESCR |
To describe tables types |
|
CL_ABAP_CLASSDESCR |
To describe classes |
|
CL_ABAP_INTFDESCR |
To describe interfaces |
All other RTTI classes are abstract, which means that you cannot instantiate them. They are used to centrally define the attribute and methods that are used in several of the other classes. For example, the METHODS attribute, which contains a list of the methods, is not defined in class CL_ABAP_CLASSDESCR, but instead in class CL_ABAP_OBJECTDESCR, because it is also needed in the same form in class CL_ABAP_INTFDESCR.
RTTI Class Instantiation
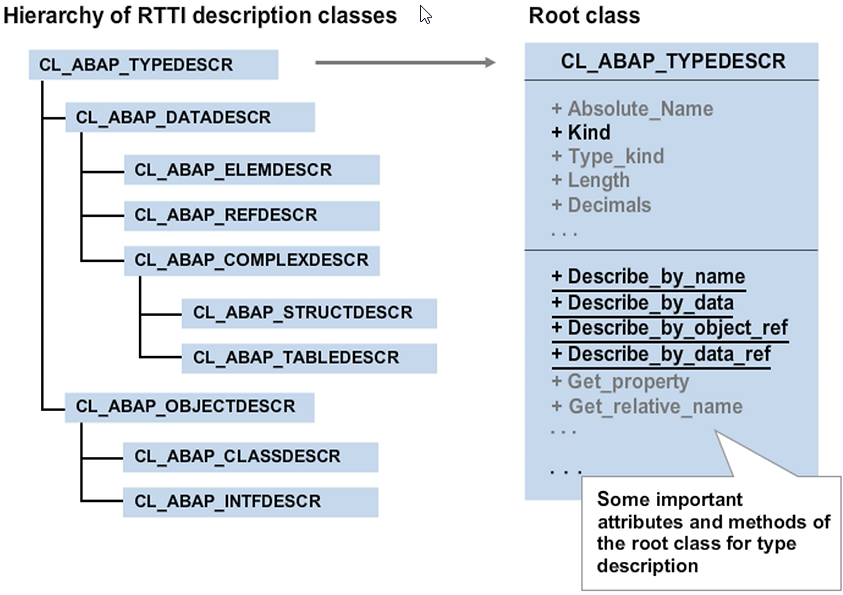
It is not possible to instantiate the RTTI description classes directly with the CREATE OBJECT statement. To retrieve a reference to a description object, call static method DESCRIBE_BY_xxx of class CL_ABAP_TYPEDESCR. The description objects are generated and the data is filled and returned using a return parameter with generic type REF TO CL_ABAP_TYPEDESCR.
Describe a Type Based on Its Name
After the call, you need to cast to a reference variable of a suitable subclass to access specific attributes and methods for the respective type. If you do not know which RTTI class was instantiated, evaluate the public KIND instance attribute whose contents match the value of one of the six constants from class CL_ABAP_TYPEDESCR. Each of these six constants corresponds to one of the six RTTI classes that the developer can instantiate.

Casting a Suitable Reference for a Type Description Object
If you know which description class is instantiated, then the downcast can also take place directly in the call of the DESCRIBE_BY_xxx functional method, for example, lo_class ?= cl_abap_typedescr=>describe_by_...
In this case, it is a good idea to catch runtime error CX_SY_MOVE_CAST_ERROR.

Methods for Description Objects
- DESCRIBE_BY_NAME