Implementing Factory Classes Using Friendship
Definition of Friendship Relationships
In some cases, classes have to work together so closely that one class needs access to the other classes protected and private components. Similarly, one class might need to be able to create instances of the other class regardless of the visibility of the constructor. To avoid making these options available to all users of the class, use the concept of class friendship. A class can grant friendship to other classes and interfaces and, hence, to all classes that implement the interface.
To create friendship, use the FRIENDS addition of the CLASS statement or the FRIENDS tab page in the Class Builder. All classes and interfaces to which friendship is granted are listed there.
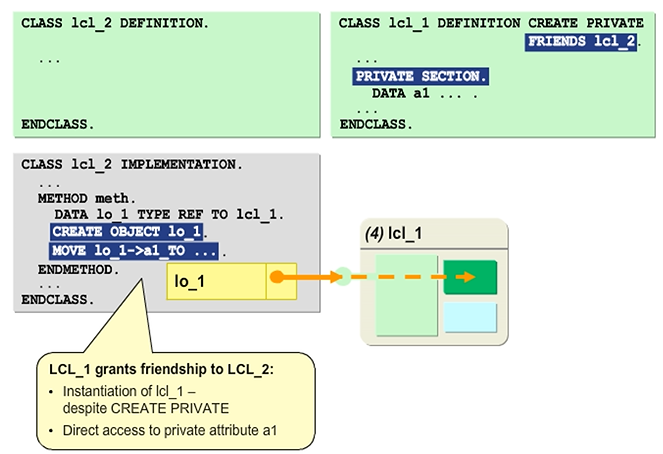
Granting friendship is unilateral.
A class granting friendship is not automatically a friend of the classes’ friends. If a class granting friendship wants to access the non-public components of a friend, this friend must also explicitly grant friendship to it.
Implementation of Factory Classes
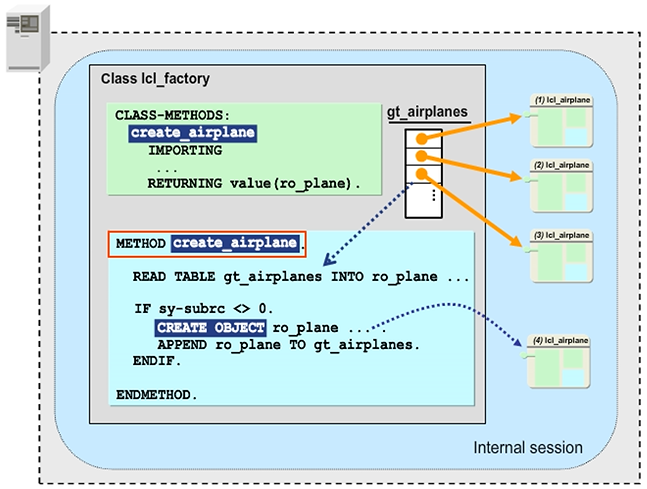
A typical application of the friends concept is the definition of a factory class. Like the factory method, a factory class creates and administrates the instances of a class. By outsourcing the administration to a dedicated class, the class itself is kept smaller and easier to understand.
In the example, LCL_FACTORY serves as a factory class for airplanes. LCL_FACTORY class provides a public method CREATE_AIRPLANE in which CREATE_AIRPLANE either instantiates class LCL_AIRPLANE or returns a reference to an already existing instance. To restrict the instantiation, class LCL_AIRPLANE is defined with addition CREATE PRIVATE. By adding FRIENDS LCL_FACTORY, the friendship allows the factory class and only the factory class to create airplane instances and to access the private attributes.
Hint: Another advantage of the dedicated factory class is that if the class has subclasses, the decision on which of the classes should be instantiated could be done inside the factory class rather than by the calling program. In the example, the CREATE_AIRPLANE method could create and return an instance of either LCL_CARGO_PLANE or LCL_PASSENGER_PLANE depending on the plane type.
Friendship and Inheritance
The friend attribute is inherited. Classes that inherit from friends and interfaces containing a friend as a component interface, also become friends. Therefore, we advise that extreme caution must be taken when granting friendship. The higher up a friend is in the inheritance tree, the more subclasses can access all components of a class that grants friendship.
Implementing Persistent Objects
Persistence Services
In principle, ABAP programs work with data and objects that are only valid at runtime. The data and objects used in ABAP programs are transient. The data in memory is temporary and disappears when the program ends. To store the data permanently and independent of the program, you must store it in a database. Theoretically, you can also use files at the operating system level.
For this purpose, the persistence services for ABAP Objects were introduced in SAP NetWeaver Application Server (SAP NetWeaver AS). On request, the ABAP developer can use these services and write the current attribute values of objects as persistent to the associated transparent tables. To read the values from the tables, persistent services can be used to import the values into an object previously defined as persistent. When doing this, the persistence services use the ABAP Open SQL interface.
You will use the persistence services with object-oriented programming techniques. In this way, you can simulate an object-oriented database management system using a relational database management system and ABAP Objects.

Persistent Classes
To ensure that the instances of persistent classes are unique, they must contain key attributes. You can type these either as worldwide unique identification numbers (object GUID) or semantic keys.
When you create a persistent class ZCL_<name>, Class Builder