Creating Data Types, Data Objects, and Objects at Runtime
Dynamic Object Creation
The CREATE OBJECT statement creates objects or specifically, instances of classes at runtime.
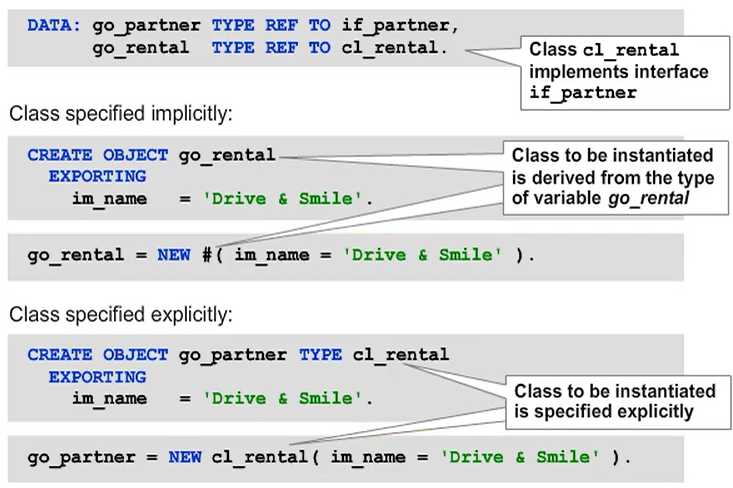
Usually, the type of the object (that is, the class to be instantiated) is defined implicitly through the static type of the reference variable used. Alternatively, you can use statement CREATE OBJECT with the TYPE addition to specify the class to be instantiated in the CREATE OBJECT statement.
As off SAP NetWeaver 7.40, you can use constructor expression NEW as an alternative for statement CREATE OBJECT. If you use it in the form NEW #( ), i.e. with the pound symbol “#”, the type of the object is defined implicitly through the context of the expression. Replacing “#” with the name of a class corresponds to statement CREATE OBJECT with addition TYPE.
Specifying the Class Dynamically
If you use the statement CREATE OBJECT with the TYPE addition you can use a token, i.e. a data object in parentheses after TYPE. This syntax enables dynamic selection of the class to be instantiated.
Expression NEW does not support tokens to specify the class. If you want to specify the class dynamically you have to use statement CREATE OBJECT.
Hint: If you want to choose from classes that are not linked through a shared superclass or the same implemented interface, you can type the reference variable completely generically with TYPE REF TO OBJECT.
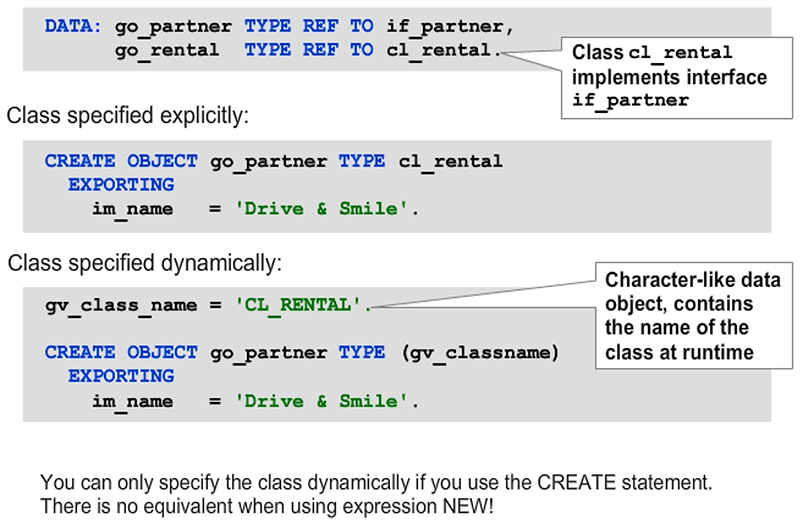
Dynamic Parameter Passing
If all potential classes have the same constructor signature, the parameters can be supplied with data statically. However, it is likely that the parameters and exceptions of the constructors will differ. In this case, you need to use dynamic parameter transfer.
As with dynamic method calls, perform dynamic parameter transfer using internal tables after the PARAMETER-TABLE and EXCEPTION-TABLE additions. These internal tables need to be typed and filled just like with dynamic method calls.
