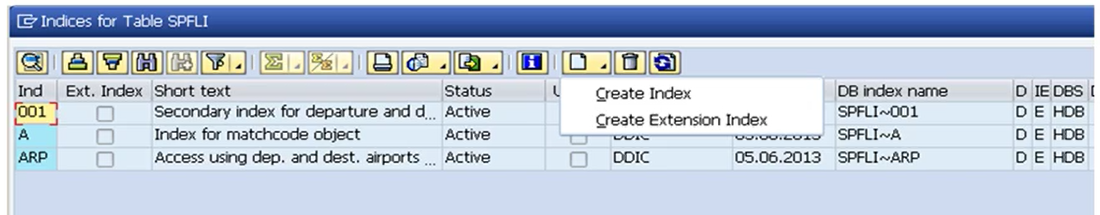
Creating Database Table indexes
Database Access Using Indexes
The following points are important when indexes are created:
- An index should be small as possible. Use only those fields that are frequently used in WHERE clauses of SELECT statement.
- An index must contain significant fields only. A field is significant if it contains considerable data content that can help to identify a table row.
- Whenever you insert, update, or delete database content, the system must adjust all of the assigned indexes. This is time-consuming. Tables whose content are frequently changed must not have too many indexes.
- Indexes on a table are as disjunct as possible.
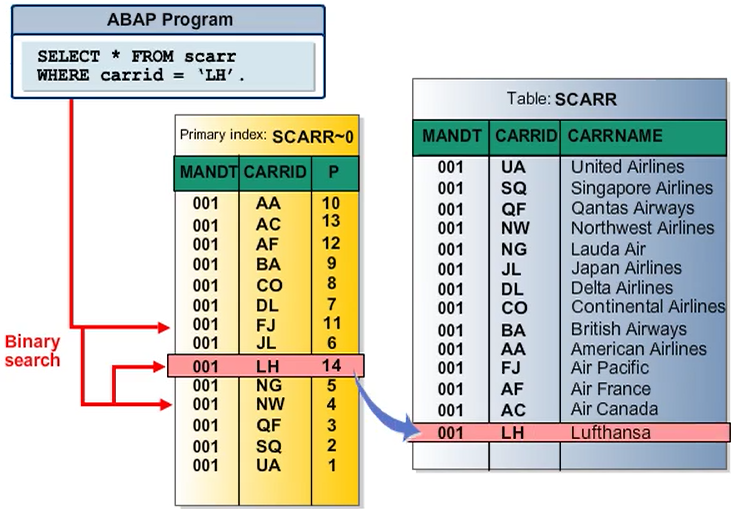
You can create an index to speed up the selection of data records from a table.
An index can be considered to be a copy of a database table reduced to certain fields. This copy stores the data in sorted form. Sorting the data enables fast access to the records of the table (for example, using a binary search). An index contains those fields of the database table which are relevant for database queries. The index also contains a pointer from the index entry to the corresponding table entry so that all the field contents can be read.
Database Indexes
Each database table has one primary index and an arbitrary number of secondary indexes and extension indexes.
- Primary index
It contains the key fields of the table. The primary index is always unique. When a table is activated for the first time , the system automatically creates the primary index.
- Secondary index
Secondary index are useful if a large table is often accessed with a selection on fields other than the table’s key fields. Most of the secondary indexes are non-unique secondary indexes are also possible.
- Extension index
An extension index is part of the enhancement framework. It is an extension of the standard. In the past, it was very common for customers to add their own secondary index to SAP tables. However during upgrade, these customer-added indexes are deleted and needed to be re-created in a system after the upgrade.
Table indexes have a three character ID. 0 is reserved for the primary index. Customers can create their own index on SAP tables. The IDs of customer indexes must begin with Y or Z.
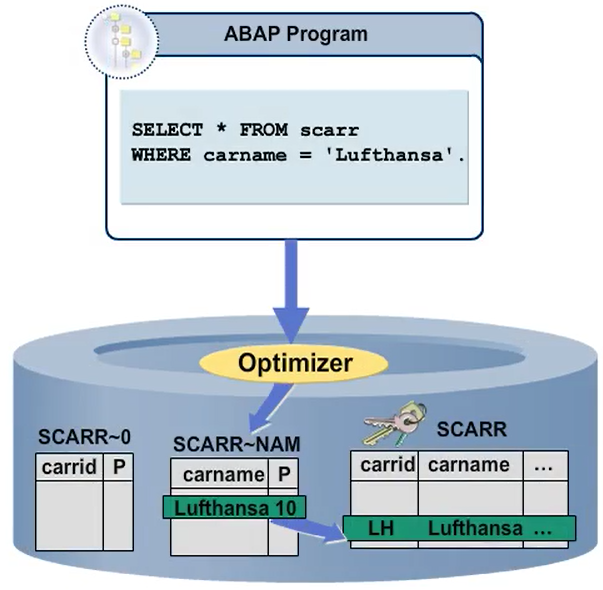
Steps to create an index
The steps to create a secondary index and extension index are the same. Go to the ABAP Dictionary (SE11) and enter a table name. Choose the Indexes button, then the Create button, and select the index fields.