Describing BAdis
BAdI – Basics
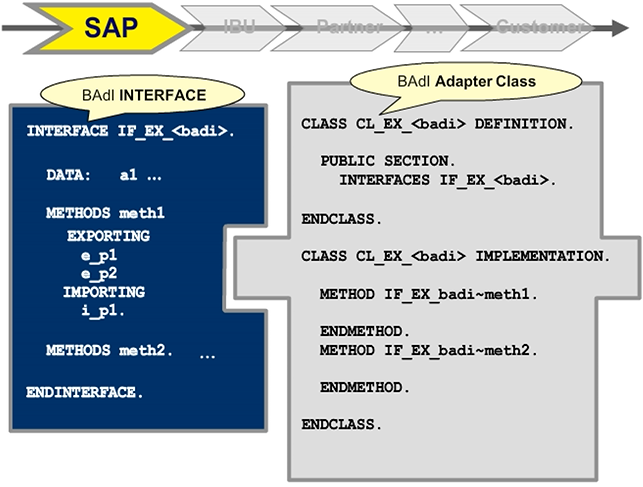
With a BAdI, an SAP application provides the enhancement option through an interface and an adapter class implementing that interface.
The interface can be implemented by several users in the delivery chain, thus, multiple BAdI implementations are possible. Additionally, a BAdI implementation itself can provide another BAdI, which can be implemented by users who appear further out in the delivery chain.

When you define a BAdI, you must specify an interface (IF_EX_<badi>) with corresponding formally defined methods. The adapter class that is automatically generated during the interface definition (CL_EX_<badi>) has, among other capabilities, the function of calling all active implementations of the BAdI. When you have several active implementations, there is no predefined processing sequence.
To Define a BAdI
Steps
- Run the transaction SE18 or, on the SAP Easy Access screen, choose Tools → ABAP Workbench → Utilities → Business Add-Ins → Definition.
As of SAP Netweaver 7.0, you cannot directly create a BAdI. First, you must create an Enhancement Spot. - Enter the Enhancement Spot name and choose the Create
A Create Enhancement Spot dialog displays. - In the Create Enhancement Spot dialog, enter a short description, and choose the Creation of an Enhancement Save the enhancement to your package.
- Choose the Create BadI
A Create BAdI Definition dialog displays. - Enter a short description and choose the Continue
- In the BAdI Definition screen area, expand the node, and double-click Interface.
- Enter your interface name ZIF_BC401_00_BADI_DEMO and press Enter.
A Class/Interface dialog box displays. - On the Class/Interface dialog, choose Yes to create the interface. Save it to your package, then save the enhancement spot.
The class builder will display on the Method tab page. - Enter an instance method and a description, and activate the interface.
The BAdI Calling Program
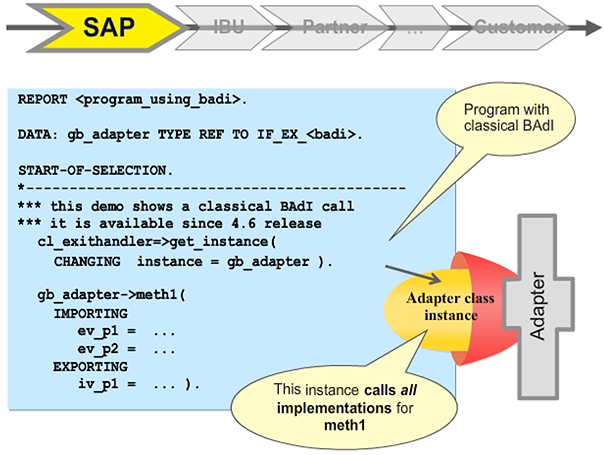
The figure shows an example of a BAdI call.
A reference variable for the type of BAdI must be defined.
An object of the adapter class is instantiated by the call of the GET_INSTANCE static method of the CL_EXITHANDLER class. The variable gb_adapter points to this instance.
The interface methods of the BAdI can be called by gb_adapter object reference.
The Search for BAdIs
You can search the BAdI using the following strategies:
- You can use the Repository Information System (transaction SE84).
- You can use the Application Hierarchy (transaction SE81).
- You can use the Customizing Guide (Implementation guide for transaction SPRO).
- You can search in the application source code for the CL_EXITHANDLER=>GET_INSTANCE statement.
- You can search in the application source code for the occurrence of the BAdI interfaces with the naming convention IF_EX_.
- As of SAP Netweaver AS 7.0, you can search in the application source code for occurrences of the GET BADI statement.
BAdI Implementation
When the name of the BAdI is determined, the BAdI can be implemented. The implementation of the BAdI is performed through the implementation maintenance under Tools → ABAP Workbench → Utilities → Business Add-Ins → Implementation (transaction code SE19). Alternatively, you can go to the implementations by navigating the menu from the BAdI definition.
To implement a BAdI, a BAdI implementation name must be issued. The naming convention is Z<impl>. A dialog box then appears for selecting the corresponding BAdI.
The code to be implemented is stored in a method of an automatically generated customer class. For this reason, the name of the implementing class must be given in a final dialog box. The default name from SAP is comprised of Y or Z (the namespace prefix), CL_ (for class), IM_ (for implementation), and <impl> (the actual name of the implementation).