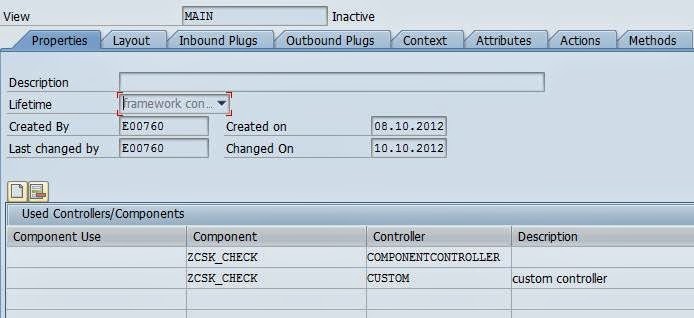
Different types of controller in Webdynpro ABAP
Custom Controller:
Custom controllers can be additionally created in the component and there are exactly similar to the component controller in terms of functionality. This means it is visible to all the elements in the component and lifetime of the controller is the lifetime of the component. Any number of the custom controllers can be created in the component and it provides the option of structuring the data and functions. It only makes sense to create a custom controller if certain functions and data are to be associated with the specific set of views.
The first three components Properties, Context, and Attributes are similarly to that of the component controller and they only difference in the events and method properties.
Events:
Events are created and implement in a similar way to the component controller except that they cannot implement cross-component communication. It can be handled only within the component.
Methods:
Unlike component controller, the custom controller does not contain a no of hook up methods. We can create our own methods in the custom controller and these methods can be used by any views provided that the custom controller is added to the used controller in the properties tab of the view.
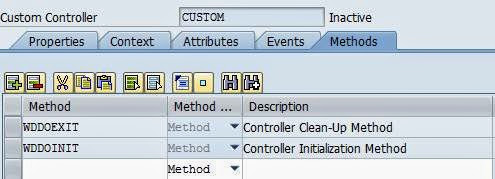
Thus these two options restrict the visibility of the custom controller to protected.
Interface Controller:
The interface controller is used for cross-component communication. The interface controller does not contain any implementation. It is the point of contact of communication for other components to use this component. Only nodes, methods, and events marked as interfaces can be used by other components.
Components of the interface:
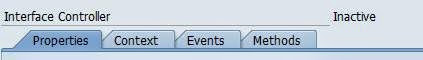
Properties:
In the Properties tab, you will be able to see the administration data and Interface that was created for the external communication(IWCI).
Context:
In the context tab, you will be able to see the context nodes of the component controller which is marked as an interface node in the node properties of the component controller.

Events:
In the events tab you will be able to see the events which are marked as interface events for cross-component implementation.
Methods:
In the methods tab, you will be able to see the interface methods that can be accessed by the other components.

View Controller:
Each view exactly consists of one view controller. No of view controllers in a component depends upon the no of views. The view controller cares about the view specific flow logic like checking user input, handling user actions, etc. The lifetime of the view controller is restricted to the lifetime of the view.
Components of view:

Properties:
The properties tab of the view controller consists of the admin data as well as the option to add the used controllers for the view.