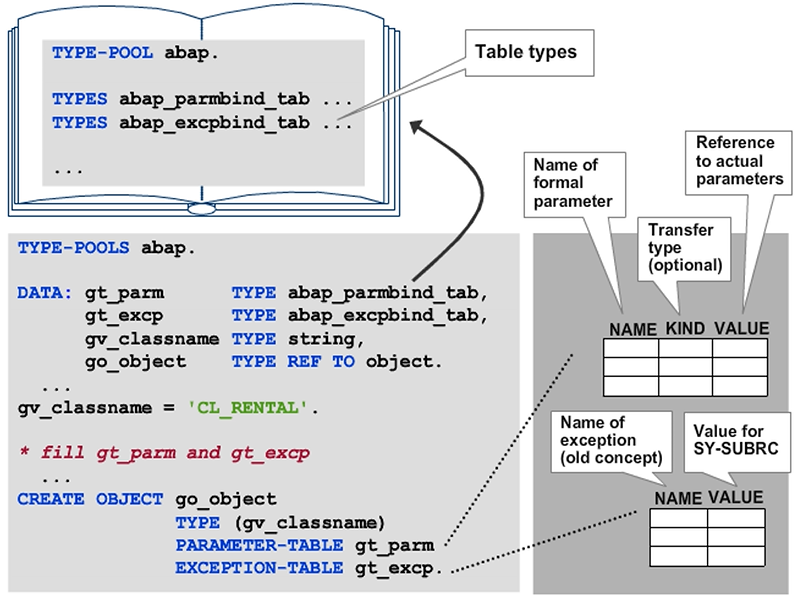
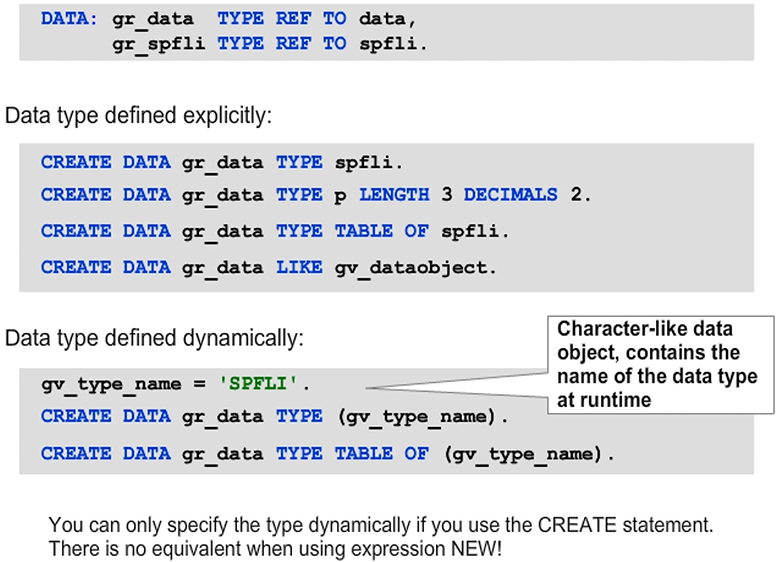
Dynamic Data Object Creation
As with CREATE OBJECT, you can define the type of the data object implicitly by using the type of the reference variable, or explicitly by using the TYPE addition. If you use explicit typing, you can use a number of variants that you might be familiar with from DATA declarations. These variants include the use of built-in types, the implicit construction of table types, and the reference to an existing data object with LIKE.
As off SAP NetWeaver 7.40, you can use constructor expression NEW as an alternative for statement CREATE DATA. If you use it in the form NEW #( ), i.e. with the pound symbol “#”, the type of the data object is defined implicitly through the context of the expression. Replacing “#” with the name of a data type corresponds to statement CREATE DATA with addition TYPE.
Note: Expression NEW only allows a single type name in place of the pound symbol. This means that you cannot “construct” types using additions or reference existing data objects with LIKE.
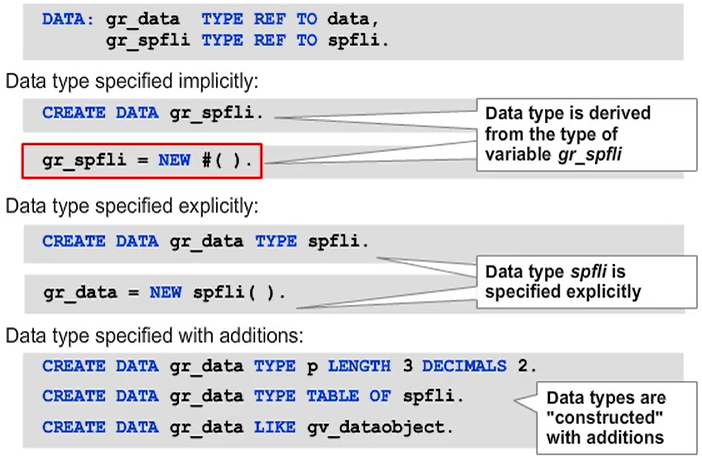
Specifying the Data Type Dynamically
To define the data type for the generated data objects dynamically, use character-type data objects in parentheses.
Note: Alternatively, use the TYPE HANDLE addition to refer to a RTTI-type description object.
Access to Dynamically Created Data Objects
If the data type is to be determined dynamically, the reference variable must be typed generically with TYPE REF TO DATA. This is the only generic type that can be used for data references at present.
The following are the reasons for assigning field symbols to the referenced data object:
- You can only dereference the generic data reference in the ASSIGN statement.
- You can use generically typed field symbols almost anywhere.
Hint: If the new data object is an internal table and you want to use it in the corresponding operand positions, the field symbol must contain at least type ANY TABLE.