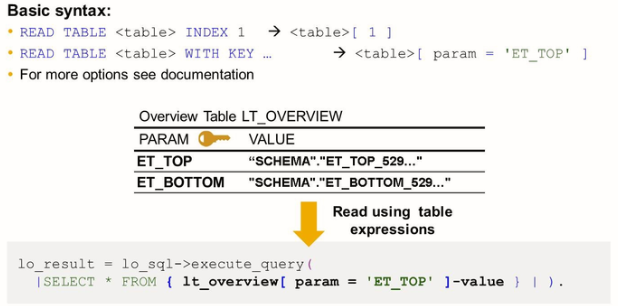
Additional ABAP Language Enhancements
Expression in ABAP
In addition to enhancements to the Open SQL language, ABAP 7.4 SPS05 also comes with considerable enhancements to the ABAP Language itself. These improvements can simplify ABAP development in general, and some of them are particularly handy when using ADBC or optimizing ABAP code for SAP HANA.
The ABAP language originally had relatively limited support for expressions and was very imperative, leading to the need for sequences of statements and intermediate variables to calculate results used in sub-sequent statements. ABAP now supports inline data and field symbol declarations, constructor expressions and even table expressions.
This allows you to write ABAP code in a style that corresponds more to what you may be used to in other programming languages like C or JAVA. It allows you to express more of what you want to calculate and less of how to calculate it. You do not have to write a statement for each intermediate step in a calculation and this way needs fewer local variables used once only.

The first example in the figure, string expressions, and string templates, for expression support, has already been introduced with ABAP 7.02: string expressions and string templates.
These expressions can be very handy when using native SQL, to compose the native SQL string typically containing literals, local or system variables, and single quotes in the result.
With classical ABAP statements, you must introduce a local variable to hold the result of the concentration and a CONCATENATE statement. In addition, you have to be very careful with trailing blanks and escaping the quotes correctly.
String expression can simply compose a native SQL statement in ABAP as follows:
- Use the pipe symbol to define so-called string templates.
- Mix in the values of variables or even expressions, enclosing them in curly braces.
- Simply use single quotes within the string templates, as the string templates are not delimited by single quotes.
- Use the string expression directly as parts of statements, for example, as the parameter of a method call. You do not have to assign the string to a local variable first.

ABAP 7.4 SPS05 introduces considerably more support for expressions. One group of expressions allows declaring data objects and creating instances of classes and data objects, as follows:
- Local variables and their type can be defined in a single step, using an expression containing the DATA () operator.
- The equivalent works for field symbols using the FIELD-SYMBOL ( ) operator.
- The NEW () operator can be used to instantiate objects. You can specify the class respectively type explicitly using NEW <type> ( ), or let the ABAP compiler infer the type using NEW #( ).
- Data references can be created inline using the REF () operator.
- You can also create value objects without introducing variables, using the VALUE() operator. Again
For type conversions, then new operator CONV () and CAST can be used – check the online documentation for details and a full list of newly supported expressions and operators.