Creating Objects
The CREATE OBJECT statement creates an object in the memory. The object attribute values are initial or assigned according to the TYPE specification.
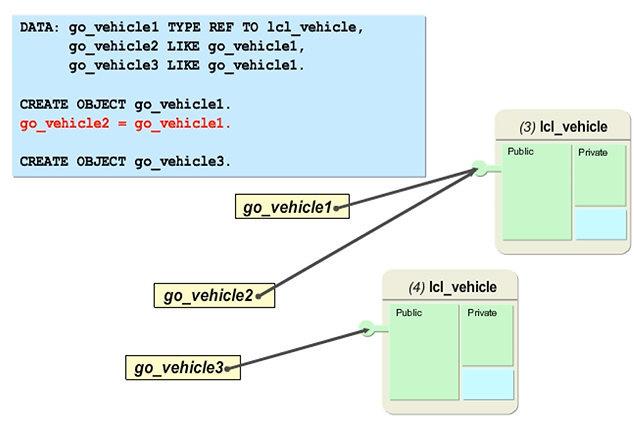
Reference Semantics of Object References
Object reference variables can be assigned to each other.
The figure illustrates an example in which, after the COMPUTE statement, GO_VEHICLE1 and GO_VEHICLE2 point to the same object.
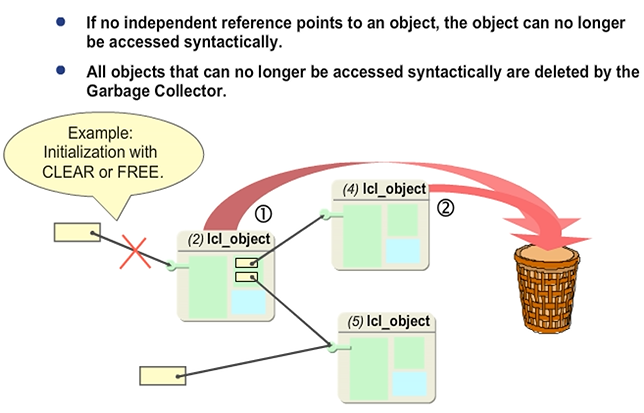
The Garbage Collector
Independent references are references that have not been defined within a class. The Garbage Collector is a routine that starts automatically whenever the runtime system does not have more important tasks to carry out.
In this example, the reference to object (2) LCL_OBJECT is initialized. However, there is no subsequent reference point to this object. Therefore, the Garbage Collector deletes the unreferenced object. Because there is no reference point to object (4) LCL_OBJECT, it is also deleted.
You can use the logical query IF go_obj IS INITIAL to determine whether go_obj contains the null reference or does not point to any object.
Caution: You can have object references and data references. In case of data references do not use IS BOUND. In the case of object references, you can work with IS INITIAL and IS BOUND.
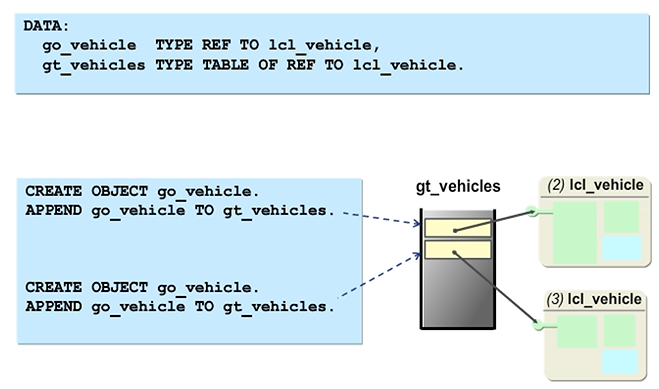
Multiple Instances
To keep several objects from the same class in your program, you can define an internal table with one column that contains the object references for this class. To maintain the objects in the table, you can use statements for internal tables, such as APPEND, READ, or LOOP.
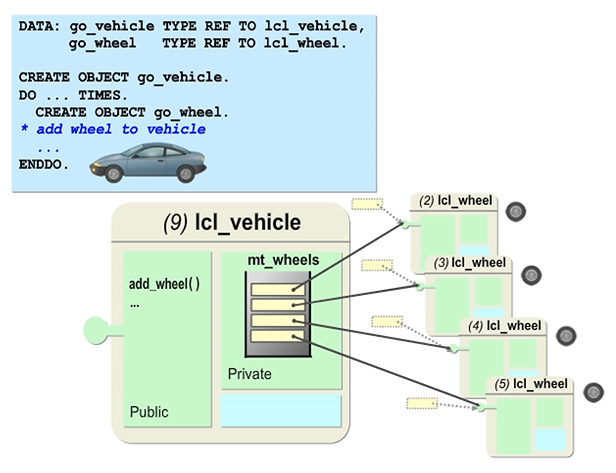
Example of Aggregation
The objects in the class LCL_WHEEL have their own identity. You can create objects regardless of the existence of an object in the class LCL_VEHICLE. References are transferred to objects in class LCL_VEHICLE to create the desired association.