Advanced Structure and Field Mapping
Structure and Field Mapping
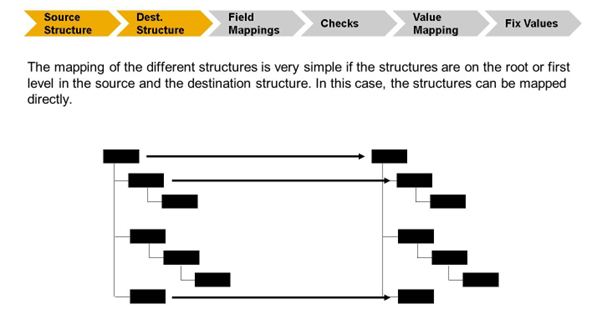
Direct Mapping is possible, when the structures are on the root level or the first level and if they are on the same level on both sides. All the examples we discussed till now were like this. More often, structures differ more. Then, AIF needs to know how a structure in the message can be reached. This will be our next step in structure mapping.
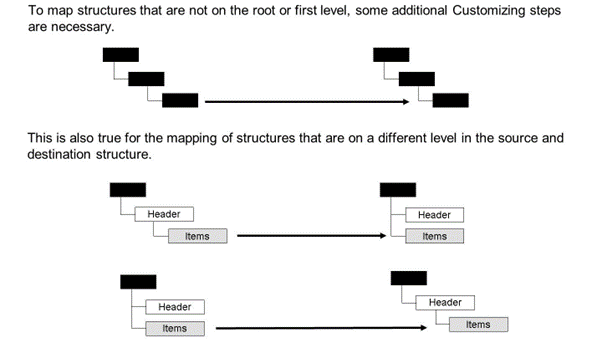
You cannot map structures directly when they are on the second level or deeper in a structure.
You cannot map structures directly when the items are on a level under the header items in the source structure but the header and items are on the same level in the destination structure.
You cannot map structures directly when the header and items are on the same level in the source structure but the items are on a level under the header items in the destination structure.
Indirect Mapping
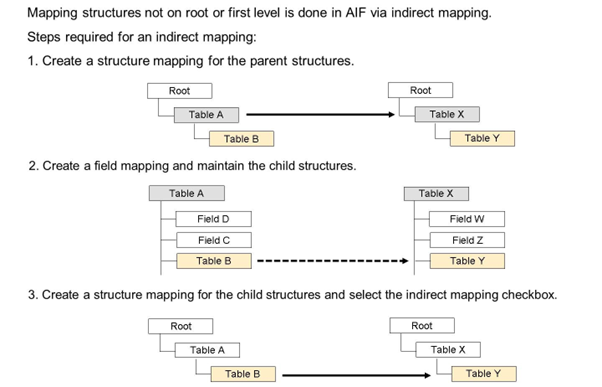
Only the root and the first level structures can be mapped directly. Therefore, all the following structures require an indirect mapping. All steps have to be repeated until the root or the first level structure is reached (they also have to be mapped).
The first step in creating an indirect mapping is to map the parent structures.
The second step is to create a field mapping and map the child structures. If a structure mapping for the child structures is created, the child destination structure is selected as Field in Destination Structure. The child source structure is selected in the Sub-Table field.
The final step is to create a structure mapping for the child structures and select the Indirect Mapping checkbox. In AIF Customizing, in the Define Structure Mappings activity, create a new entry for the child source structure in Select Source Structure. Go to Assign Destination Structure and enter the child destination structure. Furthermore, you have to select the Indirect Mapping checkbox for this structure mapping.
After you have created the structure mapping, you can do the field mappings for the structures as usual.
Indirect Mapping - Example 1
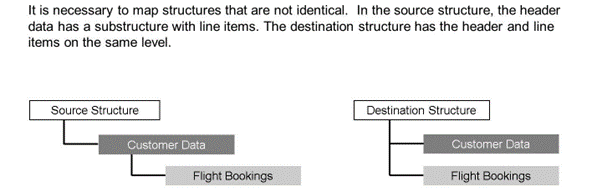
The source structure contains the customer data as a child structure. The customer data contains the flight bookings as child structure. Both structures are tables that can have several entries.
The destination structure contains the customer data and the flight bookings data on the same level.
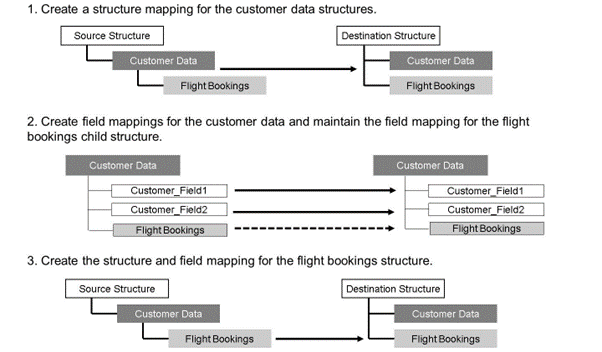
To map all structures, an indirect mapping for the flight bookings is required:
- Map the parent structure. In this case, the customer data is the parent structure.
- Create the field mappings for the customer data. Map the required fields. Create the mapping for the flight bookings child structure.
- Create the structure mapping for the flight booking structure. Select the Indirect Mapping checkbox. Create all required field mappings.
After all mappings are done, the data is mapped from the source to the destination structure.
Indirect Mapping - Example 2
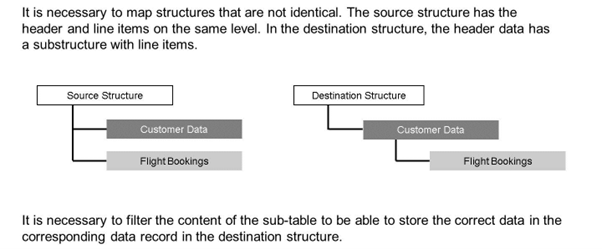
The source structure contains the customer data and the flight bookings on the first level. Both structures are tables that can have several entries.
The destination structure contains the customer data on the first level and the flight bookings data on the second level.
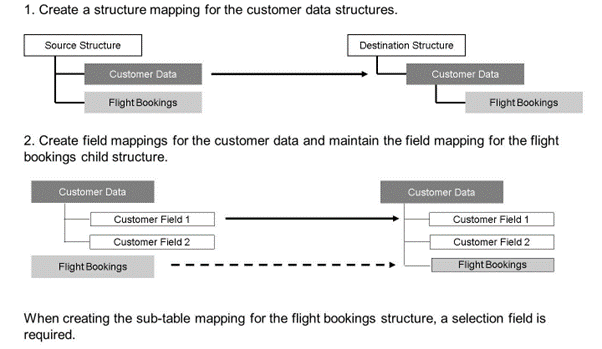
To map all structures, an indirect mapping for the flight bookings is required:
- Map the parent structure. In this case, the customer data is the parent structure.